初窥Mybatis初始化
- 2020 年 3 月 7 日
- 筆記
引言
这篇文章呢,主要是讲Mybtais的两种方式的源码剖析:传统方式以及Mapper代理方式,初次探索Mybatis源码,希望大佬勿喷并且指正错误,谢谢!
个人博客:www.fqcoder.cn
一、Mybatis架构原理
1.架构图
首先,让我们来看看下面这张图:
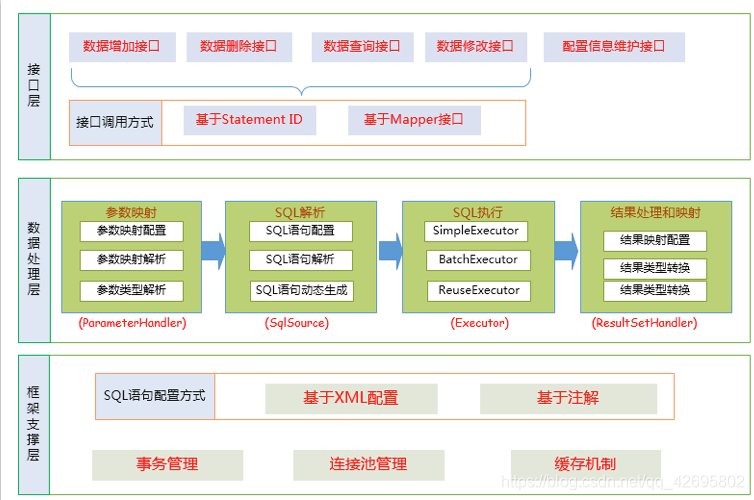
我们吧Mybtais功能架构可以分为三层:
1.接口层:提供给外部使用的接口API,开发人员通过这些本地API来操作数据库。接口一层接收到调用请求就会调用数据处理来完成具体的数据处理。
MyBatis和数据库交互有两种方式:(也是我们接下来需要死磕的目标)
a.使用传统的Mybatis提供的API
b.使用Mapper代理的方式
2.数据处理层:负责具体的SQL查找、SQL解析、SQL执行、结果处理和映射等,它主要的目的是根据调用的请求完成一次数据库的操作。
3.框架支撑层:负责最基础的功能支撑,包括连接管理、事务管理、配置加载和缓存处理,这些都是共用的东西,将他们抽取出来作为最基础的组件。为上层的数据处理层提供最基础的支撑。
2.主要构件及其相互关系
| 构件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SqlSession | 作为MyBatis工作主要顶层API,表示和数据库交互的会话,完成必要数据库 增删改查功能 |
| Executor | Mybatis执行器,是Mybatis调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护 |
| StatementHandler | 封装了JDBC Statemenet操作,负责对JDBC Statement的操作,如设置参数、 将Statement结果集转换成List集合 |
| ParameterHandler | 负责对用户传递的参数转换成JDBC Statement所需要的参数 |
| ResultSetHandler | 负责将JDBC返回的ResultSet结果集对象转换成List类型的集合 |
| TypeHandler | 负责java数据类型和jdbc数据类型之间的映射和转换 |
| MappedStatement | MappedStatement维护了一条<select | update | delete | insert>节点的封装 |
| SqlSource | 负责根据用户传递的parameterObject,动态的生成SQL语句,将信息分封装到 BoundSql对象中,并返回 |
| BoundSql | 表示动态生成的SQL语句以及相应的参数信息 |
3.层次结构图
下面这张图就是Mybatis流程的层次结构图,建议读源码的时候记得打开这张图,思路才不会乱呢
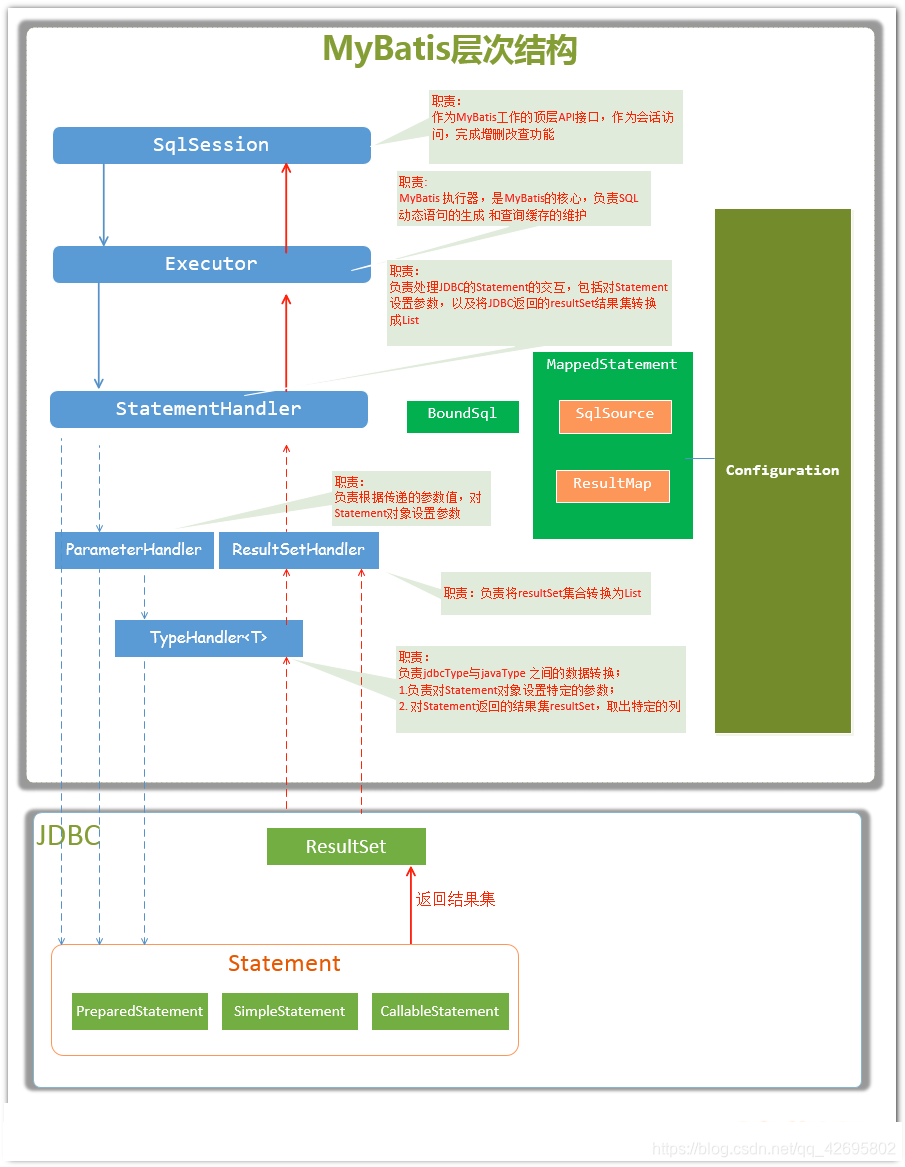
4.总体流程
(1)加载配置文件并初始化
配置来源两个地方,一个是配置文件(主配置文件confi.xml,Mapper文件.xml),一个是Java代码中的注解,将主配置为恩建内容解析封装到Configuration,将sql的配置信息加载成为一个mappedStatement对象,存储在内存之中
(2)接收调用请求
将请求传递给下层的请求处理层进行处理
(3)处理操作请求
A.根据SQL的ID查找对一个的MappedStatement对象
B.根据传入参数对象解析MappedStatement对象,得到最终要执行的SQL和执行传入参数
C.获取数据库连接,根据得到的最终SQL语句执行传入参数到数据库执行,并得到执行结果
D.根据MappedStatement对象中的结果映射配置对得到的执行结果进行转换处理,并得到最终的处理结果
E.释放连接资源
(4)返回处理结果
将最终的处理结果返回
二、死磕Mybatis源码剖析
1)传统方式的源码剖析
读取配置文件就不进去看了,第二行代码,才是初始化工作的开始
//1.读取配置文件,读成字节输入流:还未解析 InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml"); //2.解析XMl配置文件,封装成Configuration对象,创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);我们进入build()方法里看看:
//1.我们最初调用的build public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) { //调用了重载方法 return build(inputStream, null, null); }发现调用了一个重载的方法,我们点进build()去看看:
//2.调用的重载方法 public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) { try { //创建XML ConfigBuilder,XML configBuilder 是专门解析MyBatis的配置文件的类 XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); //执行XML解析 //创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象 return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } }发现创建了parser.parse()的返回值是configuration对象,是专门解析Mybatis的配置文件的类,
Mybatis在初始化的时候,会将Mybatis的配置信息全部加载到内存中,使用org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration实例来维护,我们在进去parse()方法里看看:
/** * 解析XML 成 Configuration对象 * @return Configuration对象 */ public Configuration parse() { //若已解析,抛出BuilderException异常 if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } //标记已经解析 parsed = true; //parser是XPathParser解析器对象,读取节内数据,<configuration>是Mybatis配置文件的顶层标签 //解析XML configuration节点 parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }我们看看是怎么解析configuration节点的,我们再点进parseConfiguration()方法里看看:
/** * 解析 XML * * 具体 My * @param root 根节点 */ private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first //解析<properties/>标签 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //解析<settings>标签 Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); //加载自定义的VFS实现类 loadCustomVfs(settings); //加载自定义的LOG实现类 loadCustomLogImpl(settings); //解析<typeAliases/>标签 typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); //解析<plugins/>标签 pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); //解析<objectFactory/>标签 objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); //解析<objectWrapperFactory/>标签 objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); //解析<reflectorFactory/>标签 reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); //赋值<settings/>到 Configuration 属性 settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 //解析<environments/>标签 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); //解析<databaseIdProvider/>标签 databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); //解析<typeHandlers/>标签 typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); //解析<mappers/>解析 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }是不是发现这里面都是解析配置文件里的标签,我们随便点进一个方法里,以propertiesElement()方法为例,我们再进去看看:
/** * 1.解析 <properties/> 标签,成 Properties 对象 * 2.覆盖 configuration 中的 Properties 对象到上面的结果 * 3.设置结果到 parser 和 configuration 中 * * @param context 节点 * @throws Exception 解析发生异常 */ private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { //读取子标签们,为 Properties对象 Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); //读取 resource 和 url 属性 String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = context.getStringAttribute("url"); //resource 和 url 都存在的情况下,抛出 BuilderException 异常 if (resource != null && url != null) { throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other."); } //读取本地 properties 配置文件到 defaults 中 if (resource != null) { defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource)); //读取远程 properties 配置文件到defaults中 } else if (url != null) { defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url)); } //覆盖 configuration中的 properties对象到defaults中 Properties vars = configuration.getVariables(); if (vars != null) { defaults.putAll(vars); } //设置 defaults 到 parser 和 configuration 中 parser.setVariables(defaults); configuration.setVariables(defaults); } }好了,到了这里发现,初始化配置文件的本质就是创建configuration对象,将解析的xml数据封装到Configuration内部属性中。
然后我们再回到开头,我再贴一下代码:
//1.读取配置文件,读成字节输入流:还未解析 InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml"); //2.解析XMl配置文件,封装成Configuration对象,创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream); //3.生产了DefaultSqlSession实例对象 设置了事务不自动提交 完成了executor 对象的创建 SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); 初始化完毕之后,我们就要开始执行SQL了,获得sqlSession,在这之前,我先简单介绍一下SqlSession:
SqlSession是一个接口,他有两个实现类DefaultSqlSession(默认)和SqlSessionManager(弃用) SqlSession是Mybatis中用于和数据库交互的顶层类,通常将它与ThreadLocal绑定,一个会话使用一个SqlSession,并且在使用完毕之后需要close。 public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession { private final Configuration configuration; private final Executor executor; .......略 } SqlSession中两个最重要的参数,configuration与初始化时的相同,executor为执行器我们继续,进入openSession()方法看看:
@Override public SqlSession openSession() { //getDefaultExecutorType()传递的是SimpleExecutor return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); } 我们进openSessionFromDataSource():
/** * * @param execType Executor的类型 * @param level 事务隔离级别 * @param autoCommit 是否开启事务 * @return */ //openSession的多个重载方法可以指定获得的SqlSession的Executor类型和事务的处理 private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { //获的 Environment 对象 final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); //创建 TransactionFactory 对象 final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); //创建 Executor 对象 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); //创建DefaultSqlSession 对象 return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { //如果发生异常,则关闭 Transaction 对象 closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } } 发现openSessionFromDataSource返回了一个DefaultSqlSession实例对象,设置了事务不自动提交,完成了executor 对象的创建,接下来,就要执行sqlSession中的api了:
/** * 1.根据Statement Id 来从Configuration中map集合中获取到了指定的MappedStatement对象 * 2.将查询任务委派了executor执行器 */ List<Object> objects = sqlSession.selectList("com.fqcoder.mapper.UserMapper.getUserName"); 我们进selectList()方法看看,发现是多个重载方法:
//进入 selectList 方法,多个重载方法 @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) { return this.selectList(statement, null); } @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) { return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT); } @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { //获得 MappedStatement对象 MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); //执行查询 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } } 我们进入executor.query()
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { //根据传入的参数动态获取SQL语句,最后返回用BoundSql对象表示 BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); //为本次查询创建缓存的key CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); //查询 return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } 进入query的重载方法中:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); //已经关闭,则抛出ExecutorException异常 if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } //清空本地换成,如果queryStack为零,并且要求清空本地缓存 if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { //queryStack +1 queryStack++; //从一级缓存中,获取查询结果 list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; //获取到,则进行处理 if (list != null) { handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { //获取不到,则从数据库中查询 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; } 我们继续 ,进入queryFromDatabase()方法:
//从数据库中读取操作 private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { List<E> list; //在缓存中,添加占位对象,此处的 localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try { //执行操作 list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { //从缓存中,移除占位对象 localCache.removeObject(key); } //添加到缓存中 localCache.putObject(key, list); //暂时忽略,存储过程相关 if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; } 进入doQuery()方法:SimpleExecutor中实现的父类doQuery抽象方法,发现底层是通过jdbc来操作的数据库的
@Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { //获取configuration对象 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); //传入参数创建 StatementHandler对象来执行查询 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); //创建jdbc中的statement对象 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); //执行StatementHandler,进行读操作 return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { //关闭 StatementHandler 对象 closeStatement(stmt); } } 我们在进去prepareStatement()方法看看:
//初始化 StatementHandler 对象 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; //获得 Connection对象 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); //创建 Statement 或 PrepareStatement对象 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); //设置SQL上的参数,例如 PrepareStatement 对象上的占位符 handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; } 进入getConnection方法:经过重重的调用,最后调用openConnection(),从连接池获取连接
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection"); } //从连接池获取连接的方法 connection = dataSource.getConnection(); if (level != null) { connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel()); } setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommit); } 我们停下来回想一下,上面的executor.query()方法,经过几经波折,最后会创建一个StatementHandler对象,然后将必要的参数传递给 StatementHandler,使用StatementHandler来完成对数据库的查询,最终返回List结果集。
从上面的代码中我们可以看出,Executor的功能和作用是:
1)根据传递的参数,完成SQL语句的动态解析,生产BoundSql对象,供StatementHandler使用;
2)为查询创建缓存,以提高性能
3)创建JDBC的Statement连接对象,传递给 StatemenetHandler对象,返回List查询结果
接下来我们再了解一下StatementHandler对象,它主要完成两个工作:
1)对于JDBC的PreparedStatemenet类型的对象,创建的过程中,我们使用的Sql语句字符串会包含若干个
?占位符,我们再对占位符进行设值,StatementHandler通过parameterize(statement)方法对Statement进行设值2)StatementHandler通过List query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)方法来完成执行Statement,和将Statement对象返回的ResultSet封装成List
我们进入到StatementHandler的parameterize(statement)方法的实现看看:
@Override public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException { //使用ParameterHandler对象来完成对Statement的设值 parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement); } 进入 setParameters() 方法
@Override public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) { ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); //遍历parameterMappings数组 List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); if (parameterMappings != null) { for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { //获得遍历parameterMapping对象 ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { //获得值 Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null) { value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else { MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } //获得 typeHandler、jdbcType属性 TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType(); if (value == null && jdbcType == null) { jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull(); } //设置 ? 占位符的参数 try { typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType); } catch (TypeException | SQLException e) { throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e); } } } } } 上面这些代码可以看到StatementHandler.parameterize(Statement)方法调用了ParameterHandle.setParameters(statement)方法,ParameterHandler.setParameters(Statement)方法负责根据我们输入的参数,对Statement对象的 ?占位符处进行赋值。
现在我们再回到SimpleExecutor类中的doQuery()方法,我们继续往下,进入hander.query()方法:
@Override public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { //调用PreparedStatement.execute()方法,然后将resultSet交给ResultSetHandler处理 PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; //执行查询 ps.execute(); //处理返回结果 return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps); } 从上面的代码可以看出来,StatementHandler的List query(Statement statement, ResultHandler
resultHandler)方法的实现,是调用了ResultSetHandler.handleResultSets(Statement)方法。
ResultSetHandler.handleResultSets(Statement)方法会将Statement语句执行后生产的resultSet 结果集转换成List结果集
我们再继续看handleResultSets()方法:
@Override public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId()); //多 ResultSet 的结果集合,每个ResultSet 对应一个Object 对象,实际上,每个Object 是List<Object>对象 //在不考虑存储过程的多ResultSet 的情况下,普通的查询,实际就一个ResultSet,也就是说,multipleResults最多就一个元素 final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>(); int resultSetCount = 0; //获得首个 ResultSet对象,并封装成 ResultSetWrapper对象 ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt); //获得ResultMap数组 //在不考虑存储过程的多ResultSet的情况 普通的查询,实际就是一个 ResultSet,也就是说resultMap 就一个元素 List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps(); int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size(); validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);//校验 while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) { //获得ResultMap对象 ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount); //处理ResultSet,将结果添加到multipleResults中 handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null); //获得下一个ResultSet对象,并封装成 ResultSetWrapper对象 rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt); //清理 cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet(); //resultSetCount++ resultSetCount++; } String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets(); if (resultSets != null) { while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) { ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]); if (parentMapping != null) { String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId(); ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId); handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping); } rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt); cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet(); resultSetCount++; } } //如果是 multipleResults 单元素,则取首元素返回 return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults); } 好了,看到这里,我们回想一下上面的层次结构图,接下来我们在看看Mapper代理方法的源码
2)Mapper代理方式的源码剖析
话不多说,让我们先回顾一下写法:
/** * mapper代理方式 * @throws IOException */ public void test2()throws IOException{ //前3步都是相同的 InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream); SqlSession sqlSession=sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //使用JDK动态代理对Mapper借口产生代理对象 IUserMapper userMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); List<Object> objects = userMapper.queryAll(); } 我们点进sqlSession.getMppaer()方法里:
//DefaultSqlSession里的getMapper() @Override public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { return configuration.getMapper(type, this); } //Configuration里的getMapper() public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); } //MapperRegistry里的getMapper() @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { //获得MapperProxyFactory对象 final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); //不存在 则跑出BindingException异常 if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } //通过动态代理工厂生产实例 try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } } 发现Mapper代理方式底层是利用了动态代理,我们在进mapperProxyFactory.newInstance()方法:
//MapperProxyFactory类中的newInstance方法 public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { //创建了jdk动态代理的invocationHandler接口的实现类mapperProxy final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); //调用了重载方法 return newInstance(mapperProxy); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } 然后我们再看看MapperProxy这个类的invoke()方法:
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { //如果是Object定义的方法 直接调用 if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else { return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } } 我们再点进cachedInvoker(method).invoke()方法里看看
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable { // return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } 发现 MapperMethod最终调用了execute()方法,我们继续点进去看看:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; //判断mapper中方法类型 最终调用的还是SqlSession中的方法 switch (command.getType()) { case INSERT: { //转换参数 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); //执行INSERT操作 //转换rowCount result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); break; } case UPDATE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); break; } case DELETE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); break; } case SELECT: //无返回,并且有ResulyHandler方法参数,则将查询的结果,提交给ResultHandler 进行处理 if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; //执行查询,返回列表 } else if (method.returnsMany()) { result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); //执行查询,返回Map } else if (method.returnsMap()) { result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); //返回Cursor } else if (method.returnsCursor()) { result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { //返回单个对象 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); //查询单条 result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); if (method.returnsOptional() && (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) { result = Optional.ofNullable(result); } } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); } if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); } //返回结果集 return result; } 上面代码发现,它最终调用的还是SqlSession里的方法


