STL篇–list容器
- 2020 年 3 月 26 日
- 筆記
list容器:
1.list 容器 的本质就是双向环形链表,最后一个节点刻意做成空节点,符合容器的左闭右开的原则
2.list 的迭代器 是一个智能指针,其实就是一个类,通过操作符重载模拟各种操作(++i,i++等),一个node的大小是4字节(32位机器),里面包含两个指针+一个数据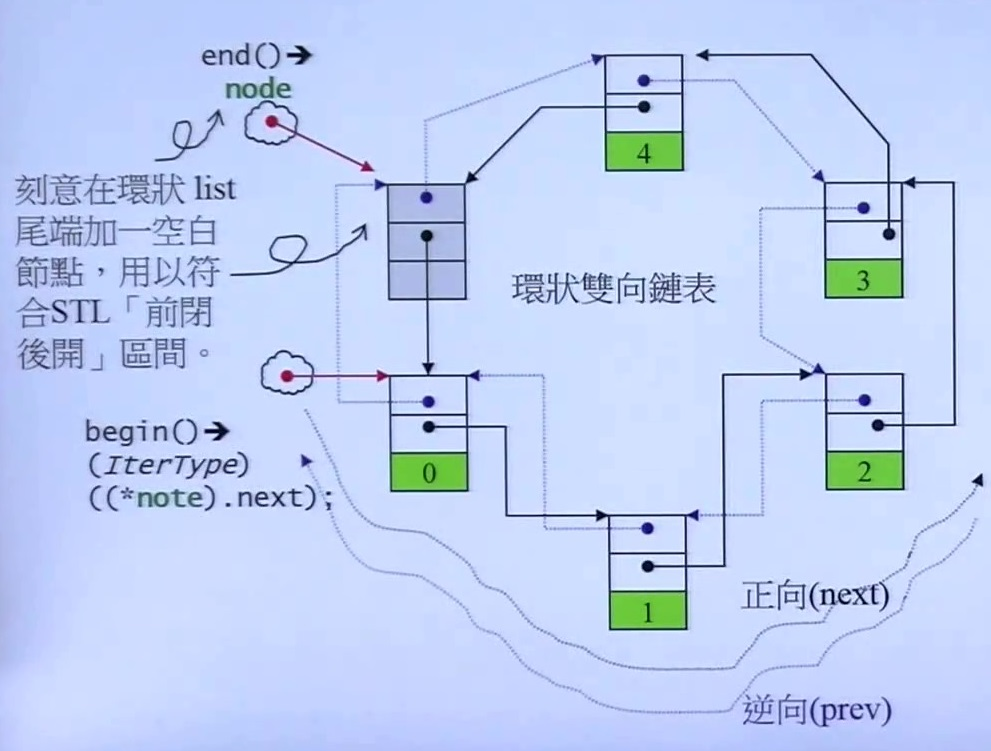
图1 截选自侯捷的STL源码剖析的课程
用例:
1 //-----------------作者:侯捷------------------ 2 #include <list> //使用list必须包含的头文件 3 #include <stdexcept> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <cstdlib> //abort() 6 #include <cstdio> //snprintf() 7 #include <algorithm> //find() 8 #include <iostream> 9 #include <ctime> 10 namespace jj03 11 { 12 void test_list(long& value) //value表示 容器的大小 13 { 14 cout << "ntest_list().......... n"; 15 16 list<string> c; 17 char buf[10]; 18 19 clock_t timeStart = clock(); 20 for(long i=0; i< value; ++i) 21 { 22 try { //防止内存不够泄露 23 snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand()); 24 c.push_back(string(buf)); 25 } 26 catch(exception& p) { 27 cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl; 28 abort(); 29 } 30 } 31 cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; 32 cout << "list.size()= " << c.size() << endl; 33 cout << "list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941 34 cout << "list.front()= " << c.front() << endl; 35 cout << "list.back()= " << c.back() << endl; 36 37 string target = get_a_target_string(); 38 timeStart = clock(); 39 auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //auto实参自行推导 调用find方法查找 40 cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; 41 42 if (pItem != c.end()) 43 cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl; 44 else 45 cout << "not found! " << endl; 46 47 timeStart = clock(); 48 c.sort(); //调用sort方法排序 49 cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; 50 51 c.clear();52 } 53 }
容器list自带的方法可自行参考书籍《c++ primer,常见的包括:
1 push_front(v):把元素v插入到链表头部 2 pop_front():删除双向队列的第一个元素 3 4 push_back(v):把元素v插入到双向队列的尾部 5 pop_back():删除双向队列的最后一个元素 6 7 begin():返回向量中第一个元素的迭代器 8 back(): 获得list容器的最后一个元素 9 10 clear(): 清空list中的所有元素 11 empty():利用empty() 判断list是否为空。