C# 基础知识系列- 3 集合数组
- 2020 年 3 月 27 日
- 筆記
简单的介绍一下集合,通俗来讲就是用来保管多个数据的方案。比如说我们是一个公司的仓库管理,公司有一堆货物需要管理,有同类的,有不同类的,总而言之就是很多、很乱。我们对照集合的概念对仓库进行管理的话,那么 数组就是将一堆货整整齐齐的码在仓库的某个地方,普通列表也是如此;Set就是在仓库里有这么一个货架,每种货品只能放一个,一旦某种货品超过一个了货架就塌了;Dictionary字典呢,在一个货架上随机摆放,然后再找一个本子把每个货品存放的位置记录下来。
1. 主要集合
C#/.NET Framework 提供了很多很有意思的集合类,数组、列表、链表、Set、字典等一系列的类。其中数组是语言的一部分,个人认为严格意义上不属于集合类这一部分。C#开发中常用的集合有数组、 List类、Set接口、Dictionary类、Queue类、LinkedList类等,其他的出镜率不高。
与其他(java)语言不同的一点是,C#的List是类,而不是接口,接口是IList,但这个接口意义不大,在使用IList的时候更多的倾向于使用IEnumerable,这主要是因为IEnumerable 有 Linq的支持再者两者的方法基本一致,能用IList的地方基本都可以用IEnumerable。
1.1 Array 数组
数组,集合的基础部分,主要特点是一经初始化就无法再次对数组本身进行增删元素。C#虽然添加了一些修改数组的扩展方法,但基本都会返回新的数组对象。
1.1.1 初始化
数组的初始化需要指定大小,可以显示指定或者隐式的指定。
// 显示指定类型与大小,具体的元素后续赋值 string[] strArr = new string[10]; //指定类型同时给元素赋值,具体大小由编译器自动推断 string[] strArr1 = new string[]{"1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"}; // 类型和大小都由编译器进行推断 string[] strArr2 = new []{"1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"}; 1.1.2 常用方法
- 访问和赋值
数组可以通过下标访问数组中的元素,下标从0开始,表示0位。代码如下:
string item0 = strArr[0]; //取出 "1" string item2 = strArr[2]; // 取出 "3" strArr[0] = "3"; // strArr = {"3","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"} - 获取长度
int length = strArr.Length;// 获取一个整型的长度 //获取一个长整型的长度,对于一个非常大的数组且长度可能会超过int的最大值 long longLength = strArr.LongLength; - 循环迭代
// 普通for 循环 for(int i = 0;i < strArr.Length;i++) { string it = strArr[i]; } // foreach 循环 foreach(string it in strArr) { // 依次循环,不需要下标,操作更快一点 } 1.1.3 不常用但有用的方法
-
CopyTo复制到public void CopyTo(Array array, int index); public void CopyTo(Array array, long index);参数说明: array 需要复制到的数组,index 目标数组的起始下标
方法说明:将 源数组的元素依次复制到 array从index下标开始的位置
string[] strArr1 = new string[]{"1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10"}; string[] strArr3 = new string[10]; strArr1.CopyTo(strArr3, 0); //strArr3 = {"1","2","3","4",'5","6","7","8","9","10"}值得注意的是
strArr3的长度不能 小于 index + strArr1.Length -
Sort排序这个方法不是数组对象的方法,而是
Array提供的一个静态方法。int[] arr1 = new[] {1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; Array.Sort(arr1);//0,1,2,3,4,5,6,9,12,13,18,28,44,81,92,98值得注意的是,该方法是直接对数组进行操作,所以不会返回新的数组。
-
ToList转成List
顾名思义,将Array对象转成List对象。这里需要额外注意的是,转换成的List是不可改变长度的。
4. Clone() 获得一个浅拷贝的数组对象
获取该对象的一个浅拷贝数组对象。
至于其他的Array类和Array对象 还有很多有意思的方法,但是平时开发的时候使用的频率比较低。这里就不一一介绍了,以后需要会介绍一下的。
1.2 List 列表
List列表为一个泛型类,泛型表示<T>,其中T表示列表中存放的元素类型,T代表C#中可实例化的类型。关于泛型的具体描述以后介绍,现在回过头来继续介绍列表。列表内部持有一个数组对象,列表有两个私有变量:一个是列表容量,即内部数组的大小;另一个是存放的元素数量,通过Count获取。
List列表通过元素数量实现了Add和Remove 的操作,列表对象操作引发元素数量变动时都会导致对容量的重新计算,如果现有容量不满足后续操作需要的话,将会对现有数组进行扩充。
1.2.1 初始化
List<string> list = new List<string>();// 初始化一个空的列表 List<string> list1 = new List<string>{"12", "2"};//初始化一个包含两个元素的列表 list1 = new List<string>(100);//初始化一个空的列表,并指定list的初始容量为100 list = new List<string>(list1);// 使用一个List/Array 初始化一个列表 1.2.2 常用方法
-
Count或LongCount获取元素的数量Count 表示获取一个int类型的的数量值,LongCount表示获取一个long类型的数量值。通常情况下两者返回的结果是一致的,但是如果列表中元素的数量超过了int允许的最大返回直接使用
Count获取将会出现数据溢出的问题,这时候就需要LongCount了。 -
访问元素/修改元素
C#的列表操作单个元素很简单 ,与数组的操作方式完全一样。
string str = list1[0];//获取 list1 的第一个元素,即下标为0的元素
list1[2] = "233"; // 将 list1 的第三个元素设置为“233” ,即下标为2 的元素,这里假设list1有至少三个元素
“`
需要注意的地方是,如果给定的下标超过了List对象的索引值范围会报ArgumentOutOfRangeException。判断方法就是 下标>= Count,如果满足就会越界。
3. Add或AddRange 添加到列表最后
将元素添加到List的末尾,`Add`添加一个,`AddRange`添加一组,支持数组、列表。 ```c# List<string> list = new List<string>();// 初始化一个空的列表 list.Add("12");//list = {"12"} List<string> list1 = new List<string>{"14", "2"}; list.AddRange(list1);// list = {"12","14","2"} ``` -
Insert(int index, T item)或InsertRange(int index,IEnumerable<T> items)插入Insert(int index,T item)在 index 下标处插入一个元素,该下标以及该下标以后的元素依次后移InsertRange(int index,IEnumerable<T> items)在index下标处插入一组元素,该下标以及之后的元素依次后移
示例:
List<int> arr1 = new List<int>{1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; arr1.Insert(3,37);// arr1 = 1,9,28,37,5,3,6,0,12,44,98,4,2,13,18,81,92 下标为3的元素变成了37,之后的元素依次后移了List<int> arr1 = new List<int>{1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr1.InsertRange(2,arr2);//arr1= 1,9,2,3,4,5,28,5,3,6,0,12,44,98,4,2,13,18,81,92 可以明显发现下标为2的元素发生了变化 -
Contains(T item)是否包含
返回一个Boolean类型的结果,如果包含则返回true,如果不包含则返回falseList<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr2.Contains(8);//false arr2.Contains(3);//true -
Remove(T item)删除指定元素List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr2.Remove(3);// arr2 = 2,4,5 arr2.Remove(6);//arr2 = 2,4,5值得注意的是,如果删除一个不存在的元素时,不会报错,列表也不会发生任何改变。
-
RemoveAt(int index)删除位于下标的元素List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr2.RemoveAt(1);//arr2 = 2,4,5如果移除的下标超过了列表的最后一个元素的下标将会抛出异常
-
RemoveRane(IEnumerable<T> items)删除一组元素与
Remove(T item)一致,如果要删除的元素不在列表中,则列表元素不会发生变化。List<int> arr1 = new List<int>{1, 9, 28, 5, 3, 6, 0, 12, 44, 98, 4, 2, 13, 18, 81, 92}; List<int> arr2 = new List<int>{2,3,4,5}; arr1.RemoveRange(arr2); -
GetRange(int index,int count)从列表中获取一个子列表,从
index开始,获取count个元素,如果源列表中从index开始剩余的元素不足count个将会报错。
1.2.3 不常用但有用的方法
-
Clear()删除所有元素将列表清空,调用方法之后,列表中将不包含任何元素
-
Reverse()调转顺序将列表按照从尾到头的顺序进行排列
-
IndexOf(T item)查找下标查找元素在列表中的下标,如果没找到元素,则返回-1
-
Sort()排序对列表进行排序,调用方法后,会按照默认排序方法返回一个排序结果
1.3 Set 集合
C#没有为Set单独设置类,一方面是因为Set出镜率不高,另一方面也因为Set本身的机制所致。Set集合不能包含重复元素,如果尝试存入重复元素集合元素将不会发生任何变化。
Set集合中元素的顺序与存放顺序不一定相同。因为Set集合中存放对于使用者而言是乱序存放的。
我们常用的Set集合有 HashSet<T>和SortSet<T>,其他的Set相关类则属于更加少见。至少在我5年多的开发经历中没有用过。
1.3.1 HashSet<T> 和SortSet<T>
HashSet俗称 哈希集合或者哈希Set,内部使用Hash值作为元素的唯一性验证,即调用对象的HashCode()方法作为Hash值的来源。SortSet顾名思义,排序集合,它每次在插入的时候都会对元素进行一次排序
1.3.2 共同点
-
初始化
两者相同的地方就是 都有以下几种初始化方法
Set<T> set = new HashSet<T>();// = new SortSet<T>(); 初始化一个空的集合 //使用一个集合对象初始化 Set<T> set1 = new HashSet<T>(IEnumerable<T> items);// = new SortSet<T>(IEnumerable<T> items); Set<T> set2 = new HashSet<T>(){T t1, T t2, T t3};// 与上一种一样 -
添加元素
set1.Add(item);// 集合只支持添加单个元素,但是可以通过集合运算的方式增加多个元素 -
移除元素
set1.Remove(item);//删除集合中与item判断相等的元素 -
访问元素
需要注意的地方是,C#对Set没有支持下标访问方式获取Set里的元素,这是因为索引位置对于集合来说意义不大,没有操作意义。
foreach (var item in set1) { // 操作 }Set 只能通过遍历访问元素,不能通过Get或者下标操作访问元素。关于
foreach循环会在下一篇《C#基础知识系列》里进行介绍。 -
集合运算
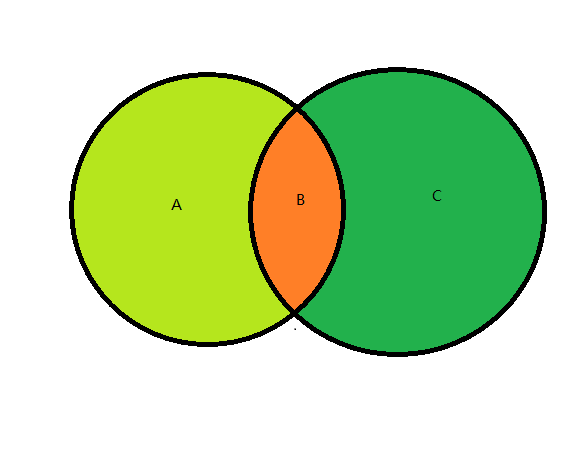
-
UnionWith并SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.UnionWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33}); // set = 0,1,3,4,5,8,17,29,33,38,48,57通过传入一个集合对象,将该集合设置为两个集合的并集,也就是说取上图 A,B,C 三个区域的和
-
ExceptWith差SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.ExceptWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33}); // set =17,29,38,48传入一个集合,从set中去掉同属于两个集合的元素,保留只存在于set的元素,也就是取上图中的A部分元素
-
IntersectWith交SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.ExceptWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33}); // set =0,1,33传入一个集合,保留set与传入集合里相同的元素,也就是说取的是上图中的B部分
-
SymmetricExceptWith余集SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.SymmetricExceptWith(new []{5,57,8,4,3,1,0,33});//set= 3,4,5,8,17,29,38,48,57传入一个集合,保留set与传入集合两个集合中不同的元素,也就是取上图的A+C这两部分。
-
-
Contains包含判断集合中是否包含目标元素,返回true/false
SortedSet<int> set = new SortedSet<int>{1,0,29,38,33,48,17}; set.Contains(1);// true
1.3.3 不同点
- 初始化
HashSet<T>支持传入一个自定义的相等比较器,该比较器需要返回一个 bool值;可以指定起始容量SortSet<T>支持传入一个自定义的大小比较器,该比较器返回一个int值;不能指定起始容量
- 其他
Comparer属性:SortSet 可以获取大小比较器;HashSet 获取一个相等比较器
1.4 Dictionary 字典
Dictionary 字典,正如它的名称一样,Dictionary 需要指定两个类型,一个作为索引键,一个作为数据值。就像字典一样,每一个词条内容都只有一个字词索引,但可以出现同义词一样。当然,作为我博大精深的中文会出现同字不同音的词组,但是一旦把音、字组合起来作为索引,那还是只会出现一个词条。
所以 Dictionary的使用方式也跟字典一样,通过索引访问和操作数据。
1.4.1 初始化
Dictionary的初始化有如下几个方法:
Dictionary<string, int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>();// 键是字符串,值是int类型 Dictionary<string,int> dict1 = new Dictionary<string, int>(10);// 指定初始容量是10 Dictionary<string,int> dict2 = new Dictionary<string, int>() { {"1",1}, {"2",2} };// 在大括号标记中 通过 {key,value}的写法创建一个 字典对象,并包含这些键值对 // 传入一个字典对象,以传入的对象为基础创建一个字典 Dictionary<string,int> dict3 = new Dictionary<string, int>(dict2); 1.4.2 常用方法
-
添加元素
Dictionary<string, int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>(); // 方法一 dict.Add("1",2);//添加一个 键为“1”,值为2的键值对。 //方法二 //字典可以类似列表的形式通过下标添加或更新键对应的值, //不过与列表不同的是,字典的下标是字符串 dict["2"] = 4;// 如果 dict中2有值,则更新为4,如果没有,则设置2对应的值为4 -
获取元素
Dictionary<string, int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>(); /* 省略数据填充阶段 */ int value = dict["2"]; // value = 4 // 如果Dictionary中不存在索引为“2”的数据 // 将会抛出 System.Collections.Generic.KeyNotFoundException 异常C# 的
Dictionary还有一个TryGetValue方法可以用来尝试获取,他的使用方法是这样的:int obj = 0; boolean isContains = dict.TryGetValue("3", out obj); // 方法会返回 dict是否包含键“3”的结果,如果有 obj 则存放了dict中对应的值,如果没有,则返回false且不改变 obj 的值 -
Count获取
Dictionary里键值对的数量。int count = dict.Count;Dictionary没有
LongCount属性,因为对于Dictionary存放数据需要比对Key的相等性,如果存放巨量数据将会对数据的访问和操作效率有影响。 -
Keys获取
Dictionary里所有的键,返回一个KeyCollection对象,不需要关心这是一个什么类型,可以简单的把它当做一个存放了键的HashSet。 -
ContainsKey()是否包含键:通常与获取元素一起使用,可以先判断
Dictionary里是否有这个键,然后再进行后续操作。 -
Remove()删除
Dictionary中键对应的元素,删除后再次访问会报错。如果删除一个不存在的元素将返回flase。
操作示例:Dictionary<string,int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>(); //省略赋值操作 bool result = dict.Remove("2");// 如果dict里包含键为“2”的元素,则result为true,否则为false另一种方法:
int value = 0; bool result = dict.Remove("2", out value); // 如果dict 里包含键为“2”的元素,则result 为 false且value为对应的值
1.4.3 不常用但有用的方法
-
ContainsValue()是否包含值,与
ContainsKey的用法一样,只不过遍历的是值;用处不大。 -
Values获取值的集合类似与
KeyValues。
2. 传统集合(非泛型)
C#的传统集合基本都存放在System.Collections命名空间里,详细的可以查看微软官方文档。这个命名空间里的集合类使用都不多,不过C#的集合体系的接口规范都是在这个里面定义的。
2.1 常见类介绍
-
ArrayListList的非泛型版,与List操作方法一致,不过返回值是Object类型 -
SortedList一个排序的键值对集合,我没用过,不过官方给了如下示例:using System; using System.Collections; public class SamplesSortedList { public static void Main() { // Creates and initializes a new SortedList. SortedList mySL = new SortedList(); mySL.Add("Third", "!"); mySL.Add("Second", "World"); mySL.Add("First", "Hello"); // Displays the properties and values of the SortedList. Console.WriteLine( "mySL" ); Console.WriteLine( " Count: {0}", mySL.Count ); Console.WriteLine( " Capacity: {0}", mySL.Capacity ); Console.WriteLine( " Keys and Values:" ); PrintKeysAndValues( mySL ); } public static void PrintKeysAndValues( SortedList myList ) { Console.WriteLine( "t-KEY-t-VALUE-" ); for ( int i = 0; i < myList.Count; i++ ) { Console.WriteLine( "t{0}:t{1}", myList.GetKey(i), myList.GetByIndex(i) ); } Console.WriteLine(); } } -
HashTable表示根据键的哈希代码进行组织的键/值对的集合。HashTable的结构类似于Dictionary但又与其不同,它的键值存储用的是Hash值。以下是官方给出的示例代码:using System; using System.Collections; class Example { public static void Main() { // Create a new hash table. // Hashtable openWith = new Hashtable(); // Add some elements to the hash table. There are no // duplicate keys, but some of the values are duplicates. openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // The Add method throws an exception if the new key is // already in the hash table. try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = "txt" already exists."); } // The Item property is the default property, so you // can omit its name when accessing elements. Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // The default Item property can be used to change the value // associated with a key. openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // If a key does not exist, setting the default Item property // for that key adds a new key/value pair. openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // ContainsKey can be used to test keys before inserting // them. if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = "ht": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // When you use foreach to enumerate hash table elements, // the elements are retrieved as KeyValuePair objects. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( DictionaryEntry de in openWith ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", de.Key, de.Value); } // To get the values alone, use the Values property. ICollection valueColl = openWith.Values; // The elements of the ValueCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for hash table values. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in valueColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // To get the keys alone, use the Keys property. ICollection keyColl = openWith.Keys; // The elements of the KeyCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for hash table keys. Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in keyColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // Use the Remove method to remove a key/value pair. Console.WriteLine("nRemove("doc")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key "doc" is not found."); } } } /* This code example produces the following output: An element with Key = "txt" already exists. For key = "rtf", value = wordpad.exe. For key = "rtf", value = winword.exe. Value added for key = "ht": hypertrm.exe Key = dib, Value = paint.exe Key = txt, Value = notepad.exe Key = ht, Value = hypertrm.exe Key = bmp, Value = paint.exe Key = rtf, Value = winword.exe Key = doc, Value = winword.exe Value = paint.exe Value = notepad.exe Value = hypertrm.exe Value = paint.exe Value = winword.exe Value = winword.exe Key = dib Key = txt Key = ht Key = bmp Key = rtf Key = doc Remove("doc") Key "doc" is not found. */虽然C#框架保留了非泛型集合元素,但不建议使用非泛型集合进行开发。
3 一些不常用的集合类
除了之前所说的几个集合类,C#还设置了一些在开发中不常用但在特定场合很有用的集合类。
3.1 Queue<T> 和 Queue
这两个类是一对的,一个是泛型类,一个是非泛型类。该类中文名称是队列,如其名,队列讲究一个先进先出,所以队列每次取元素都是从头取,存放是放到队列尾。
操作代码如下:
-
加入队列
Queue queue = new Queue(); queue.Enqueue(1); queue.Enqueue("2"); Queue<string> queue1 = new Queue<string>(); queue1.Enqueue("stri");// -
读取队首的元素
读取有两种:-
读取但不移除元素:
object obj= queue.Peek(); string str = queue.Peek(); -
读取并移除元素:
object obj = queue.Dequeue(); string str = queue.Dequeue();
- Count 获取元素数量
-
3.2 LinkedList<T>
LinkedList,链表。与List不同的地方是,LinkedList的元素是LinkedListNode对象,该对象有四个属性,分别是List
-指向列表对象,Previous指向前一个对象如果有的话,Next指向后一个对象如果有的话。所以根据元素的属性可以发现链表的工作方式,链表就像一条锁链一样,一个元素分三块,一个指向前一个元素,一个用来存放值,一个指向下一个元素,简单如下图所示:
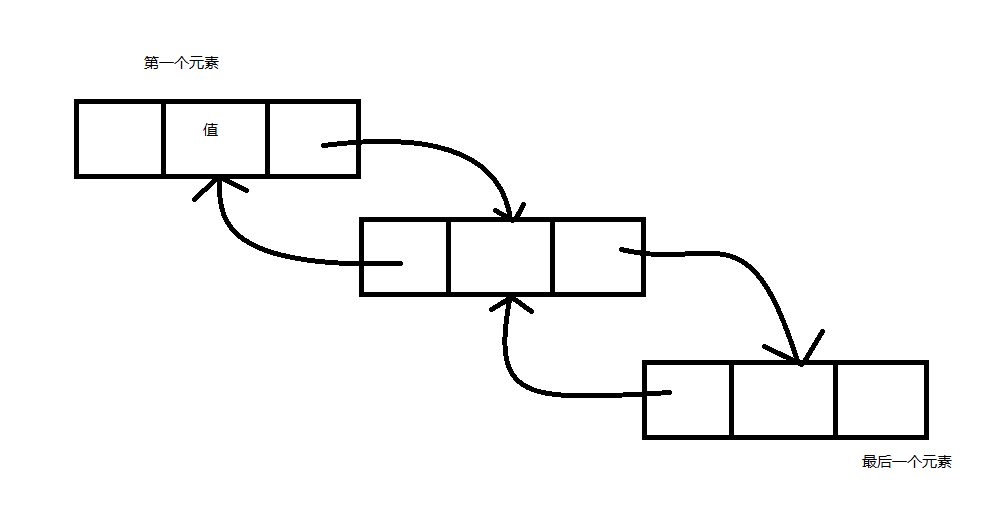
所以可以明显的发现LinkedList在随机插取上比一般的要快,因为它不用维护一个数组,但是在查找和坐标操作上明显要慢很多。
LinkedList简单介绍这么多,可以看看它的一些常见操作:
-
First第一个元素获取第一个元素
-
Last最后一个元素获取最后一个元素
-
AddAfter/AddBefore
在某个节点后/在某个节点前插入数据
支持以下参数列表:- (LinkedListNode
node, T value) - (LinkedListNode
node, LinkedListNode newNode)
第一个参数表示要插入的节点位置,第二个表示要插入的节点/元素。第一个参数会校验是否属于该链表,如果不属于则会抛出一个异常。第二个可以是值,也可以是初始化好的节点对象。如果是节点对象,则判断是否归属其他链表,如果是其他链表抛出异常。
- (LinkedListNode
-
AddFirst/AddLast添加元素到头或者尾,可以使用
LinkedListNode或者添加值。 -
Remove删除,可以传递某个节点,或者要删除的节点里存放的值。
-
RemoveFirst/RemoveLast
删除第一个节点,删除最后一个节点,不含参数
下面是微软官方的一些示例
using System; using System.Text; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Example { public static void Main() { // Create the link list. string[] words = { "the", "fox", "jumps", "over", "the", "dog" }; LinkedList<string> sentence = new LinkedList<string>(words); Display(sentence, "The linked list values:"); Console.WriteLine("sentence.Contains("jumps") = {0}", sentence.Contains("jumps")); // Add the word 'today' to the beginning of the linked list. sentence.AddFirst("today"); Display(sentence, "Test 1: Add 'today' to beginning of the list:"); // Move the first node to be the last node. LinkedListNode<string> mark1 = sentence.First; sentence.RemoveFirst(); sentence.AddLast(mark1); Display(sentence, "Test 2: Move first node to be last node:"); // Change the last node to 'yesterday'. sentence.RemoveLast(); sentence.AddLast("yesterday"); Display(sentence, "Test 3: Change the last node to 'yesterday':"); // Move the last node to be the first node. mark1 = sentence.Last; sentence.RemoveLast(); sentence.AddFirst(mark1); Display(sentence, "Test 4: Move last node to be first node:"); // Indicate the last occurence of 'the'. sentence.RemoveFirst(); LinkedListNode<string> current = sentence.FindLast("the"); IndicateNode(current, "Test 5: Indicate last occurence of 'the':"); // Add 'lazy' and 'old' after 'the' (the LinkedListNode named current). sentence.AddAfter(current, "old"); sentence.AddAfter(current, "lazy"); IndicateNode(current, "Test 6: Add 'lazy' and 'old' after 'the':"); // Indicate 'fox' node. current = sentence.Find("fox"); IndicateNode(current, "Test 7: Indicate the 'fox' node:"); // Add 'quick' and 'brown' before 'fox': sentence.AddBefore(current, "quick"); sentence.AddBefore(current, "brown"); IndicateNode(current, "Test 8: Add 'quick' and 'brown' before 'fox':"); // Keep a reference to the current node, 'fox', // and to the previous node in the list. Indicate the 'dog' node. mark1 = current; LinkedListNode<string> mark2 = current.Previous; current = sentence.Find("dog"); IndicateNode(current, "Test 9: Indicate the 'dog' node:"); // The AddBefore method throws an InvalidOperationException // if you try to add a node that already belongs to a list. Console.WriteLine("Test 10: Throw exception by adding node (fox) already in the list:"); try { sentence.AddBefore(current, mark1); } catch (InvalidOperationException ex) { Console.WriteLine("Exception message: {0}", ex.Message); } Console.WriteLine(); // Remove the node referred to by mark1, and then add it // before the node referred to by current. // Indicate the node referred to by current. sentence.Remove(mark1); sentence.AddBefore(current, mark1); IndicateNode(current, "Test 11: Move a referenced node (fox) before the current node (dog):"); // Remove the node referred to by current. sentence.Remove(current); IndicateNode(current, "Test 12: Remove current node (dog) and attempt to indicate it:"); // Add the node after the node referred to by mark2. sentence.AddAfter(mark2, current); IndicateNode(current, "Test 13: Add node removed in test 11 after a referenced node (brown):"); // The Remove method finds and removes the // first node that that has the specified value. sentence.Remove("old"); Display(sentence, "Test 14: Remove node that has the value 'old':"); // When the linked list is cast to ICollection(Of String), // the Add method adds a node to the end of the list. sentence.RemoveLast(); ICollection<string> icoll = sentence; icoll.Add("rhinoceros"); Display(sentence, "Test 15: Remove last node, cast to ICollection, and add 'rhinoceros':"); Console.WriteLine("Test 16: Copy the list to an array:"); // Create an array with the same number of // elements as the inked list. string[] sArray = new string[sentence.Count]; sentence.CopyTo(sArray, 0); foreach (string s in sArray) { Console.WriteLine(s); } // Release all the nodes. sentence.Clear(); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("Test 17: Clear linked list. Contains 'jumps' = {0}", sentence.Contains("jumps")); Console.ReadLine(); } private static void Display(LinkedList<string> words, string test) { Console.WriteLine(test); foreach (string word in words) { Console.Write(word + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine(); } private static void IndicateNode(LinkedListNode<string> node, string test) { Console.WriteLine(test); if (node.List == null) { Console.WriteLine("Node '{0}' is not in the list.n", node.Value); return; } StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder("(" + node.Value + ")"); LinkedListNode<string> nodeP = node.Previous; while (nodeP != null) { result.Insert(0, nodeP.Value + " "); nodeP = nodeP.Previous; } node = node.Next; while (node != null) { result.Append(" " + node.Value); node = node.Next; } Console.WriteLine(result); Console.WriteLine(); } } //This code example produces the following output: // //The linked list values: //the fox jumps over the dog //Test 1: Add 'today' to beginning of the list: //today the fox jumps over the dog //Test 2: Move first node to be last node: //the fox jumps over the dog today //Test 3: Change the last node to 'yesterday': //the fox jumps over the dog yesterday //Test 4: Move last node to be first node: //yesterday the fox jumps over the dog //Test 5: Indicate last occurence of 'the': //the fox jumps over (the) dog //Test 6: Add 'lazy' and 'old' after 'the': //the fox jumps over (the) lazy old dog //Test 7: Indicate the 'fox' node: //the (fox) jumps over the lazy old dog //Test 8: Add 'quick' and 'brown' before 'fox': //the quick brown (fox) jumps over the lazy old dog //Test 9: Indicate the 'dog' node: //the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy old (dog) //Test 10: Throw exception by adding node (fox) already in the list: //Exception message: The LinkedList node belongs a LinkedList. //Test 11: Move a referenced node (fox) before the current node (dog): //the quick brown jumps over the lazy old fox (dog) //Test 12: Remove current node (dog) and attempt to indicate it: //Node 'dog' is not in the list. //Test 13: Add node removed in test 11 after a referenced node (brown): //the quick brown (dog) jumps over the lazy old fox //Test 14: Remove node that has the value 'old': //the quick brown dog jumps over the lazy fox //Test 15: Remove last node, cast to ICollection, and add 'rhinoceros': //the quick brown dog jumps over the lazy rhinoceros //Test 16: Copy the list to an array: //the //quick //brown //dog //jumps //over //the //lazy //rhinoceros //Test 17: Clear linked list. Contains 'jumps' = False // 3.3 Stack<T> 和 Stack
Stack广泛的翻译是栈,是一种后进先出的集合。在一些特殊场景里,使用十分广泛。
Stack有两个很重要的方法Pop 和Push,出/进。Pop 获取最后一个元素,并退出栈,Push 向栈推入一个元素。
具体可以参照官方文档
4 集合相关命名空间
C# 的集合还有其他的一些命名空间里藏着宝贝,不过在实际开发中使用频率并不大,可以按需查看。
4.1 System.Collections.Concurrent 线程安全
这个命名空间,提供了一系列线程安全的集合类,当出现多线程操作集合的时候,应当使用这个命名空间的集合。名称和常用的类是一一对应的,不过只提供了ConcurrentDictionary<TKey,TValue>、ConcurrentQueue<T>、ConcurrentStack<T>等几个集合类。具体可以查看官方文档
4.2 System.Collections.Immutable 不可变集合
命名空间包含用于定义不可变集合的接口和类,如果需要使用这个命名空间,则需要使用NuGet下载。
-
- 共享集合,使其使用者可以确保集合永远不会发生更改。
- 提供多线程应用程序中的隐式线程安全(无需锁来访问集合)。
- 遵循函数编程做法。
- 在枚举过程中修改集合,同时确保该原始集合不会更改。
更多内容烦请关注我的博客



