通過源碼學習@functools.lru_cache
一、前言
通常在一些代碼中包含了重複運算,而這些重複運算會大大增加代碼運行所耗費的時間,比如使用遞歸實現斐波那契數列。
舉個例子,當求 fibonacci(5) 時,需要求得 fibonacci(3) 和 fibonacci(4) 的結果,而求 fibonacci(4) 時,又需要求 fibonacci(2) 和 fibonacci(3) ,但此時 fibonacci(3) 就被重新計算一遍了,繼續遞歸下去,重複計算的內容就更多了。求 fibonacci(5) 的代碼和運行結果如下:
1 def fibonacci(n): 2 # 遞歸實現斐波那契數列 3 print("n is {}".format(n)) 4 if n < 2: 5 return n 6 return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1) 7 8 9 if __name__ == '__main__': 10 fibonacci(5) 11 12 # n is 5 13 # n is 3 14 # n is 1 15 # n is 2 16 # n is 0 17 # n is 1 18 # n is 4 19 # n is 2 20 # n is 0 21 # n is 1 22 # n is 3 23 # n is 1 24 # n is 2 25 # n is 0 26 # n is 1
從打印的結果來看,有很多重複計算的部分,傳入的 n 越大,重複計算的部分就越多,程序的耗時也大大增加,例如當 n = 40 時,運行耗時已經很長了,代碼如下:
1 import time 2 3 4 def fibonacci(n): 5 # 遞歸實現斐波那契數列 6 if n < 2: 7 return n 8 return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1) 9 10 11 if __name__ == '__main__': 12 print("Start: {}".format(time.time())) 13 print("Fibonacci(40) = {}".format(fibonacci(40))) 14 print("End: {}".format(time.time())) 15 16 # Start: 1594197671.6210408 17 # Fibonacci(40) = 102334155 18 # End: 1594197717.8520994
二、@functools.lru_cache
1.使用方法
@functools.lru_cache 是一個裝飾器,所謂裝飾器,就是在不改變原有代碼的基礎上,為其增加額外的功能,例如打印日誌、計算運行時間等,該裝飾器的用法如下:
1 import functools 2 3 4 @functools.lru_cache(100) 5 def fibonacci(n): 6 # 遞歸實現斐波那契數列 7 print("n is {}".format(n)) 8 if n < 2: 9 return n 10 return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1) 11 12 13 if __name__ == '__main__': 14 fibonacci(5) 15 16 # n is 5 17 # n is 3 18 # n is 1 19 # n is 2 20 # n is 0 21 # n is 4
從打印的結果來看,從0到5都只計算了一遍,沒有出現重複計算的情況,那當 n = 40 時,程序的耗時情況又是如何呢?代碼如下:
1 import time 2 import functools 3 4 5 @functools.lru_cache(100) 6 def fibonacci(n): 7 # 遞歸實現斐波那契數列 8 if n < 2: 9 return n 10 return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1) 11 12 13 if __name__ == '__main__': 14 print("Start: {}".format(time.time())) 15 print("Fibonacci(40) = {}".format(fibonacci(40))) 16 print("End: {}".format(time.time())) 17 18 # Start: 1594197813.2185402 19 # Fibonacci(40) = 102334155 20 # End: 1594197813.2185402
從結果可知,沒有了這些重複計算,程序運行所耗費的時間也大大減少了。
2.源碼解析
在 Pycharm 中點擊 lru_cache 可以查看源碼,其源碼如下:
def lru_cache(maxsize=128, typed=False): """Least-recently-used cache decorator. If *maxsize* is set to None, the LRU features are disabled and the cache can grow without bound. If *typed* is True, arguments of different types will be cached separately. For example, f(3.0) and f(3) will be treated as distinct calls with distinct results. Arguments to the cached function must be hashable. View the cache statistics named tuple (hits, misses, maxsize, currsize) with f.cache_info(). Clear the cache and statistics with f.cache_clear(). Access the underlying function with f.__wrapped__. See: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_algorithms#Least_Recently_Used """ # Users should only access the lru_cache through its public API: # cache_info, cache_clear, and f.__wrapped__ # The internals of the lru_cache are encapsulated for thread safety and # to allow the implementation to change (including a possible C version). # Early detection of an erroneous call to @lru_cache without any arguments # resulting in the inner function being passed to maxsize instead of an # integer or None. if maxsize is not None and not isinstance(maxsize, int): raise TypeError('Expected maxsize to be an integer or None') def decorating_function(user_function): wrapper = _lru_cache_wrapper(user_function, maxsize, typed, _CacheInfo) return update_wrapper(wrapper, user_function) return decorating_function
注釋的第一行就指明了這是一個 LRU 緩存裝飾器(「Least-recently-used cache decorator」)。如果 maxsize 參數被設置為 None,則禁用了 LRU 特性,且緩存可以無限制地增長;如果 typed 參數被設置為 True,則不同類型的參數會被視為不同的調用,例如 f(3.0) 和 f(3) 就會被視為不同的調用,其結果也就不同了。
再看代碼部分,maxsize 只能為 None 或者 int 類型數據,然後就是一個裝飾的函數 decorating_function,包含了兩個函數 _lru_cache_wrapper 和 update_wrapper,而其中主要功能包含在 _lru_cache_wrapper() 函數中,其源碼如下:
1 def _lru_cache_wrapper(user_function, maxsize, typed, _CacheInfo): 2 # Constants shared by all lru cache instances: 3 sentinel = object() # unique object used to signal cache misses 4 make_key = _make_key # build a key from the function arguments 5 PREV, NEXT, KEY, RESULT = 0, 1, 2, 3 # names for the link fields 6 7 cache = {} 8 hits = misses = 0 9 full = False 10 cache_get = cache.get # bound method to lookup a key or return None 11 cache_len = cache.__len__ # get cache size without calling len() 12 lock = RLock() # because linkedlist updates aren't threadsafe 13 root = [] # root of the circular doubly linked list 14 root[:] = [root, root, None, None] # initialize by pointing to self 15 16 if maxsize == 0: 17 18 def wrapper(*args, **kwds): 19 # No caching -- just a statistics update after a successful call 20 nonlocal misses 21 result = user_function(*args, **kwds) 22 misses += 1 23 return result 24 25 elif maxsize is None: 26 27 def wrapper(*args, **kwds): 28 # Simple caching without ordering or size limit 29 nonlocal hits, misses 30 key = make_key(args, kwds, typed) 31 result = cache_get(key, sentinel) 32 if result is not sentinel: 33 hits += 1 34 return result 35 result = user_function(*args, **kwds) 36 cache[key] = result 37 misses += 1 38 return result 39 40 else: 41 42 def wrapper(*args, **kwds): 43 # Size limited caching that tracks accesses by recency 44 nonlocal root, hits, misses, full 45 key = make_key(args, kwds, typed) 46 with lock: 47 link = cache_get(key) 48 if link is not None: 49 # Move the link to the front of the circular queue 50 link_prev, link_next, _key, result = link 51 link_prev[NEXT] = link_next 52 link_next[PREV] = link_prev 53 last = root[PREV] 54 last[NEXT] = root[PREV] = link 55 link[PREV] = last 56 link[NEXT] = root 57 hits += 1 58 return result 59 result = user_function(*args, **kwds) 60 with lock: 61 if key in cache: 62 # Getting here means that this same key was added to the 63 # cache while the lock was released. Since the link 64 # update is already done, we need only return the 65 # computed result and update the count of misses. 66 pass 67 elif full: 68 # Use the old root to store the new key and result. 69 oldroot = root 70 oldroot[KEY] = key 71 oldroot[RESULT] = result 72 # Empty the oldest link and make it the new root. 73 # Keep a reference to the old key and old result to 74 # prevent their ref counts from going to zero during the 75 # update. That will prevent potentially arbitrary object 76 # clean-up code (i.e. __del__) from running while we're 77 # still adjusting the links. 78 root = oldroot[NEXT] 79 oldkey = root[KEY] 80 oldresult = root[RESULT] 81 root[KEY] = root[RESULT] = None 82 # Now update the cache dictionary. 83 del cache[oldkey] 84 # Save the potentially reentrant cache[key] assignment 85 # for last, after the root and links have been put in 86 # a consistent state. 87 cache[key] = oldroot 88 else: 89 # Put result in a new link at the front of the queue. 90 last = root[PREV] 91 link = [last, root, key, result] 92 last[NEXT] = root[PREV] = cache[key] = link 93 # Use the cache_len bound method instead of the len() function 94 # which could potentially be wrapped in an lru_cache itself. 95 full = (cache_len() >= maxsize) 96 misses += 1 97 return result 98 99 def cache_info(): 100 """Report cache statistics""" 101 with lock: 102 return _CacheInfo(hits, misses, maxsize, cache_len()) 103 104 def cache_clear(): 105 """Clear the cache and cache statistics""" 106 nonlocal hits, misses, full 107 with lock: 108 cache.clear() 109 root[:] = [root, root, None, None] 110 hits = misses = 0 111 full = False 112 113 wrapper.cache_info = cache_info 114 wrapper.cache_clear = cache_clear 115 return wrapper
可以看到根據 maxsize 的值會返回不同的 wrapper 函數。當 maxsize 為零時,定義了一個局部變量 misses,並在每次調用時加1;當 maxsize 為 None 時,在函數調用時會先從緩存中獲取,若緩存中有就返回結果,若緩存中沒有則運行函數並將結果加入到緩存中;當 maxsize 為非零整數時,可以緩存最多 maxsize 個此函數的調用結果,此時使用了一個雙向鏈表 root,其初始化如下:
root = [] # root of the circular doubly linked list
root[:] = [root, root, None, None] # initialize by pointing to self
當調用時也會先從緩存中進行獲取,如果有則更新 root 並返回結果,如果沒有則調用函數,此時需要判斷緩存是否達到最大數量,若已滿,則刪除 root 中最久未訪問的數據並更新 root 和緩存。
三、LRU Cache
1.基本認識
我們知道計算機的緩存容量有限,如果緩存滿了就要刪除一些內容,給新內容騰位置。但問題是,刪除哪些內容呢?
LRU 緩存策略就是一種常用的策略。LRU,全稱 least recently used,表示最近最少使用。LRU 緩存策略認為最近使用過的數據應該是是有用的,而很久都沒用過的數據應該是無用的,內存滿了就優先刪那些很久沒用過的數據。
2.自定義實現
實現 lru cache 需要兩個數據結構:雙向鏈表和哈希表,雙向鏈表用於記錄存儲數據的順序,用於淘汰最久未使用的數據,哈希表用於記錄元素位置,可在 O(1) 的時間複雜度下獲取元素。
然後要實現兩個操作,分別是 get 和 put:
1)get 操作:根據傳入的 key 從哈希表中獲取元素的位置,若沒有返回 None,若有則從鏈表中獲取元素並將該元素移到鏈表尾部;
2)put 操作:首先判斷傳入的 key 是否在哈希表中存在,若有則進行更新,並將該元素移到鏈表尾部;若沒有,表示是一個新元素,需要添加到哈希表中,再判斷數據量是否超過最大容量,若達到最大容量則刪除最久未使用的數據,即鏈表頭部元素,再將新元素添加到鏈表尾部,若未達到最大容量則直接添加到鏈表尾部。
首先要實現雙向鏈表,代碼如下:
1 # Node of the list 2 class Node: 3 def __init__(self, val): 4 self.val = val 5 self.prev = None 6 self.next = None 7 8 def __str__(self): 9 return "The value is " + str(self.val) 10 11 12 # Double Linked List 13 class DoubleList: 14 def __init__(self): 15 self.head = None 16 self.tail = None 17 18 def is_empty(self): 19 """ 20 returns true if the list is empty, false otherwise 21 :return: 22 """ 23 return self.head is None 24 25 def append(self, value): 26 """ 27 append element after the list 28 :param value: the value of node 29 :return: 30 """ 31 node = Node(value) 32 if self.is_empty(): 33 self.head = node 34 self.tail = node 35 return 36 cur = self.head 37 # find the tail of the list 38 while cur.next: 39 cur = cur.next 40 cur.next = node 41 node.prev = cur 42 self.tail = node 43 44 def remove(self, value): 45 """ 46 if value in the list, remove the element 47 :param value: the value of node 48 :return: 49 """ 50 if self.is_empty(): 51 return 52 cur = self.head 53 while cur: 54 if cur.val == value: 55 if len(self) == 1: 56 # when the list has only one node 57 self.head, self.tail = None, None 58 else: 59 if cur == self.head: 60 self.head = cur.next 61 elif cur == self.tail: 62 self.tail = cur.prev 63 else: 64 cur.prev.next = cur.next 65 return 66 else: 67 cur = cur.next 68 69 def traverse(self): 70 """ 71 iterate through the list 72 :return: 73 """ 74 cur = self.head 75 index = 1 76 while cur: 77 print("Index: {}".format(index) + cur) 78 cur = cur.next 79 index += 1 80 81 def __len__(self): 82 count = 0 83 cur = self.head 84 while cur: 85 count += 1 86 cur = cur.next 87 return count 88 89 def __str__(self): 90 cur = self.head 91 ret = "" 92 while cur: 93 ret += str(cur.val) + "->" if cur.next else str(cur.val) 94 cur = cur.next 95 return ret
其中實現了添加節點、刪除節點、獲取長度等方法,已經足夠作為我們需要的雙向鏈表來使用了,最後就是實現 LRU Cache,主要實現 get(獲取數據) 和 put(添加數據)方法,下面是自定義實現的 LRU Cache 類的代碼:
1 # LRU Cache 2 class LRU: 3 def __init__(self, size): 4 self.size = size 5 self._list = DoubleList() 6 self._cache = dict() 7 8 def _set_recent(self, node): 9 """ 10 set the node to most recently used 11 :param node: node 12 :return: 13 """ 14 # when the node is the tail of the list 15 if node == self._list.tail: 16 return 17 cur = self._list.head 18 while cur: 19 # remove the node from the list 20 if cur == node: 21 if cur == self._list.head: 22 self._list.head = cur.next 23 else: 24 prev = cur.prev 25 prev.next = cur.next 26 if cur.next: 27 cur = cur.next 28 else: 29 break 30 # set node to the tail of the list 31 cur.next = node 32 node.next = None 33 node.prev = cur 34 self._list.tail = node 35 36 def get(self, key): 37 """ 38 get value of the key 39 :param key: key 40 :return: 41 """ 42 node = self._cache.get(key, None) 43 if not node: 44 return 45 self._set_recent(node) 46 return node.val 47 48 def put(self, key, value): 49 """ 50 set value of the key and add to the cache 51 :param key: key 52 :param value: value 53 :return: 54 """ 55 node = self._cache.get(key, None) 56 if not node: 57 if len(self._list) < self.size: 58 self._list.append(value) 59 else: 60 # when the quantity reaches the maximum, delete the head node 61 name = None 62 for k, v in self._cache.items(): 63 if v == self._list.head: 64 name = k 65 if name: 66 del self._cache[name] 67 self._list.head = self._list.head.next 68 self._list.append(value) 69 else: 70 self._set_recent(node) 71 self._list.tail.val = value 72 # add to cache 73 self._cache[key] = self._list.tail 74 75 def show(self): 76 """ 77 show data of the list 78 :return: 79 """ 80 return "The list is: {}".format(self._list)
下面是測試代碼:
1 if __name__ == '__main__': 2 lru = LRU(8) 3 for i in range(10): 4 lru.put(str(i), i) 5 print(lru.show()) 6 for i in range(10): 7 if i % 3 == 0: 8 print("Get {}: {}".format(i, lru.get(str(i)))) 9 print(lru.show()) 10 lru.put("2", 22) 11 lru.put("4", 44) 12 lru.put("6", 66) 13 print(lru.show())
最後是運行結果的截圖:
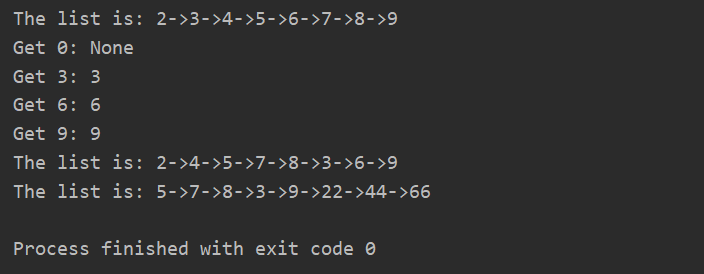
- 當插入數據時,因為最大容量為8,而插入了10個數據,那麼最開始添加進去的0和1就會被刪掉;
- 當獲取數據時,不存在則返回None,存在則返回對應的值,並將該節點移到鏈表的尾部;
- 當更新數據時,會將對應節點的值進行更新,並將節點移到鏈表的尾部。
完整代碼已上傳到 GitHub!


