深入理解Java:注解(Annotation)自定义注解入门
深入理解Java:注解(Annotation)自定义注解入门
注解的定义
Java注解又称Java标注,是JDK5.0版本开始支持加入源代码的特殊语法元数据。
Java语言中的类、方法、变量、参数和包等都可以被标注。和Javadoc不同,Java标注可以通过反射获取标注内容。在编译器生成类文件时,标注可以被嵌入到字节码中。Java虚拟机可以保留标注内容,在运行时可以获取到标注内容。 当然它也支持自定义Java标注。
元注解的源码位置

元注解解析及实例
@Documented
指示某一类型的注释将通过默认javadoc和类似的工具来记录。这种类型应该用于注释类型的注释影响他们的客户使用注释元素的声明。如果一个类型声明归档的注解,注解它成为注释元素的公共API的一部分
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Dog {
public String name() default "wangcai";
public int age() default 0;
}
@Inherited
此注解是标识性的元注解,表示当前注解可以由子注解来继承
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
@Inherited
public @interface testInherited {
Sring name();
}
@Target
用于注解类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明,用逗号分隔隔开来表示作用域。

关键代码
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
/**
* Returns an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to.
* @return an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to
*/
ElementType[] value();
}
public enum ElementType {
/** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */
/**类、接口或枚举的声明*/
TYPE,
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
/**字段的声明*/
FIELD,
/** Method declaration */
/**方法的声明*/
METHOD,
/** Formal parameter declaration */
/**方法形式参数声明*/
PARAMETER,
/** Constructor declaration */
/**构造方法的声明*/
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Local variable declaration */
/**本地局部变量声明*/
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Annotation type declaration */
/**注解类型声明*/
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** Package declaration */
/**包声明*/
PACKAGE,
/**
* Type parameter declaration
*
* @since 1.8
*/
/**参数声明*
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/**
* Use of a type
*
* @since 1.8
*/
/**类型使用*
TYPE_USE
}
@Retention
生命周期注解,表示注解保留的时间长短,被描述的注解在什么范围内有效

@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
/**
* Returns the retention policy.
* @return the retention policy
*/
RetentionPolicy value();
}
public enum RetentionPolicy {
/**
* Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler.
*/
/**注释将被编译时丢弃*/
SOURCE,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler
* but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default
* behavior.
*/
/**编译试记录在class文件中,但VM运行时丢弃*/
CLASS,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and
* retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively.
*
* @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
*/
/**运行时存在,可以通过反射获取*/
RUNTIME
}
自定义注解
定义标记需要使用元注解
- 使用元注解@Target来标记该注解的作用范围(空间范围,在哪些地方可以使用)
- 使用元注解@Retention来标记该注解的作用时间范围(时间范围,在什么时候起作用)
- 使用元注解@Inherited来标记该注解是否可以由子注解来继承
- 使用元注解@Documented来标记该注解是否需要自动生成文档
- 使用@interface关键词来定义注解
- 在注解内部定义一些相关的属性,一般是方法的形式来定义属性
自定义注解实例
- 新建自定义注解,这里以idea为例,在想新建注解的位置,鼠标右键->New->Java Class
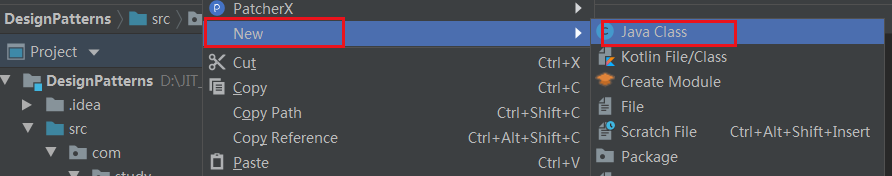
- 选择想要的方式,添加名称
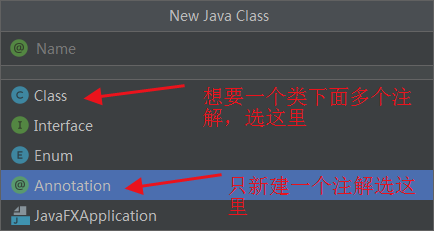
- 选择Annotation,新建一个Food的接口
/**
* 该注解为一个字段注解
* Description:
*
* @author: jieya
* Date: 2021-05-19
* Time: 18:05
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Food {
String name() default "";
}
- 选择Class,新建一个
/**
* 这里定义了食物的相关注解
* Description:
*
* @author: jieya
* Date: 2021-05-19
* Time: 18:11
*/
public class FoodAnnotation {
// 这里是单独定义
// @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
// @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// public @interface red {
// }
//
// @Target(ElementType.FIELD)
// @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// public @interface green {
// }
// 这里使用枚举类经营定义
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface color {
/**
* 颜色枚举
*
*/
public enum Color{RED,GREEN};
/**
* 颜色属性
*/
Color color() default color.Color.GREEN;
}
}
/**
* 定义了一个食物的实体对象类
* Description:
*
* @author: jieya
* Date: 2021-05-19
* Time: 18:34
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class FoodTest {
@Food
@FoodAnnotation.color(color = FoodAnnotation.color.Color.GREEN)
private String bread;
/**
* 饮料不算食物,就不加注解
*/
private String drinks;
@Food
@FoodAnnotation.color(color = FoodAnnotation.color.Color.RED)
private String biscuits;
/**
* 以下为使用反射获取注解的内容
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个食物实体对象
FoodTest food = new FoodTest("桃李面包", "百世", "达利园");
// 获取类模板
Class c = food.getClass();
// 获取所有字段
for (Field f : c.getDeclaredFields()) {
// 判断该字段是否有Food注解
if (f.isAnnotationPresent(Food.class)) {
Food annotation = f.getAnnotation(Food.class);
System.out.println("字段:[" + f.getName() + "]," + "该字段使用了Food注解");
// 判断该字段是否有color注解
if (f.isAnnotationPresent(FoodAnnotation.color.class)) {
FoodAnnotation.color.Color color = f.getAnnotation(FoodAnnotation.color.class).color();
System.out.println("字段:[" + f.getName() + "]," + "该字段使用了color注解" + "颜色为" + color);
}
} else {
System.out.println("字段:[" + f.getName() + "]," + "该字段没有使用注解");
}
}
}
}
FIELD注解是最常使用的,其他的注解方法的使用在这里就不在赘述了,都是大同小异的。



