Mybaits 源码解析 (十)—– 全网最详细,没有之一:Spring-Mybatis框架使用与源码解析
- 2019 年 11 月 11 日
- 筆記
在前面几篇文章中我们主要分析了Mybatis的单独使用,在实际在常规项目开发中,大部分都会使用mybatis与Spring结合起来使用,毕竟现在不用Spring开发的项目实在太少了。本篇文章便来介绍下Mybatis如何与Spring结合起来使用,并介绍下其源码是如何实现的。
Spring-Mybatis使用
添加maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>4.3.8.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis-spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency>
在src/main/resources下添加mybatis-config.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <typeAliases> <typeAlias alias="User" type="com.chenhao.bean.User" /> </typeAliases> <plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"> <property name="helperDialect" value="mysql"/> </plugin> </plugins> </configuration>
在src/main/resources/mapper路径下添加User.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.chenhao.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="getUser" parameterType="int" resultType="com.chenhao.bean.User"> SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
在src/main/resources/路径下添加beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test"></property> <property name="username" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> </bean> <bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"></property> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml" /> </bean> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <property name="basePackage" value="com.chenhao.mapper" /> </bean> </beans>
注解的方式
- 以上分析都是在spring的XML配置文件applicationContext.xml进行配置的,mybatis-spring也提供了基于注解的方式来配置sqlSessionFactory和Mapper接口。
- sqlSessionFactory主要是在@Configuration注解的配置类中使用@Bean注解的名为sqlSessionFactory的方法来配置;
- Mapper接口主要是通过在@Configuration注解的配置类中结合@MapperScan注解来指定需要扫描获取mapper接口的包。
@Configuration @MapperScan("com.chenhao.mapper") public class AppConfig { @Bean public DataSource dataSource() { return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder() .addScript("schema.sql") .build(); } @Bean public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager() { return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource()); } @Bean public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception { //创建SqlSessionFactoryBean对象 SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); //设置数据源 sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource()); //设置Mapper.xml路径 sessionFactory.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mapper/*.xml")); // 设置MyBatis分页插件 PageInterceptor pageInterceptor = new PageInterceptor(); Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty("helperDialect", "mysql"); pageInterceptor.setProperties(properties); sessionFactory.setPlugins(new Interceptor[]{pageInterceptor}); return sessionFactory.getObject(); } }
对照Spring-Mybatis的方式,也就是对照beans.xml文件来看
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"></property> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml" /> </bean>
就对应着SqlSessionFactory的生成,类似于原生Mybatis使用时的以下代码
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build( Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
而UserMapper代理对象的获取,是通过扫描的形式获取,也就是MapperScannerConfigurer这个类
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <property name="basePackage" value="com.chenhao.mapper" /> </bean>
对应着Mapper接口的获取,类似于原生Mybatis使用时的以下代码:
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
接着我们就可以在Service中直接从Spring的BeanFactory中获取了,如下
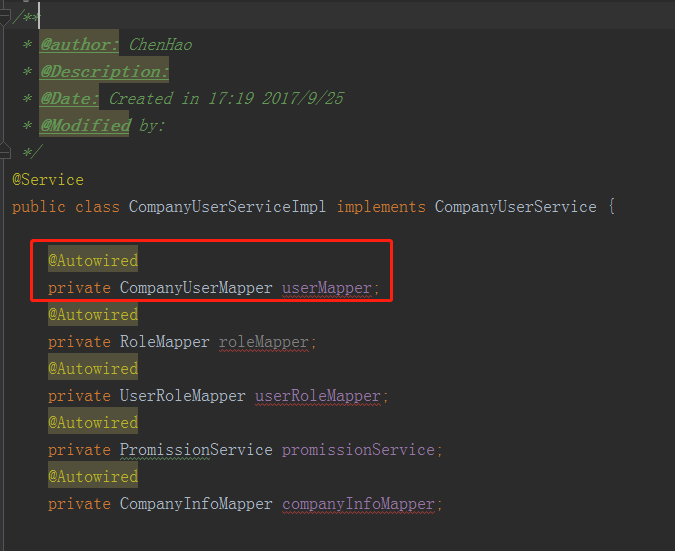
所以我们现在就主要分析下在Spring中是如何生成SqlSessionFactory和Mapper接口的
SqlSessionFactoryBean的设计与实现
大体思路
- mybatis-spring为了实现spring对mybatis的整合,即将mybatis的相关组件作为spring的IOC容器的bean来管理,使用了spring的FactoryBean接口来对mybatis的相关组件进行包装。spring的IOC容器在启动加载时,如果发现某个bean实现了FactoryBean接口,则会调用该bean的getObject方法,获取实际的bean对象注册到IOC容器,其中FactoryBean接口提供了getObject方法的声明,从而统一spring的IOC容器的行为。
- SqlSessionFactory作为mybatis的启动组件,在mybatis-spring中提供了SqlSessionFactoryBean来进行包装,所以在spring项目中整合mybatis,首先需要在spring的配置,如XML配置文件applicationContext.xml中,配置SqlSessionFactoryBean来引入SqlSessionFactory,即在spring项目启动时能加载并创建SqlSessionFactory对象,然后注册到spring的IOC容器中,从而可以直接在应用代码中注入使用或者作为属性,注入到mybatis的其他组件对应的bean对象。在applicationContext.xml的配置如下:
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> // 数据源 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> // mapper.xml的资源文件,也就是SQL文件 <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mybatis/mapper/**/*.xml" /> //mybatis配置mybatisConfig.xml的资源文件 <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis/mybitas-config.xml" /> </bean>
接口设计与实现
SqlSessionFactory的接口设计如下:实现了spring提供的FactoryBean,InitializingBean和ApplicationListener这三个接口,在内部封装了mybatis的相关组件作为内部属性,如mybatisConfig.xml配置资源文件引用,mapper.xml配置资源文件引用,以及SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构造器和SqlSessionFactory引用。
// 解析mybatisConfig.xml文件和mapper.xml,设置数据源和所使用的事务管理机制,将这些封装到Configuration对象 // 使用Configuration对象作为构造参数,创建SqlSessionFactory对象,其中SqlSessionFactory为单例bean,最后将SqlSessionFactory单例对象注册到spring容器。 public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SqlSessionFactoryBean.class); // mybatis配置mybatisConfig.xml的资源文件 private Resource configLocation; //解析完mybatisConfig.xml后生成Configuration对象 private Configuration configuration; // mapper.xml的资源文件 private Resource[] mapperLocations; // 数据源 private DataSource dataSource; // 事务管理,mybatis接入spring的一个重要原因也是可以直接使用spring提供的事务管理 private TransactionFactory transactionFactory; private Properties configurationProperties; // mybatis的SqlSessionFactoryBuidler和SqlSessionFactory private SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; // 实现FactoryBean的getObject方法 @Override public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception { //... } // 实现InitializingBean的 @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { //... } // 为单例 public boolean isSingleton() { return true; } }
我们重点关注FactoryBean,InitializingBean这两个接口,spring的IOC容器在加载创建SqlSessionFactoryBean的bean对象实例时,会调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法进行对该bean对象进行相关初始化处理。
InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法
大家最好看一下我前面关于Spring源码的文章,有Bean的生命周期详细源码分析,我们现在简单回顾一下,在getBean()时initializeBean方法中调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet,而在前一步操作populateBean中,以及将该bean对象实例的属性设值好了,InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet进行一些后置处理。此时我们要注意,populateBean方法已经将SqlSessionFactoryBean对象的属性进行赋值了,也就是xml中property配置的dataSource,mapperLocations,configLocation这三个属性已经在SqlSessionFactoryBean对象的属性进行赋值了,后面调用afterPropertiesSet时直接可以使用这三个配置的值了。
// bean对象实例创建的核心实现方法 protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // 使用构造函数或者工厂方法来创建bean对象实例 // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } ... // 初始化bean对象实例,包括属性赋值,初始化方法,BeanPostProcessor的执行 // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { // 1. InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor执行: // (1). 调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInstantiation, // (2). 调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessProperties和postProcessPropertyValues // 2. bean对象的属性赋值 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); // 1. Aware接口的方法调用 // 2. BeanPostProcess执行:调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization // 3. 调用init-method:首先InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet,然后应用配置的init-method // 4. BeanPostProcess执行:调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
如上,在populateBean阶段,dataSource,mapperLocations,configLocation这三个属性已经在SqlSessionFactoryBean对象的属性进行赋值了,调用afterPropertiesSet时直接可以使用这三个配置的值了。那我们来接着看看afterPropertiesSet方法
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required"); notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required"); state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null), "Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together"); // 创建sqlSessionFactory this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory(); }
SqlSessionFactoryBean的afterPropertiesSet方法实现如下:调用buildSqlSessionFactory方法创建用于注册到spring的IOC容器的sqlSessionFactory对象。我们接着来看看buildSqlSessionFactory
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException { // 配置类 Configuration configuration; // 解析mybatis-Config.xml文件, // 将相关配置信息保存到configuration XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null; if (this.configuration != null) { configuration = this.configuration; if (configuration.getVariables() == null) { configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties); } else if (this.configurationProperties != null) { configuration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties); } //资源文件不为空 } else if (this.configLocation != null) { //根据configLocation创建xmlConfigBuilder,XMLConfigBuilder构造器中会创建Configuration对象 xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties); //将XMLConfigBuilder构造器中创建的Configuration对象直接赋值给configuration属性 configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration(); } //略.... if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) { try { //解析mybatis-Config.xml文件,并将相关配置信息保存到configuration xmlConfigBuilder.parse(); if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'"); } } catch (Exception ex) { throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex); } } if (this.transactionFactory == null) { //事务默认采用SpringManagedTransaction,这一块非常重要,我将在后买你单独写一篇文章讲解Mybatis和Spring事务的关系 this.transactionFactory = new SpringManagedTransactionFactory(); } // 为sqlSessionFactory绑定事务管理器和数据源 // 这样sqlSessionFactory在创建sqlSession的时候可以通过该事务管理器获取jdbc连接,从而执行SQL configuration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource)); // 解析mapper.xml if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) { for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) { if (mapperLocation == null) { continue; } try { // 解析mapper.xml文件,并注册到configuration对象的mapperRegistry XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(), configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments()); xmlMapperBuilder.parse(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'"); } } } else { if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found"); } } // 将Configuration对象实例作为参数, // 调用sqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建sqlSessionFactory对象实例 return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration); }
buildSqlSessionFactory的核心逻辑:解析mybatis配置文件mybatisConfig.xml和mapper配置文件mapper.xml并封装到Configuration对象中,最后调用mybatis的sqlSessionFactoryBuilder来创建SqlSessionFactory对象。这一点相当于前面介绍的原生的mybatis的初始化过程。另外,当配置中未指定事务时,mybatis-spring默认采用SpringManagedTransaction,这一点非常重要,请大家先在心里做好准备。此时SqlSessionFactory已经创建好了,并且赋值到了SqlSessionFactoryBean的sqlSessionFactory属性中。
FactoryBean的getObject方法定义
FactoryBean:创建某个类的对象实例的工厂。
spring的IOC容器在启动,创建好bean对象实例后,会检查这个bean对象是否实现了FactoryBean接口,如果是,则调用该bean对象的getObject方法,在getObject方法中实现创建并返回实际需要的bean对象实例,然后将该实际需要的bean对象实例注册到spring容器;如果不是则直接将该bean对象实例注册到spring容器。
SqlSessionFactoryBean的getObject方法实现如下:由于spring在创建SqlSessionFactoryBean自身的bean对象时,已经调用了InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法创建了sqlSessionFactory对象,故可以直接返回sqlSessionFactory对象给spring的IOC容器,从而完成sqlSessionFactory的bean对象的注册,之后可以直接在应用代码注入或者spring在创建其他bean对象时,依赖注入sqlSessionFactory对象。
@Override public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception { if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) { afterPropertiesSet(); } // 直接返回sqlSessionFactory对象 // 单例对象,由所有mapper共享 return this.sqlSessionFactory; }
总结
由以上分析可知,spring在加载创建SqlSessionFactoryBean的bean对象实例时,调用SqlSessionFactoryBean的afterPropertiesSet方法完成了sqlSessionFactory对象实例的创建;在将SqlSessionFactoryBean对象实例注册到spring的IOC容器时,发现SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean接口,故不是SqlSessionFactoryBean对象实例自身需要注册到spring的IOC容器,而是SqlSessionFactoryBean的getObject方法的返回值对应的对象需要注册到spring的IOC容器,而这个返回值就是SqlSessionFactory对象,故完成了将sqlSessionFactory对象实例注册到spring的IOC容器。创建Mapper的代理对象我们下一篇文章再讲