Android 点九图机制讲解及在聊天气泡中的应用
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
点九图简介
Android为了使用同一张图作为不同数量文字的背景,设计了一种可以指定区域拉伸的图片格式“.9.png”,这种图片格式就是点九图。
注意:这种图片格式只能被使用于Android开发。在ios开发中,可以在代码中指定某个点进行拉伸,而在Android中不行,所以在Android中想要达到这个效果,只能使用点九图(下文会啪啪打脸,其实是可以的,只是很少人这样使用,兼容性不知道怎么样,点击跳转)

点九图实质
点九图的本质实际上是在图片的四周各增加了1px的像素,并使用纯黑(#FF000000)的线进行标记,其它的与原图没有任何区别。可以参考以下图片:
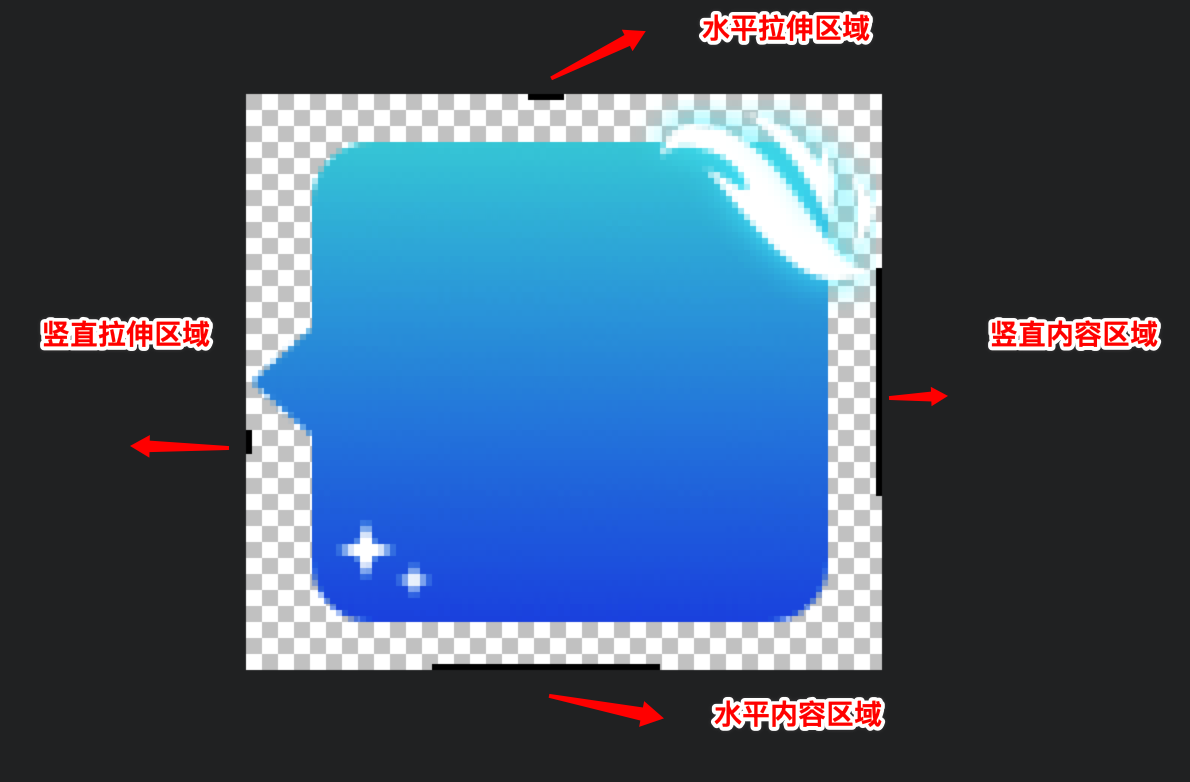

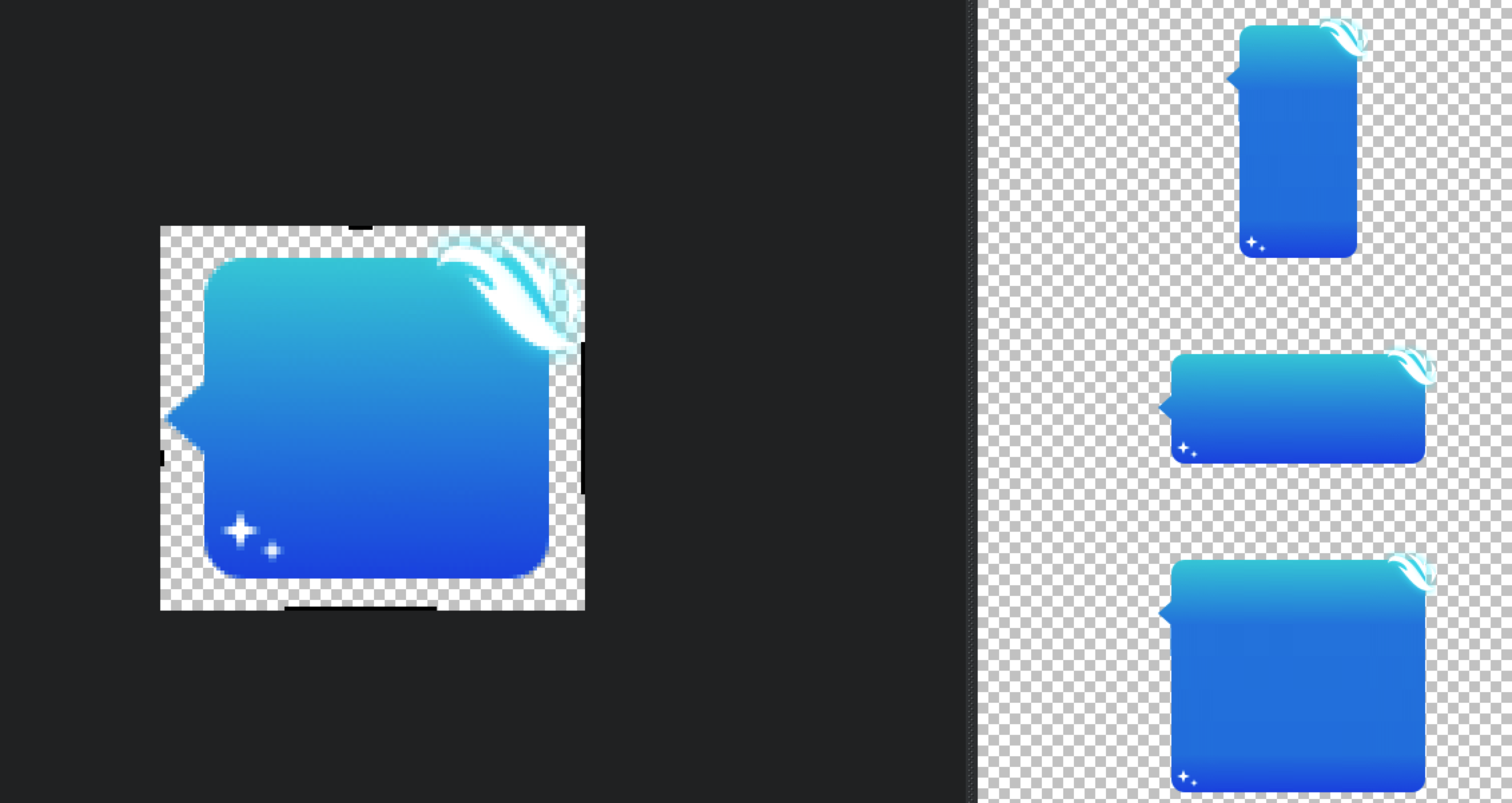
| 标记位置 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 左-黑点 | 纵向拉伸区域 |
| 上-黑点 | 横向拉伸区域 |
| 右-黑线 | 纵向显示区域 |
| 下-黑线 | 横向显示区域 |
点九图在 Android 中的应用
点九图在 Android 中主要有三种应用方式
- 直接放在 res 目录中的 drawable 或者 mipmap 目录中
- 放在 assert 目录中
- 从网络下载
第一种方式是我们最常用的,直接调用 setBackgroundResource 或者 setImageResource 方法,这样的话图片及可以做到自动拉伸。
而对于第二种或者第三种方式,如果我们直接去加载 .9.png,你会发现图片或者图片背景根本无法拉伸。纳尼,这是为甚么呢。下面,且听老衲慢慢道来。
Android 并不是直接使用点九图,而是在编译时将其转换为另外一种格式,这种格式是将其四周的黑色像素保存至Bitmap类中的一个名为 mNinePatchChunk 的 byte[] 中,并抹除掉四周的这一个像素的宽度;接着在使用时,如果 Bitmap 的这个 mNinePatchChunk 不为空,且为 9patch chunk,则将其构造为 NinePatchDrawable,否则将会被构造为 BitmapDrawable,最终设置给 view。
因此,在 Android 中,我们如果想动态使用网络下载的点九图,一般需要经过以下步骤:
- 使用 sdk 目录下的 aapt 工具将点九图转化为 png 图片
- 解析图片的时候,判断是否含有 NinePatchChunk,有的话,转化为 NinePatchDrawable
public static void setNineImagePatch(View view, File file, String url) { if (file.exists()) { Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(file.getAbsolutePath()); byte[] chunk = bitmap.getNinePatchChunk(); if (NinePatch.isNinePatchChunk(chunk)) { NinePatchDrawable patchy = new NinePatchDrawable(view.getResources(), bitmap, chunk, new Rect(), null); view.setBackground(patchy); } } }点九图上传服务器流程

aapt 转换命令
单个图片文件转换
./aapt s -i xxx.9.png -o xxx.png批量转换
# 批量转换 ./aapt c -S inputDir -C outputDir # inputDir 为原始.9图文件夹,outputDir 为输出文件夹执行成功实例
jundeMacBook-Pro:一期气泡 junxu$ ./aapt c -S /Users/junxu/Desktop/一期气泡/气泡需求整理 -C /Users/junxu/Desktop/一期气泡/output Crunching PNG Files in source dir: /Users/junxu/Desktop/一期气泡/气泡需求整理 To destination dir: /Users/junxu/Desktop/一期气泡/output注意:
若不是标准的点九图,在转换的过程会报错,这时候请设计重新提供新的点九图
实际开发当中遇到的问题
小屏手机适配问题
刚开始,我们的切图是按照 2 倍图切的,这样在小屏幕手机上会手机气泡高度过大的问题。

原因分析:
该现象的本质是点九图图片的高度大于单行文本消息的高度。
解决方案一(暂时不可取):
- 我尝试去压缩点九图,但最终再部分手机上面显示错乱,不知道是不是压缩点九图的方法错了。
解决方案二
对于低分辨率的手机和高分辨的手机分别下发不同的图片 url,我们尝试过得方案是当 density < 2 的时候,采用一倍图图片,density >= 2 采用二倍图图片。
解决方案三
可能有人会有这样的疑问呢,为什么要采用一倍图,两倍图的解决方案呢?直接让 UI 设计师给一套图,点九图图片的高度适中不就解决了。是啊,我们也是这样想得,但他们说对于有一些装饰的点九图,如果缩小高度,一些装饰图案他们不太好切。比如下面图片中的星星。

小结
说到底,方案二,方案三其实都是折中的一种方案,如果直接能够做到点九图缩放,那就完美解决了。而 Android 中 res 目录中的 drawable 或者 mipmap 的点九图确实能做到,去看了相关的代码,目前也没有发现什么好的解决方案,如果你有好的解决方案话,欢迎留言交流。
点九图的 padding 在部分手机上面失效
这个是部分 Android 手机的 bug,解决方法见:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11065996/ninepatchdrawable-does-not-get-padding-from-chunk
public class NinePatchChunk { private static final String TAG = "NinePatchChunk"; public final Rect mPaddings = new Rect(); public int mDivX[]; public int mDivY[]; public int mColor[]; private static float density = IMO.getInstance().getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; private static void readIntArray(final int[] data, final ByteBuffer buffer) { for (int i = 0, n = data.length; i < n; ++i) data[i] = buffer.getInt(); } private static void checkDivCount(final int length) { if (length == 0 || (length & 0x01) != 0) throw new IllegalStateException("invalid nine-patch: " + length); } public static Rect getPaddingRect(final byte[] data) { NinePatchChunk deserialize = deserialize(data); if (deserialize == null) { return new Rect(); } } public static NinePatchChunk deserialize(final byte[] data) { final ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(data).order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); if (byteBuffer.get() == 0) { return null; // is not serialized } final NinePatchChunk chunk = new NinePatchChunk(); chunk.mDivX = new int[byteBuffer.get()]; chunk.mDivY = new int[byteBuffer.get()]; chunk.mColor = new int[byteBuffer.get()]; try { checkDivCount(chunk.mDivX.length); checkDivCount(chunk.mDivY.length); } catch (Exception e) { return null; } // skip 8 bytes byteBuffer.getInt(); byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.left = byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.right = byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.top = byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.bottom = byteBuffer.getInt(); // skip 4 bytes byteBuffer.getInt(); readIntArray(chunk.mDivX, byteBuffer); readIntArray(chunk.mDivY, byteBuffer); readIntArray(chunk.mColor, byteBuffer); return chunk; } } NinePatchDrawable patchy = new NinePatchDrawable(view.getResources(), bitmap, chunk, NinePatchChunk.getPaddingRect(chunk), null); view.setBackground(patchy); 动态下载点九图会导致聊天气泡闪烁
- 这里我们采取的方案是预下载(预下载 10 个)
- 聊天气泡采用内存缓存,磁盘缓存,确保 RecyclerView 快速滑动的时候不会闪烁
理解点九图
以下内容参考腾讯音乐的 Android动态布局入门及NinePatchChunk解密
回顾NinePatchDrawable的构造方法第三个参数bitmap.getNinePatchChunk(),作者猜想,aapt命令其实就是在bitmap图片中,加入了NinePatchChunk的信息,那么我们是不是只要能自己构造出这个东西,就可以让任何图片按照我们想要的方式拉升了呢?
可是查了一堆官方文档,似乎并找不到相应的方法来获得这个byte[]类型的chunk参数。
既然无法知道这个chunk如何生成,那么能不能从解析的角度逆向得出这个NinePatchChunk的生成方法呢?
下面就需要从源码入手了。
NinePatchChunk.java
public static NinePatchChunk deserialize(byte[] data) { ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(data).order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); byte wasSerialized = byteBuffer.get(); if (wasSerialized == 0) return null; NinePatchChunk chunk = new NinePatchChunk(); chunk.mDivX = new int[byteBuffer.get()]; chunk.mDivY = new int[byteBuffer.get()]; chunk.mColor = new int[byteBuffer.get()]; checkDivCount(chunk.mDivX.length); checkDivCount(chunk.mDivY.length); // skip 8 bytes byteBuffer.getInt(); byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.left = byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.right = byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.top = byteBuffer.getInt(); chunk.mPaddings.bottom = byteBuffer.getInt(); // skip 4 bytes byteBuffer.getInt(); readIntArray(chunk.mDivX, byteBuffer); readIntArray(chunk.mDivY, byteBuffer); readIntArray(chunk.mColor, byteBuffer); return chunk; }其实从这部分解析byte[] chunk的源码,我们已经可以反推出来大概的结构了。如下图,
按照上图中的猜想以及对.9.png的认识,直觉感受到,mDivX,mDivY,mColor这三个数组是最关键的,但是具体是什么,就要继续看源码了。
ResourceTypes.h
/** * This chunk specifies how to split an image into segments for * scaling. * * There are J horizontal and K vertical segments. These segments divide * the image into J*K regions as follows (where J=4 and K=3): * * F0 S0 F1 S1 * +-----+----+------+-------+ * S2| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | * +-----+----+------+-------+ * | | | | | * | | | | | * F2| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | * | | | | | * | | | | | * +-----+----+------+-------+ * S3| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | * +-----+----+------+-------+ * * Each horizontal and vertical segment is considered to by either * stretchable (marked by the Sx labels) or fixed (marked by the Fy * labels), in the horizontal or vertical axis, respectively. In the * above example, the first is horizontal segment (F0) is fixed, the * next is stretchable and then they continue to alternate. Note that * the segment list for each axis can begin or end with a stretchable * or fixed segment. * /正如源码中,注释的一样,这个NinePatch Chunk把图片从x轴和y轴分成若干个区域,F区域代表了固定,S区域代表了拉伸。mDivX,mDivY描述了所有S区域的位置起始,而mColor描述了,各个Segment的颜色,通常情况下,赋值为源码中定义的NO_COLOR = 0x00000001就行了。就以源码注释中的例子来说,mDivX,mDivY,mColor如下:
mDivX = [ S0.start, S0.end, S1.start, S1.end]; mDivY = [ S2.start, S2.end, S3.start, S3.end]; mColor = [c[0],c[1],...,c[11]]对于mColor这个数组,长度等于划分的区域数,是用来描述各个区域的颜色的,而如果我们这个只是描述了一个bitmap的拉伸方式的话,是不需要颜色的,即源码中NO_COLOR = 0x00000001
说了这么多,我们还是通过一个简单例子来说明如何构造一个按中心点拉伸的 NinePatchDrawable 吧,
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(filepath); int[] xRegions = new int[]{bitmap.getWidth() / 2, bitmap.getWidth() / 2 + 1}; int[] yRegions = new int[]{bitmap.getWidth() / 2, bitmap.getWidth() / 2 + 1}; int NO_COLOR = 0x00000001; int colorSize = 9; int bufferSize = xRegions.length * 4 + yRegions.length * 4 + colorSize * 4 + 32; ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bufferSize).order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); // 第一个byte,要不等于0 byteBuffer.put((byte) 1); //mDivX length byteBuffer.put((byte) 2); //mDivY length byteBuffer.put((byte) 2); //mColors length byteBuffer.put((byte) colorSize); //skip byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); //padding 先设为0 byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); //skip byteBuffer.putInt(0); // mDivX byteBuffer.putInt(xRegions[0]); byteBuffer.putInt(xRegions[1]); // mDivY byteBuffer.putInt(yRegions[0]); byteBuffer.putInt(yRegions[1]); // mColors for (int i = 0; i < colorSize; i++) { byteBuffer.putInt(NO_COLOR); } return byteBuffer.array();create-a-ninepatch-ninepatchdrawable-in-runtime
在 stackoverflow 上面也找到牛逼的类,可以动态创建点九图,并拉伸图片,啪啪打脸,刚开始说到 android 中无法想 ios 一样动态指定图片拉伸区域。
public class NinePatchBuilder { int width, height; Bitmap bitmap; Resources resources; private ArrayList<Integer> xRegions = new ArrayList<Integer>(); private ArrayList<Integer> yRegions = new ArrayList<Integer>(); public NinePatchBuilder(Resources resources, Bitmap bitmap) { width = bitmap.getWidth(); height = bitmap.getHeight(); this.bitmap = bitmap; this.resources = resources; } public NinePatchBuilder(int width, int height) { this.width = width; this.height = height; } public NinePatchBuilder addXRegion(int x, int width) { xRegions.add(x); xRegions.add(x + width); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addXRegionPoints(int x1, int x2) { xRegions.add(x1); xRegions.add(x2); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addXRegion(float xPercent, float widthPercent) { int xtmp = (int) (xPercent * this.width); xRegions.add(xtmp); xRegions.add(xtmp + (int) (widthPercent * this.width)); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addXRegionPoints(float x1Percent, float x2Percent) { xRegions.add((int) (x1Percent * this.width)); xRegions.add((int) (x2Percent * this.width)); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addXCenteredRegion(int width) { int x = (int) ((this.width - width) / 2); xRegions.add(x); xRegions.add(x + width); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addXCenteredRegion(float widthPercent) { int width = (int) (widthPercent * this.width); int x = (int) ((this.width - width) / 2); xRegions.add(x); xRegions.add(x + width); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addYRegion(int y, int height) { yRegions.add(y); yRegions.add(y + height); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addYRegionPoints(int y1, int y2) { yRegions.add(y1); yRegions.add(y2); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addYRegion(float yPercent, float heightPercent) { int ytmp = (int) (yPercent * this.height); yRegions.add(ytmp); yRegions.add(ytmp + (int) (heightPercent * this.height)); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addYRegionPoints(float y1Percent, float y2Percent) { yRegions.add((int) (y1Percent * this.height)); yRegions.add((int) (y2Percent * this.height)); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addYCenteredRegion(int height) { int y = (int) ((this.height - height) / 2); yRegions.add(y); yRegions.add(y + height); return this; } public NinePatchBuilder addYCenteredRegion(float heightPercent) { int height = (int) (heightPercent * this.height); int y = (int) ((this.height - height) / 2); yRegions.add(y); yRegions.add(y + height); return this; } public byte[] buildChunk() { if (xRegions.size() == 0) { xRegions.add(0); xRegions.add(width); } if (yRegions.size() == 0) { yRegions.add(0); yRegions.add(height); } int NO_COLOR = 1;//0x00000001; int COLOR_SIZE = 9;//could change, may be 2 or 6 or 15 - but has no effect on output int arraySize = 1 + 2 + 4 + 1 + xRegions.size() + yRegions.size() + COLOR_SIZE; ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(arraySize * 4).order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); byteBuffer.put((byte) 1);//was translated byteBuffer.put((byte) xRegions.size());//divisions x byteBuffer.put((byte) yRegions.size());//divisions y byteBuffer.put((byte) COLOR_SIZE);//color size //skip byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); //padding -- always 0 -- left right top bottom byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); byteBuffer.putInt(0); //skip byteBuffer.putInt(0); for (int rx : xRegions) byteBuffer.putInt(rx); // regions left right left right ... for (int ry : yRegions) byteBuffer.putInt(ry);// regions top bottom top bottom ... for (int i = 0; i < COLOR_SIZE; i++) byteBuffer.putInt(NO_COLOR); return byteBuffer.array(); } public NinePatch buildNinePatch() { byte[] chunk = buildChunk(); if (bitmap != null) return new NinePatch(bitmap, chunk, null); return null; } public NinePatchDrawable build() { NinePatch ninePatch = buildNinePatch(); if (ninePatch != null) return new NinePatchDrawable(resources, ninePatch); return null; } } 运行一下测试代码
mLlRoot = findViewById(R.id.ll_root); try { InputStream is = getAssets().open("sea.png"); Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { NinePatchDrawable ninePatchDrawable = NinePatchHelper.buildMulti(this, bitmap); TextView textView = new TextView(this); textView.setTextSize(25); textView.setPadding(20, 10, 20, 10); textView.setText(strArray[i]); textView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL); LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); layoutParams.leftMargin = 20; layoutParams.rightMargin = 20; textView.setLayoutParams(layoutParams); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN) { textView.setBackground(ninePatchDrawable); } mLlRoot.addView(textView); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } 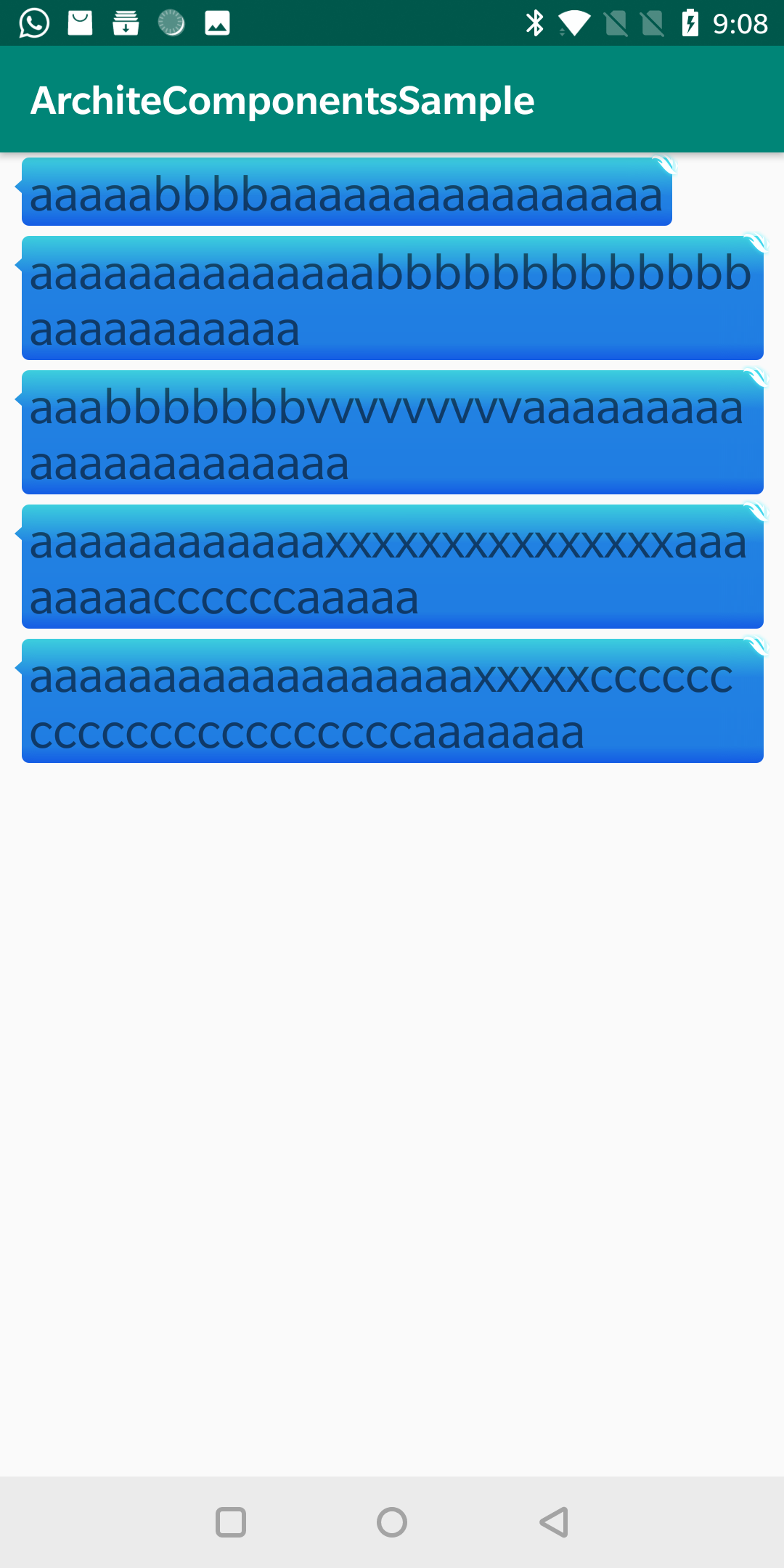
可以看到,我们的图片完美拉伸
参考文章
- https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1168755?
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI1NjEwMTM4OA==&mid=2651232105&idx=1&sn=fcc4fa956f329f839f2a04793e7dd3b9&mpshare=1&scene=21&srcid=0719Nyt7J8hsr4iYwOjVPXQE#wechat_redirect
推荐阅读
Rxjava 2.x 源码系列 – 变换操作符 Map(上)
java 源码系列 – 带你读懂 Reference 和 ReferenceQueue
扫一扫,欢迎关注我的微信公众号 stormjun94(徐公码字), 目前是一名程序员,不仅分享 Android开发相关知识,同时还分享技术人成长历程,包括个人总结,职场经验,面试经验等,希望能让你少走一点弯路。

