一文看尽Java-Thread
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
一、前言
主要分成两部说起:Thread源码解读和常见面试题解答,废话不多说开始;
二、源码解读
首先看下构造函数,构造函数都是通过调用init方法对属性进行初始化,主要是对线程组、线程名字、栈大小等信息进行初始化;init内部通过调用currentThread本地方法,获取当前的线程,这个本地方法封装在JVM中,有兴趣的可以看下这个这个链接查找下JVM实现https://hg.openjdk.java.net/jdk8u,接下来对ThreadGroup的判断,如果没有传入线程组的话, 第一是使用SecurityManager中的ThreadGroup, 如果从SecurityManager 中获取不到ThreadGroup(), 那么就从当前线程中获取线程组,最后做了检验和些参数的赋值,整体上相对比较简单;

private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(g, target, name, stackSize, null); } private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc) { if (name == null) { throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null"); } this.name = name.toCharArray(); Thread parent = currentThread(); SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); if (g == null) { /* Determine if it's an applet or not */ /* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager what to do. */ if (security != null) { g = security.getThreadGroup(); } /* If the security doesn't have a strong opinion of the matter use the parent thread group. */ if (g == null) { g = parent.getThreadGroup(); } } /* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is explicitly passed in. */ g.checkAccess(); /* * Do we have the required permissions? */ if (security != null) { if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) { security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION); } } g.addUnstarted(); this.group = g; this.daemon = parent.isDaemon(); this.priority = parent.getPriority(); if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass())) this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader(); else this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader; this.inheritedAccessControlContext = acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext(); this.target = target; setPriority(priority); if (parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null) this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals); /* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */ this.stackSize = stackSize; /* Set thread ID */ tid = nextThreadID(); } public Thread() { init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); } public Thread(Runnable target) { init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); } Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) { init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0, acc); } // 线程名 public Thread(String name) { init(null, null, name, 0); } //线程组和线程名 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) { init(group, null, name, 0); } //线程任务,线程名 public Thread(Runnable target, String name){ init(null, target, name, 0); } // 线程组, 线程任务, 线程名 ,栈大小 public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(group, target, name, stackSize); }
View Code
接下来看下主要的属性:

// 类加载的时候,调用本地的注册本地方静态方法, 这个方法是本地方法 private static native void registerNatives(); static { registerNatives(); } private volatile char name[]; private int priority; private Thread threadQ; private long eetop; /* Whether or not to single_step this thread. */ private boolean single_step; /* Whether or not the thread is a daemon thread. */ // 设设置这个线程是否是守护线程 private boolean daemon = false; /* JVM state */ private boolean stillborn = false; /* What will be run. */ // 要执行的run方法的对象 private Runnable target; /* The group of this thread */ // 这个线程的线程组 private ThreadGroup group; /* The context ClassLoader for this thread */ // 这个线程的上下文类加载器 private ClassLoader contextClassLoader; /* The inherited AccessControlContext of this thread */ private AccessControlContext inheritedAccessControlContext; /* For autonumbering anonymous threads. */ private static int threadInitNumber; private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() { return threadInitNumber++; } /* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained * by the ThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null; /* * InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is * maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null; /* * The requested stack size for this thread, or 0 if the creator did * not specify a stack size. It is up to the VM to do whatever it * likes with this number; some VMs will ignore it. */ // 给这个线程设置的栈的大小,默认为0 private long stackSize; /* * JVM-private state that persists after native thread termination. */ private long nativeParkEventPointer; /* * Thread ID */ //线程id private long tid; /* For generating thread ID */ private static long threadSeqNumber; /* Java thread status for tools, * initialized to indicate thread 'not yet started' */ private volatile int threadStatus = 0; private static synchronized long nextThreadID() { return ++threadSeqNumber; } /** * The argument supplied to the current call to * java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport.park. * Set by (private) java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport.setBlocker * Accessed using java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport.getBlocker */ volatile Object parkBlocker; /* The object in which this thread is blocked in an interruptible I/O * operation, if any. The blocker's interrupt method should be invoked * after setting this thread's interrupt status. */ private volatile Interruptible blocker; private final Object blockerLock = new Object(); /* Set the blocker field; invoked via sun.misc.SharedSecrets from java.nio code */ void blockedOn(Interruptible b) { synchronized (blockerLock) { blocker = b; } } /** * The minimum priority that a thread can have. */ // 线程执行的最低优先级 为1 public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1; /** * The default priority that is assigned to a thread. */ // 线程默认的执行优先级为 5 public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5; /** * The maximum priority that a thread can have. */ // 线程执行的最高的优先级为 10 public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
View Code
最后介绍下方法的作用和线程状态,源码都比较简单,没必进行过多的介绍,都是通过调用JVM的本地方法实现;
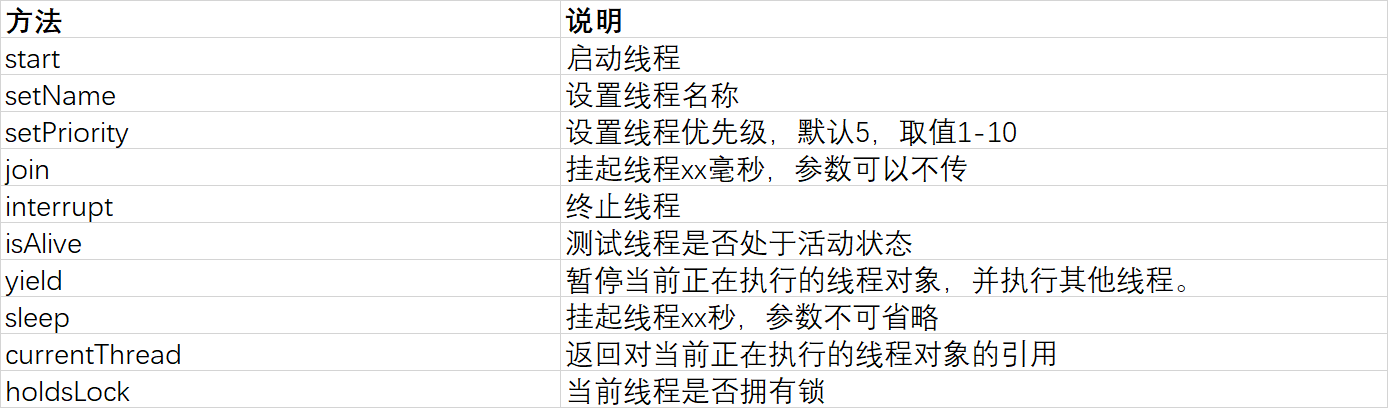
线程状态:

三、常见面试题
1.线程与进程的区别?
进程是资源分配最小的单位,线程是CPU调度最小的单位;
线程属于进程,共享进程分配的资源;
进程属于抢占式调度,资源不相互共享;
2.start和run的区别?
run是Thread的一个普通的方法;
start方法会创建一个新的子线程并启动;
3.sleep与wait的区别?
sleep是Thread方法,wait是Object的方法;
wait方法只能在synchroized方法或者块中使用;
Thread.sleep只会让出CPU,不会改变锁的行为;
Object.wait不仅会让出CPU,同时还会释放占有同步资源的锁;
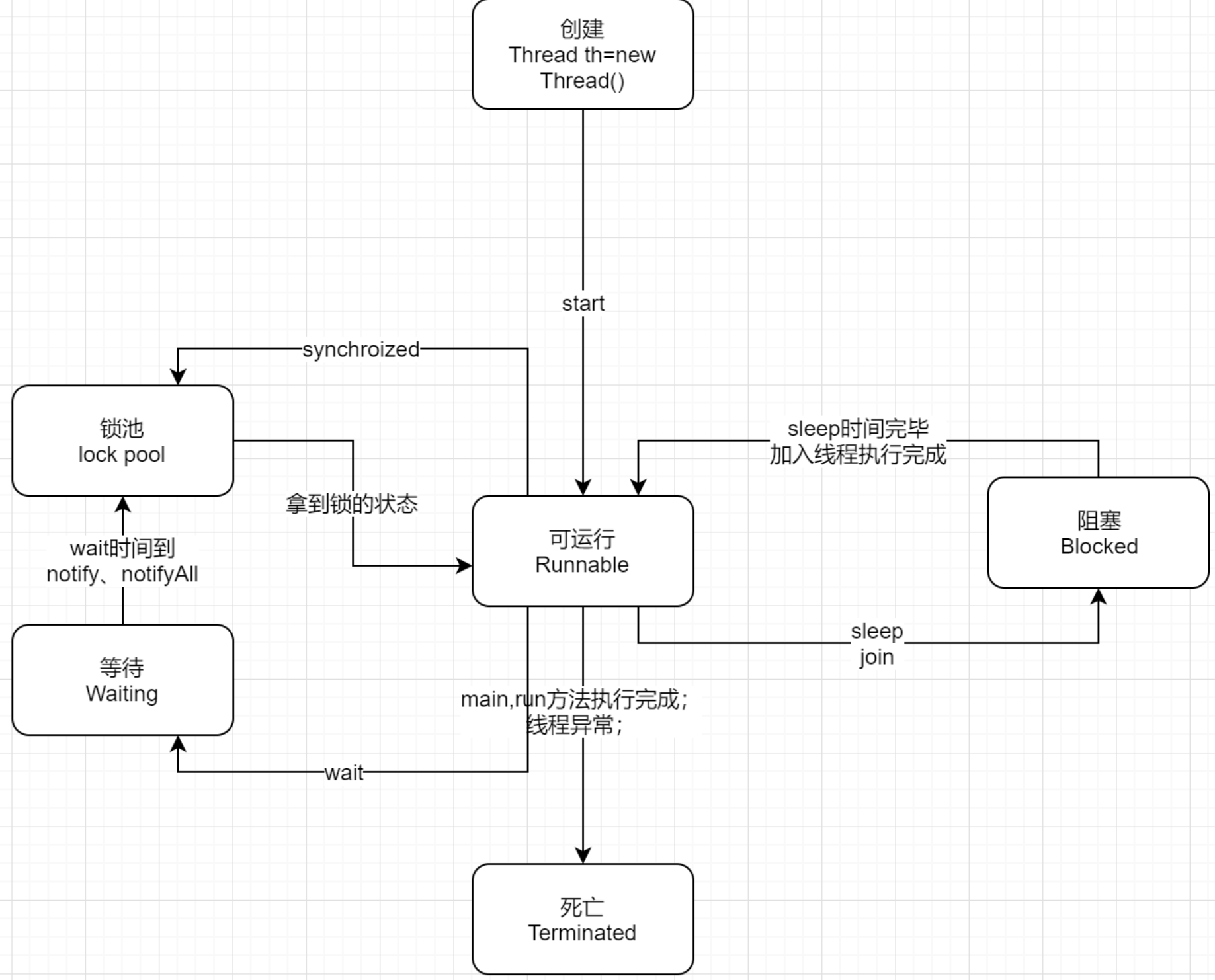
4.线程状态的转化?
图中将WAITING 和TIMED_WAITING 两个状态合并为WAITING ,没有分开,大家不要搞错;
5.如何处理线程的返回值?
主线程等待法,使用while等待主线程返回值;
join阻塞当前线程以等待子线程;
通过FuTureTask获取子线程的返回值;

public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> { @Override public String call() throws Exception { String value="test"; System.out.println("start"); Thread.sleep(5000); System.out.println("end"); return value; } } public class FutureTaskDemo { public static void main(String[] main) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { FutureTask<String> futureTask=new FutureTask<String>(new MyCallable()); new Thread(futureTask).start(); if (!futureTask.isDone()){ System.out.println("waiting"); } System.out.println("return"+futureTask.get()); } }
View Code
通过线程池获取返回值;

public class ThreadPoolDemo { public static void main(String[] args){ ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Future<String> futureTask=executorService.submit(new MyCallable()); if (!futureTask.isDone()){ System.out.println("wait"); } try { System.out.println(futureTask.get()); }catch (InterruptedException ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); }catch (ExecutionException ex){ ex.printStackTrace(); }finally { executorService.shutdown(); } } }
View Code
6.Thread和Runnable?
Thread是类,Runnable是接口,Thread是Runnable实现;
类的继承单一原则,Runnable是更高层次的抽象;
四、结束
欢迎大家加群438836709!欢迎大家关注我!


