【分布式锁】06-Zookeeper实现分布式锁:可重入锁源码分析
- 2020 年 3 月 30 日
- 筆記
前言
前面已经讲解了Redis的客户端Redission是怎么实现分布式锁的,大多都深入到源码级别。
在分布式系统中,常见的分布式锁实现方案还有Zookeeper,接下来会深入研究Zookeeper是如何来实现分布式锁的。
Zookeeper初识
文件系统
Zookeeper维护一个类似文件系统的数据结构
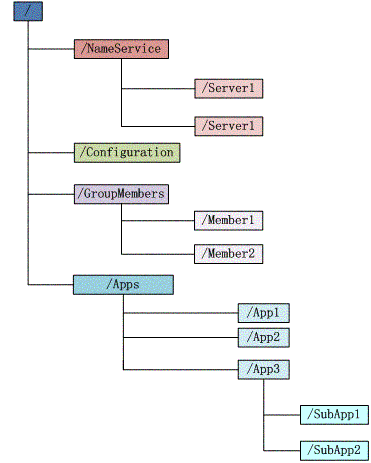 image.png
image.png
每个子目录项如NameService都被称为znoed,和文件系统一样,我们能够自由的增加、删除znode,在znode下增加、删除子znode,唯一不同的在于znode是可以存储数据的。
有4种类型的znode
-
PERSISTENT–持久化目录节点客户端与zookeeper断开连接后,该节点依旧存在
-
PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL-持久化顺序编号目录节点客户端与zookeeper断开连接后,该节点依旧存在,只是Zookeeper给该节点名称进行顺序编号
-
EPHEMERAL-临时目录节点客户端与zookeeper断开连接后,该节点被删除
-
EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL-临时顺序编号目录节点客户端与zookeeper断开连接后,该节点被删除,只是Zookeeper给该节点名称进行顺序编号
通知机制
客户端注册监听它关心的目录节点,当目录节点发生变化(数据改变、被删除、子目录节点增加删除)等,zookeeper会通知客户端。
分布式锁
有了zookeeper的一致性文件系统,锁的问题变得容易。锁服务可以分为两类,一个是保持独占,另一个是控制时序。
-
对于第一类,我们将zookeeper上的一个znode看作是一把锁,通过create znode的方式来实现。所有客户端都去创建 /distribute_lock 节点,最终成功创建的那个客户端也即拥有了这把锁。厕所有言:来也冲冲,去也冲冲,用完删除掉自己创建的distribute_lock 节点就释放出锁。
-
对于第二类, /distribute_lock 已经预先存在,所有客户端在它下面创建临时顺序编号目录节点,和选master一样,编号最小的获得锁,用完删除自己创建的znode节点。
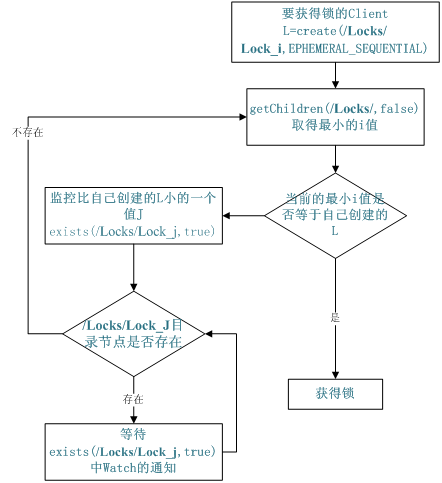 image.png
image.png
注明:以上内容参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/dream-to-pku/p/9513188.html
Curator框架初识
Curator是Netflix公司开源的一套Zookeeper客户端框架。目前已经作为Apache的顶级项目出现,是最流行的Zookeeper客户端之一。
我们看下Apache Curator官网的介绍:
 image.png
image.png
接着看下quick start中关于分布式锁相关的内容
地址为:http://curator.apache.org/getting-started.html
InterProcessMutex lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, lockPath); if ( lock.acquire(maxWait, waitUnit) ) { try { // do some work inside of the critical section here } finally { lock.release(); } }
使用很简单,使用InterProcessMutex类,使用其中的acquire()方法,就可以获取一个分布式锁了。
Curator分布式锁使用示例
启动两个线程t1和t2去争夺锁,拿到锁的线程会占用5秒。运行多次可以观察到,有时是t1先拿到锁而t2等待,有时又会反过来。Curator会用我们提供的lock路径的结点作为全局锁,这个结点的数据类似这种格式:[_c_64e0811f-9475-44ca-aa36-c1db65ae5350-lock-00000000001],每次获得锁时会生成这种串,释放锁时清空数据。
接下来看看加锁的示例:
public class Application { private static final String ZK_ADDRESS = "192.20.38.58:2181"; private static final String ZK_LOCK_PATH = "/locks/lock_01"; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient( ZK_ADDRESS, new RetryNTimes(10, 5000) ); client.start(); System.out.println("zk client start successfully!"); Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { doWithLock(client); }, "t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { doWithLock(client); }, "t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } private static void doWithLock(CuratorFramework client) { InterProcessMutex lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, ZK_LOCK_PATH); try { if (lock.acquire(10 * 1000, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " hold lock"); Thread.sleep(5000L); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " release lock"); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { lock.release(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
运行结果:
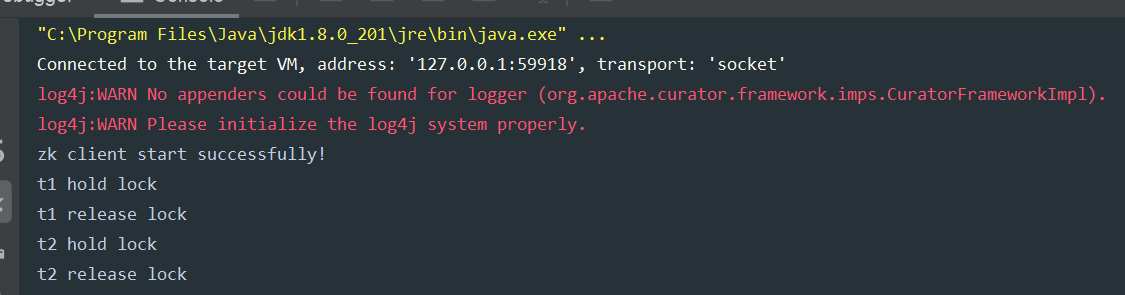 image.png
image.png
Curator 加锁实现原理
直接看Curator加锁的代码:
public class InterProcessMutex implements InterProcessLock, Revocable<InterProcessMutex> { private final ConcurrentMap<Thread, LockData> threadData = Maps.newConcurrentMap(); private static class LockData { final Thread owningThread; final String lockPath; final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1); private LockData(Thread owningThread, String lockPath) { this.owningThread = owningThread; this.lockPath = lockPath; } } @Override public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { return internalLock(time, unit); } private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { /* Note on concurrency: a given lockData instance can be only acted on by a single thread so locking isn't necessary */ Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread(); LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread); if ( lockData != null ) { // re-entering lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet(); return true; } String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes()); if ( lockPath != null ) { LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath); threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData); return true; } return false; } }
直接看internalLock()方法,首先是获取当前线程,然后查看当前线程是否在一个concurrentHashMap中,这里是重入锁的实现,如果当前已经已经获取了锁,那么这个线程获取锁的次数再+1
如果没有获取锁,那么就是用attemptLock()方法去尝试获取锁,如果lockPath不为空,说明获取锁成功,并将当前线程放入到map中。
接下来看看核心的加锁逻辑attemptLock()方法:
入参:time : 获取锁等待的时间unit:时间单位lockNodeBytes:默认为null
public class LockInternals { String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception { final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); final Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null; final byte[] localLockNodeBytes = (revocable.get() != null) ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes; int retryCount = 0; String ourPath = null; boolean hasTheLock = false; boolean isDone = false; while ( !isDone ) { isDone = true; try { if ( localLockNodeBytes != null ) { ourPath = client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path, localLockNodeBytes); } else { ourPath = client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path); } hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath); } catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e ) { // gets thrown by StandardLockInternalsDriver when it can't find the lock node // this can happen when the session expires, etc. So, if the retry allows, just try it all again if ( client.getZookeeperClient().getRetryPolicy().allowRetry(retryCount++, System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis, RetryLoop.getDefaultRetrySleeper()) ) { isDone = false; } else { throw e; } } } if ( hasTheLock ) { return ourPath; } return null; } }
ourPath = client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path);
使用的临时顺序节点,首先他是临时节点,如果当前这台机器如果自己宕机的话,他创建的这个临时节点就会自动消失,如果有获取锁的客户端宕机了,zk可以保证锁会自动释放的
创建的数据结构类似于:
客户端A获取锁的代码,生成的ourPath=xxxx01
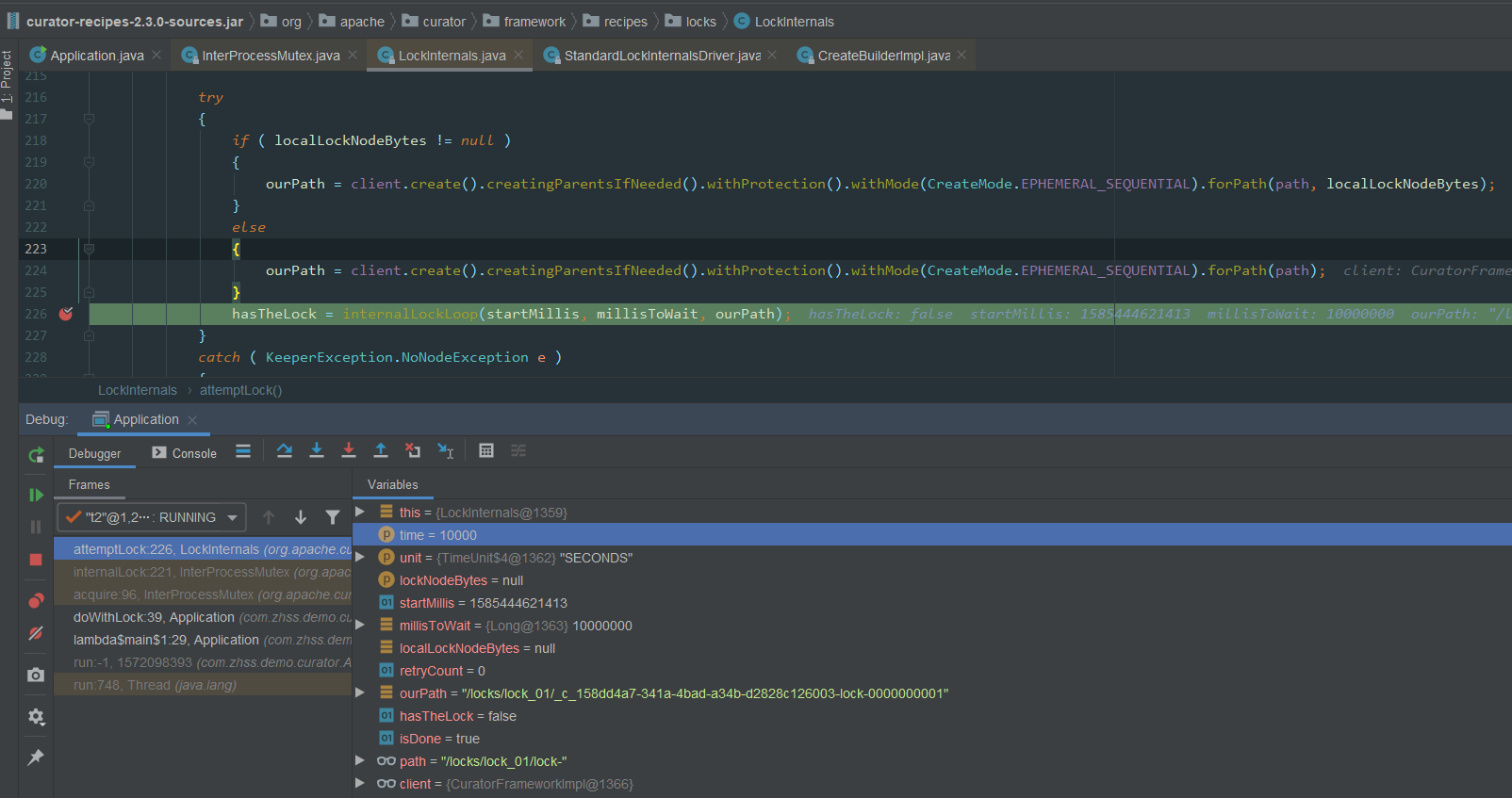
客户端B获取锁的代码,生成的ourPath=xxxx02
查看Zookeeper中/locks/lock_01下所有临时节点数据:
 PS:01/02的图没有截到,这里又跑了一次截图所示 03/04 的顺序节点在ZK中的显示
PS:01/02的图没有截到,这里又跑了一次截图所示 03/04 的顺序节点在ZK中的显示
接着重点看interalLockLoop()的逻辑:
public class LockInternals { private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception { boolean haveTheLock = false; boolean doDelete = false; try { if ( revocable.get() != null ) { client.getData().usingWatcher(revocableWatcher).forPath(ourPath); } while ( (client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock ) { List<String> children = getSortedChildren(); String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases); if ( predicateResults.getsTheLock() ) { haveTheLock = true; } else { String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch(); synchronized(this) { Stat stat = client.checkExists().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath); if ( stat != null ) { if ( millisToWait != null ) { millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis); startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); if ( millisToWait <= 0 ) { doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node break; } wait(millisToWait); } else { wait(); } } } // else it may have been deleted (i.e. lock released). Try to acquire again } } } // 省略部分代码 return haveTheLock; } }
重点看while循环中的逻辑
首先是获取锁的逻辑:
- 获取
/locks/lock_01下排好序的znode节点,上面看图已经知道,会有xxx01和xxx02两个节点 - 调用
getsTheLock()方法获取锁,其中maxLeases为1,默认只能一个线程获取锁 - 定位到
StandardLockInternalsDriver.getsTheLock()方法,其中代码核心如下:int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases; - 上面
sequenceNodeName参数为xxx01的全路径名,然后查看在排好序的children列表中是否为第一个元素,如果是第一个元素,返回的ourIndex=0,此时则认为获取锁成功 - 如果为有序列表中的第一个元素,那么
predicateResults.getsTheLock()为true,获取锁的标志位havaTheLock为true,直接返回获取锁成功
然后是获取锁失败的逻辑:
获取锁失败的核心代码:
String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch(); synchronized(this) { Stat stat = client.checkExists().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath); if ( stat != null ) { if ( millisToWait != null ) { millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis); startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); if ( millisToWait <= 0 ) { doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node break; } wait(millisToWait); } else { wait(); } } }
- 针对上一个节点添加监听器
- 如果加锁有过期时间,到了过期时间后直接break退出循环
- 当前线程处于wait()状态,等待上一个线程释放锁
Curator 释放锁实现原理
释放锁其实很简单,直接删除当前临时节点,因为下一个节点监听了上一个节点信息,所以上一个节点删除后,当前节点就会被唤醒重新获取锁。
private void deleteOurPath(String ourPath) throws Exception { try { client.delete().guaranteed().forPath(ourPath); } catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e ) { // ignore - already deleted (possibly expired session, etc.) } }
总结
一张图总结:

04_Zookeeper分布式锁实现原理.jpg
原图可查看我的分享:
https://www.processon.com/view/link/5e80508de4b06b85300175d2