【数据结构与算法】二叉树
二叉树节点结构
class Node<V>{
V value;
Node left;
Node right;
}
二叉树的遍历(递归)
先序遍历
顺序:根左右
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
中序遍历
顺序:左根右
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
后序遍历
顺序:左右根
public static void posOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
posOrderRecur(head.left);
posOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
}
二叉树的遍历(非递归)
先序遍历
顺序:根左右
先把根节点压入栈中,每次
-
从栈中弹出一个节点cur
-
处理节点cur
-
先压入cur的右节点,再压入cur的左节点(如果有的话)
只要栈不为空,周而复始
public static void preOrder(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
if (head.right != null)
stack.push(head.right);
if (head.left != null)
stack.push(head.left);
}
System.out.println();
}
中序遍历
顺序:左根右
-
每棵子树整棵树左边界进栈
-
依次弹出的过程中处理节点
-
对弹出节点右树做同样操作
周而复始
public static void inOrder(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) { //刚开始stack为空,head不为null
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
后序遍历
顺序:左右根
反过来就是根右左,准备两个栈。
先把根节点压入栈1中,每次
-
从栈1中弹出一个节点cur
-
把节点cur压入栈2
-
先在栈1中压入cur的右节点,再压入cur的左节点(如果有的话)
只要栈1不为空,周而复始
最后依次弹出栈2中的节点,其顺序就是后序遍历的顺序
public static void postOrder(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> stack2 = new Stack<>();
stack1.push(head);
while (!stack1.isEmpty()){
head = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(head);
if(head.left!=null){
stack1.push(head.left);
}
if(head.right!=null){
stack1.push(head.right);
}
}
while (!stack2.isEmpty()){
head = stack2.pop();
System.out.print(head.value+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
二叉树层序(宽度)遍历
先把根节点放入队列中,每次
-
弹出节点cur
-
处理节点cur
-
先把cur的左节点放入队列,再把cur的右节点放入队列(如果存在的话)
周而复始,直到队列为空
public static void leverOrder(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
if (head.left != null) {
queue.add(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
queue.add(head.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void leverOrder(Node head) {
if (head == null) return;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int n = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { //一次处理一层节点
head = queue.poll();
System.out.printf(head.value + " ");
if (head.left != null) queue.add(head.left);
if (head.right != null) queue.add(head.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
二叉树应用题
二叉树深度
递归
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
层序遍历bfs
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int ans = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
ans++; //每次处理一层,处理完ans加一
int n = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++){
root = queue.poll();
if(root.left!=null) queue.add(root.left);
if(root.right!=null) queue.add(root.right);
}
}
return ans;
}
求二叉树最大宽度
层序遍历的过程中使用HashMap记录节点层数
public static void maxWidth(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
HashMap<Node, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<>();
levelMap.put(head, 1);
int curLevel = 1; //当前层数
int curLevelNodes = 0; //当前层数的节点数
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
int curNodeLevel = levelMap.get(cur); //获取当前节点层数
if (curNodeLevel == curLevel) { //当前节点层数等于当前层数,节点数加一
curLevelNodes++;
} else {
max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes); //否则max取较大值
curLevel++; //当前层数加一
curLevelNodes = 1; //重置当前层数的节点数为1
}
if (cur.left != null) {
levelMap.put(cur.left, curNodeLevel + 1);
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
levelMap.put(cur.right, curNodeLevel + 1);
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
}
判断是否为搜索二叉树

中序遍历递增就是搜索二叉树
递归方式
public static int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean checkBST(Node head){
if(head!=null){
boolean isLeftBst = checkBST(head.left);
if(!isLeftBst){
return false;
}
if(head.value<=preValue){
return false;
}else{
preValue = head.value;
}
return checkBST(head.right);
}
return true;
}
非递归方式
public static boolean checkBST(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) { //刚开始stack为空,head不为null
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {
head = stack.pop();
if(head.value<=preValue){
return false;
}else {
preValue = head.value;
}
head = head.right;
}
}
}
return true;
}
树形DP处理
-
左子树是搜索二叉树
-
右子树是搜索二叉树
-
根节点大于左子树最大值
-
根节点小于右子树最小值
public static boolean isBST(Node head){
return process(head).isBST;
}
public static class ReturnType {
public boolean isBST;
public int max;
public int min;
public ReturnType(boolean isBST, int max, int min) {
this.isBST = isBST;
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node x){
if(x==null) {
return null;
}
ReturnType leftData = process(x.left); //获取左子树处理信息
ReturnType rightData = process(x.right); //获取右子树处理信息
int min = x.value;
int max = x.value;
if(leftData!=null){ //获取当前树的最大值最小值
min = Math.min(min,leftData.min);
max = Math.max(max,leftData.max);
}
if(rightData!=null){
min = Math.min(min,rightData.min);
max = Math.max(max,rightData.max);
}
boolean isBST = true;
//左子树存在并且(左子树不是BST或者左子树最大值大于x)
if(leftData!=null&&(!leftData.isBST||leftData.max>=x.value)){
isBST = false;
}
//右子树存在并且(右子树不是BST或者右子树最小值小于x)
if(rightData!=null&&(!rightData.isBST||x.value>=rightData.min)){
isBST = false;
}
return new ReturnType(isBST,max,min);
}
判断是否是完全二叉树

-
层序遍历
-
任何一个节点有右孩子没左孩子,则不是完全二叉树(1)
-
在(1)的前提下,遇到第一个左右不双全节点,那其后面必须都是叶子节点,否则不是二叉树
public static boolean checkCBT(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
boolean leaf = false; //是否遇到过左右不双全节点
Node l = null;
Node r = null;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
l = head.left;
r = head.right;
if ((leaf && !(l == null && r == null)) //遇到第一个左右不双全节点,那么以后的节点都必须是叶子节点
||
(l == null && r != null)) { //任何一个节点有右孩子没左孩子
return false;
}
if (l != null) {
queue.add(l);
}
if (r != null) {
queue.add(r);
}
if (l == null || r == null) {
leaf = true;
}
}
}
return true;
}
判断是否是平衡二叉树
-
左子树是平衡的
-
右子树是平衡的
-
左右子树高度差的绝对值小于2
获取左树信息和右树信息后,结合处理。属于树形DP
public static boolean isBalancd(Node head) {
return process(head).isBalanced;
}
public static class ReturnType { //封装了平衡状态和高度
public boolean isBalanced;
public int height;
public ReturnType(boolean isB, int hei) {
isBalanced = isB;
height = hei;
}
}
public static ReturnType process(Node x) {
if (x == null) { //空树是平衡的,高度为0
return new ReturnType(true, 0);
}
ReturnType leftData = process(x.left); //左树
ReturnType rightData = process(x.right); //右树
int height = Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1; //获取左子树和右子树的最高高度+1
boolean isBalanced = leftData.isBalanced && rightData.isBalanced && //如果左子树平衡,右子树平衡
Math.abs(leftData.height - rightData.height) < 2; //左右子树的高度差的绝对值小于2
return new ReturnType(isBalanced, height); //返回新状态
}
判断是否是满二叉树
如果一个二叉树的层数为K,且结点总数是 (2^k) -1 ,则它就是满二叉树。
树形DP问题
public static boolean isFull(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
Info data = process(head);
return data.nodes == ((1 << data.height) - 1);//是否层数为K,且结点总数是 (2^k) -1
}
public static class Info { //封装树的高度和节点数
public int height;
public int nodes;
public Info(int h, int n) {
height = h;
nodes = n;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
Info leftData = process(x.left); //获取左子树信息
Info rightData = process(x.right); //获取右子树信息
int height = Math.max(leftData.height, rightData.height) + 1; //求新高度
int nodes = leftData.nodes + rightData.nodes + 1; //求总的节点数
return new Info(height, nodes);
}
在二叉树中找到一个节点的后继节点
现在有一种新的二叉树节点类型如下:
public class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int val) {
value = val;
}
}
该结构比普通二叉树节点结构多了一个指向父节点的parent指针。
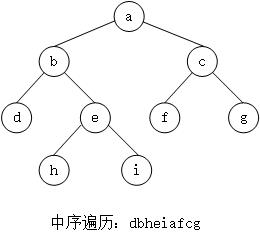
假设有一棵Node类型的节点组成的二叉树,树中每个节点的parent指针都正确地指向自己的父节点,头节 点的parent指向null。 只给一个在二叉树中的某个节点node,请实现返回node的后继节点的函数。
在二叉树的中序遍历的序列中, node的下一个节点叫作node的后继节点。
-
一个节点有右子树,那么它的下一个节点就是它的右子树中的最左子节点。例如b的后继节点是h。
-
一个节点没有右子树时分两种情况:
- 当前节点是它父节点的左子节点,那么它的下一个节点就是它的父节点。 例如节点f的后继节点是c,节点d的后继节点是b。
- 当前节点是它父节点的右子节点,此时沿着指向父节点的指针一直向上遍历,直到找到一个是它父节点的左子节点的节点,如果这个节点存在,那么这个节点的父节点就是我们要找的下一个节点。如下图所示: f的下一个节点是a。
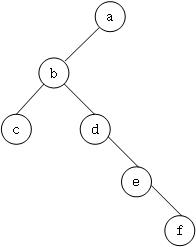
- 当前节点是它父节点的左子节点,那么它的下一个节点就是它的父节点。 例如节点f的后继节点是c,节点d的后继节点是b。
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
if (node.right != null) {
return getLeftMost(node.right);
} else {
Node parent = node.parent;
while (parent != null && parent.left != node) {
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
public static Node getLeftMost(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
折纸问题
请把一段纸条竖着放在桌子上,然后从纸条的下边向上方对折1次,压出折痕后 展开。 此时折痕是凹下去的,即折痕突起的方向指向纸条的背面。 如果从纸条的下边向上方连续对折2次,压出折痕后展开,此时有三条折痕,从 上到下依次是下折痕、下折痕和上折痕。 给定一个输入参数N,代表纸条都从下边向上方连续对折N次。 请从上到下打印所有折痕的方向。
例如:
N=1时,打印: down
N=2时,打印: down down up
分析:

发现第n+1次的折痕中凹折痕一定在第n次折痕的左边,第n+1次折痕中凸折痕一定在第n次折痕的右边
形成一棵二叉树

中序遍历该二叉树就可得到答案
public static void printAllFolds(int N) {
printProcess(1, N, true);
}
public static void printProcess(int i, int N, boolean down) {
if (i > N) {
return;
}
printProcess(i + 1, N, true);
System.out.println(down ? "down " : "up ");
printProcess(i + 1, N, false);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 1;
printAllFolds(N);
}



