手把手教你使用Java实现一个神经网络
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
首先看一下运行效果:
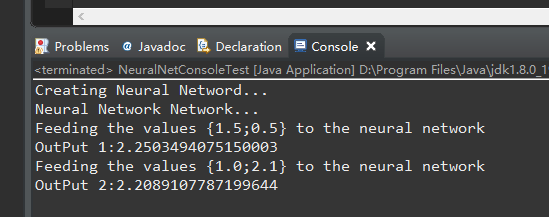
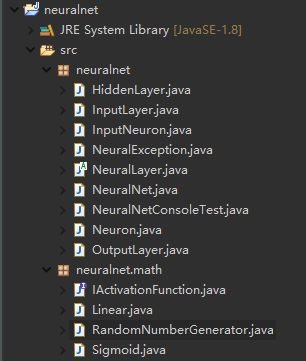
下面是项目整体目录:
0.实现神经网络总览
神经网络由层、神经元、权重、激活函数和偏置组成。每层都有一个或者多个神经元,每一个神经元都和神经输入/输出连接,这些连接就是权重。
需要重点强调一下,一个神经网络可能有很多隐含层,也可能一个没有,因为每层的神经元数目也可能不同。然而,输入输出层的神经元个数分别等于神经输入/输出的个数。
我们为了实现,需要定义以下的类:
- Neuron: 定义人工神经元
- NeuralLayer: 抽象类,定义一个神经元层。
- InputLayer: 定义神经输入层
- HiddenLayer:定义输入层和输出层之间的层
- OutputLayer: 定义神经输出层。
- InputNeuron: 定义神经网络输入中出现的神经元。
- NeuralNet:将前面定义的所有类组成一个ANN结构。
除了以上的类,我们还需要为激活函数定义一个IActivationFunction接口。这是必要的,因为激活函数与方法类似,需要作为神经元的一个属性进行分配。所以要为激活函数定义类,这些类需要实现IActivationFunction接口:
- Linear
- Sigmoid
- Step
- HyperTan
第一章的编码基本完成。除此之外,还需要定义俩个类。一个用于异常处理(NeuralException),另一个用于产生随机数(RandomNumberGenerator)。最后,将这些类分别放到俩个包。
1.神经元Neuron类
神经元类是本章代码的基础类。根据理论,人工神经元有如下属性
- 输入
- 权重
- 偏置
- 激活函数
- 输出
首先定义神经元的各种属性:
public class Neuron { //神经元相关的权重 protected ArrayList<Double> weight; //神经元的输入 private ArrayList<Double> input; //这个神经元的输出,由激活函数产生 private Double output; //传递给激活函数的值 private Double outputBeforeActivation; //输入的数量。如果为0,则表示神经元尚未初始化。 private int numberOfInputs = 0; //神经元的偏差。除了第一层,其他都应该是1.0。 protected Double bias = 1.0; //神经元的激活函数 private IActivationFunction activationFunction; } 当实例化神经元时,需要指定输入数据的个数以及激活函数。构造函数如下:
public Neuron(int numberofinputs,IActivationFunction iaf){ numberOfInputs=numberofinputs; weight=new ArrayList<>(numberofinputs+1); input=new ArrayList<>(numberofinputs); activationFunction=iaf; }注意,为偏置定义另一个权重。一个重要的步骤是初始化神经元,也就是为权重赋初始值。这主要在init()方法中完成,通过随机数生成器静态类RandomNumberGenerator生成随机数,赋值权重。注意:设置权重值时需要防止权重数组越界。
public void init(){ if(numberOfInputs>0){ for(int i=0;i<=numberOfInputs;i++){ double newWeight = RandomNumberGenerator.GenerateNext(); try{ this.weight.set(i, newWeight); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ this.weight.add(newWeight); } } } } 最后,在calc()方法中计算输出值:
public void calc(){ outputBeforeActivation=0.0; if(numberOfInputs>0){ if(input!=null && weight!=null){ for(int i=0;i<=numberOfInputs;i++){ outputBeforeActivation+=(i==numberOfInputs?bias:input.get(i))*weight.get(i); } } } output=activationFunction.calc(outputBeforeActivation); }首先需要对所有输入和权重的成绩进行求和(偏置乘最后一个权重,i==Number-OfInputs),然后将得出的结果保存在属性outputBeforeActivation中。激活函数用这个值计算神经元的输出。
总代码如下:
package neuralnet; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Neuron { //神经元相关的权重 protected ArrayList<Double> weight; //神经元的输入 private ArrayList<Double> input; //这个神经元的输出,由激活函数产生 private Double output; //传递给激活函数的值 private Double outputBeforeActivation; //输入的数量。如果为0,则表示神经元尚未初始化。 private int numberOfInputs = 0; //神经元的偏差。除了第一层,其他都应该是1.0。 protected Double bias = 1.0; //神经元的激活函数 private IActivationFunction activationFunction; public Neuron(){ } public Neuron(int numberofinputs){ numberOfInputs=numberofinputs; weight=new ArrayList<>(numberofinputs+1); input=new ArrayList<>(numberofinputs); } public Neuron(int numberofinputs,IActivationFunction iaf){ numberOfInputs=numberofinputs; weight=new ArrayList<>(numberofinputs+1); input=new ArrayList<>(numberofinputs); activationFunction=iaf; } public void init(){ if(numberOfInputs>0){ for(int i=0;i<=numberOfInputs;i++){ double newWeight = RandomNumberGenerator.GenerateNext(); try{ this.weight.set(i, newWeight); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ this.weight.add(newWeight); } } } } public void setInputs(double [] values){ if(values.length==numberOfInputs){ for(int i=0;i<numberOfInputs;i++){ try{ input.set(i, values[i]); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ input.add(values[i]); } } } } public void setInputs(ArrayList<Double> values){ if(values.size()==numberOfInputs){ input=values; } } public ArrayList<Double> getArrayInputs(){ return input; } public double[] getInputs(){ double[] inputs = new double[numberOfInputs]; for (int i=0;i<numberOfInputs;i++){ inputs[i]=this.input.get(i); } return inputs; } public void setInput(int i,double value){ if(i>=0 && i<numberOfInputs){ try{ input.set(i, value); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ input.add(value); } } } public double getInput(int i){ return input.get(i); } public double[] getWeights(){ double[] weights = new double[numberOfInputs+1]; for(int i=0;i<=numberOfInputs;i++){ weights[i]=weight.get(i); } return weights; } public ArrayList<Double> getArrayWeights(){ return weight; } public void updateWeight(int i, double value){ if(i>=0 && i<=numberOfInputs){ weight.set(i, value); } } public int getNumberOfInputs(){ return this.numberOfInputs; } public void setWeight(int i,double value) throws NeuralException{ if(i>=0 && i<numberOfInputs){ this.weight.set(i, value); } else{ throw new NeuralException("Invalid weight index"); } } public double getOutput(){ return output; } public void calc(){ outputBeforeActivation=0.0; if(numberOfInputs>0){ if(input!=null && weight!=null){ for(int i=0;i<=numberOfInputs;i++){ outputBeforeActivation+=(i==numberOfInputs?bias:input.get(i))*weight.get(i); } } } output=activationFunction.calc(outputBeforeActivation); } public void setActivationFunction(IActivationFunction iaf){ this.activationFunction=iaf; } public double getOutputBeforeActivation(){ return outputBeforeActivation; } } 2.NeuralLayer类
在这个类中,将把在同一层中对齐的神经元分成一组。因为一层需要将值传递给另一层,也需要定义层与层之间的连接。类的属性定义如下:
//这一层的神经元数量 protected int numberOfNeuronsInLayer; //这一层的神经元 private ArrayList<Neuron> neuron; //激励函数 protected IActivationFunction activationFnc; //将值提供给此层的前一层 protected NeuralLayer previousLayer; protected NeuralLayer nextLayer; protected ArrayList<Double> input; protected ArrayList<Double> output; protected int numberOfInputs;这个类是抽象的,整整可实例化的层类是InputLayer、HiddenLayer和Outp-utLayer。创建一个类是,必须使用另一个类的构造函数,这几个类具有相似的构造函数。
而层的初始化和计算都和神经元一样,他们也实现了init()方法和calc() 方法。生命欸protected类型,确保了只有子类可以调用或覆盖这些方法。
全部的代码如下:
package neuralnet; import java.util.ArrayList; public abstract class NeuralLayer { //这一层的神经元数量 protected int numberOfNeuronsInLayer; //这一层的神经元 private ArrayList<Neuron> neuron; //激励函数 protected IActivationFunction activationFnc; //将值提供给此层的前一层 protected NeuralLayer previousLayer; protected NeuralLayer nextLayer; protected ArrayList<Double> input; protected ArrayList<Double> output; protected int numberOfInputs; public NeuralLayer(int numberofneurons){ this.numberOfNeuronsInLayer=numberofneurons; neuron = new ArrayList<>(numberofneurons); output = new ArrayList<>(numberofneurons); } public NeuralLayer(int numberofneurons,IActivationFunction iaf){ this.numberOfNeuronsInLayer=numberofneurons; this.activationFnc=iaf; neuron = new ArrayList<>(numberofneurons); output = new ArrayList<>(numberofneurons); } public int getNumberOfNeuronsInLayer(){ return numberOfNeuronsInLayer; } public ArrayList<Neuron> getListOfNeurons(){ return neuron; } protected NeuralLayer getPreviousLayer(){ return previousLayer; } protected NeuralLayer getNextLayer(){ return nextLayer; } protected void setPreviousLayer(NeuralLayer layer){ previousLayer=layer; } protected void setNextLayer(NeuralLayer layer){ nextLayer=layer; } protected void init(){ if(numberOfNeuronsInLayer>=0){ for(int i=0;i<numberOfNeuronsInLayer;i++){ try{ neuron.get(i).setActivationFunction(activationFnc); neuron.get(i).init(); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ neuron.add(new Neuron(numberOfInputs,activationFnc)); neuron.get(i).init(); } } } } protected void setInputs(ArrayList<Double> inputs){ this.numberOfInputs=inputs.size(); this.input=inputs; } protected void calc(){ if(input!=null && neuron!=null){ for(int i=0;i<numberOfNeuronsInLayer;i++){ neuron.get(i).setInputs(this.input); neuron.get(i).calc(); try{ output.set(i,neuron.get(i).getOutput()); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ output.add(neuron.get(i).getOutput()); } } } } protected ArrayList<Double> getOutputs(){ return output; } protected Neuron getNeuron(int i){ return neuron.get(i); } protected void setNeuron(int i, Neuron _neuron){ try{ this.neuron.set(i, _neuron); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ this.neuron.add(_neuron); } } }3.ActivationFunction接口
在定义NeerualNetwork类之前,先看接口的Java代码示例:
public interface IActivationFunction { double calc(double x); public enum ActivationFunctionENUM { STEP, LINEAR, SIGMOID, HYPERTAN } } 其中calc()方法属于实现IActivationFunction接口的特定的激活函数类,例如Sigmoid函数。
public class Sigmoid implements IActivationFunction { private double a=1.0; public Sigmoid(){ } public Sigmoid(double value){ this.setA(value); } public void setA(double value){ this.a=value; } @Override public double calc(double x){ return 1.0/(1.0+Math.exp(-a*x)); } } 这也是多态性的一个示例,即在相同的函数名下,类和方法呈现不同的行为,产生灵活的应用。
4.神经网络(NeuralNet)类
最后,定义神经网络类。到目前为止,我们已经知道,神经网络在神经层中组织神经元,且每个神经网络至少有俩层,一个用来接收收入,一个用来处理输出,还有一个数量可变的隐含层。因此,除了具有和神经元以及NeuralLary类相似的属性之外,Neural还将拥有这几个属性,如numberOfInputs,numberOfOutputs等。
private InputLayer inputLayer; private ArrayList<HiddenLayer> hiddenLayer; private OutputLayer outputLayer; private int numberOfHiddenLayers; private int numberOfInputs; private int numberOfOutputs; private ArrayList<Double> input; private ArrayList<Double> output; 这个类的构造函数比前面类的参数更多:
public NeuralNet(int numberofinputs,int numberofoutputs, int [] numberofhiddenneurons,IActivationFunction[] hiddenAcFnc, IActivationFunction outputAcFnc)如果隐含层的数量是可变的,我们还应该考虑到可能有多个隐含层或0个隐含层,且对每个隐含层来说,隐藏神经元的数量也是可变的。处理这种可变性的最好方法就是把每个隐含层中的神经元数量表示为一个整数向量(参数 numberofhiddenlayers)。此外,需要为每个隐含层定义激活函数,包括输出层,完成这个目标所需要的参数分别为hiddenActivationFnc和outputAcFnc。
完整实现如下:
public NeuralNet(int numberofinputs,int numberofoutputs, int [] numberofhiddenneurons,IActivationFunction[] hiddenAcFnc, IActivationFunction outputAcFnc){ numberOfHiddenLayers=numberofhiddenneurons.length; numberOfInputs=numberofinputs; numberOfOutputs=numberofoutputs; if(numberOfHiddenLayers==hiddenAcFnc.length){ input=new ArrayList<>(numberofinputs); inputLayer=new InputLayer(numberofinputs); if(numberOfHiddenLayers>0){ hiddenLayer=new ArrayList<>(numberOfHiddenLayers); } for(int i=0;i<numberOfHiddenLayers;i++){ if(i==0){ try{ hiddenLayer.set(i,new HiddenLayer(numberofhiddenneurons[i], hiddenAcFnc[i], inputLayer.getNumberOfNeuronsInLayer())); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ hiddenLayer.add(new HiddenLayer(numberofhiddenneurons[i], hiddenAcFnc[i], inputLayer.getNumberOfNeuronsInLayer())); } inputLayer.setNextLayer(hiddenLayer.get(i)); } else{ try{ hiddenLayer.set(i, new HiddenLayer(numberofhiddenneurons[i], hiddenAcFnc[i],hiddenLayer.get(i-1) .getNumberOfNeuronsInLayer() )); } catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe){ hiddenLayer.add(new HiddenLayer(numberofhiddenneurons[i], hiddenAcFnc[i],hiddenLayer.get(i-1) .getNumberOfNeuronsInLayer() )); } hiddenLayer.get(i-1).setNextLayer(hiddenLayer.get(i)); } } if(numberOfHiddenLayers>0){ outputLayer=new OutputLayer(numberofoutputs,outputAcFnc, hiddenLayer.get(numberOfHiddenLayers-1) .getNumberOfNeuronsInLayer() ); hiddenLayer.get(numberOfHiddenLayers-1).setNextLayer(outputLayer); } else{ outputLayer=new OutputLayer(numberofinputs, outputAcFnc, numberofoutputs); inputLayer.setNextLayer(outputLayer); } } }5.运行程序
代码如下:
package neuralnet; import neuralnet.math.IActivationFunction; import neuralnet.math.Linear; import neuralnet.math.RandomNumberGenerator; import neuralnet.math.Sigmoid; public class NeuralNetConsoleTest { public static void main(String[] args){ RandomNumberGenerator.seed=0; int numberOfInputs=2; int numberOfOutputs=1; int[] numberOfHiddenNeurons= { 3 }; IActivationFunction[] hiddenAcFnc = { new Sigmoid(1.0) } ; Linear outputAcFnc = new Linear(1.0); System.out.println("Creating Neural Netword..."); NeuralNet nn = new NeuralNet(numberOfInputs,numberOfOutputs, numberOfHiddenNeurons,hiddenAcFnc,outputAcFnc); System.out.println("Neural Network Network..."); double [] neuralInput = { 1.5 , 0.5 }; System.out.println("Feeding the values {1.5;0.5} to the neural network"); double [] neuralOutput; nn.setInputs(neuralInput); nn.calc(); neuralOutput=nn.getOutputs(); System.out.println("OutPut 1:" + neuralOutput[0]); neuralInput[0] = 1.0; neuralInput[1] = 2.1; System.out.println("Feeding the values {1.0;2.1} to the neural network"); nn.setInputs(neuralInput); nn.calc(); neuralOutput=nn.getOutputs(); System.out.println("OutPut 2:" + neuralOutput[0]); } }到此就完成了我们神经网络的全部代码:下面是源代码压缩包。有需要的同学可以下载运行。
