策略模式和工厂模式搭配使用
- 2019 年 11 月 2 日
- 筆記
策略模式和工厂模式的搭配使用可以很好地消除代码
if-else的多层嵌套
需求
针对店下商铺,有这样一个需求,对用户客户分为了普通客户、vip客户、超级vip用户、专属vip用户4个等级,每当用户购买商品时,针对不同的用户等级和消费金额采取不同的打折优惠策略。在平常的开发当中,必然会出现多层的if-else嵌套判断,先判断用户的等级再判断用户购买商品的消费金额。
弊端
以上的情况出现了多层的if-else嵌套,除此之外,以后如果需求再有变动,需要再增加一个用户等级,那么又会再次添加if-else的嵌套判断,那么如何解决上述的弊端呢,采用策略模式和工厂模式的搭配使用,可以很好地优化多层if-else的多层嵌套
实现
编写用户等级枚举类
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; /** * 用户类型枚举类 */ public enum UserPayServiceEnum { VIP(1,"Vip"), SUPERVIP(2,"SuperVip"), PARTICULALYVIP(3,"ParticularlyVip"), NORMAL(4,"NormalPayService"); /** * 状态值 */ private int code; /** * 类型描述 */ private String value; private UserPayServiceEnum(int code, String value) { this.code = code; this.value = value; } public int getCode() { return code; } public String getValue() { return value; } public static UserPayServiceEnum valueOf(int code) { for (UserPayServiceEnum type : UserPayServiceEnum.values()) { if (type.getCode()==code) { return type; } } return null; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(UserPayServiceEnum.VIP.getValue()); } } 编写不同的用户等级策略类
以下需要注意的是每个策略类实现了InitializingBean接口的作用是每当策略类被spring容器启动初始化后会调用afterPropertiesSet方法,而在这个方法里面的作用是会往工厂里针对不同用户等级保存其对应的用户策略引用
编写打折接口
不同的用户等级策略类实现该接口,该接口包含了打折方法
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import java.math.BigDecimal; public interface UserPayService { /** * 计算应付价格 */ public BigDecimal quote(BigDecimal orderPrice); } 编写普通用户策略类
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.math.BigDecimal; /** * 普通会员不打折原价 */ //实现InitializingBean接口,容器启动后会调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,往工厂里写入打折策略 @Service public class NormalPayService implements UserPayService, InitializingBean { @Override public BigDecimal quote(BigDecimal orderPrice) { return new BigDecimal("10"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { UserPayServiceStrategyFactory.register(UserPayServiceEnum.NORMAL.getValue(), this); } } 编写vip用户策略类
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.math.BigDecimal; /** * 普通会员打9折,消费超100打8折 */ //实现InitializingBean接口,容器启动后会调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,往工厂里写入打折策略 @Service public class VipPayService implements UserPayService, InitializingBean { @Override public BigDecimal quote(BigDecimal orderPrice) { if (orderPrice.compareTo(new BigDecimal("100")) > 1) { return new BigDecimal("8"); } return new BigDecimal("9"); } public void myShow(){ System.out.println("myShow method invoke----->"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { UserPayServiceStrategyFactory.register(UserPayServiceEnum.VIP.getValue(), this); } } 编写超级vip用户策略类
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.math.BigDecimal; /** * 超级会员打8折 */ @Service public class SuperVipPayService implements UserPayService , InitializingBean { @Override public BigDecimal quote(BigDecimal orderPrice) { return new BigDecimal("8"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { UserPayServiceStrategyFactory.register(UserPayServiceEnum.SUPERVIP.getValue(),this); } } 编写专属用户vip策略类
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.math.BigDecimal; /** * 专属会员 下单消费超30打七折 */ @Service public class ParticularlyVipPayService implements UserPayService, InitializingBean { @Override public BigDecimal quote(BigDecimal orderPrice) { if (orderPrice.compareTo(new BigDecimal("30"))>0) { return new BigDecimal("7"); } return new BigDecimal("8"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { UserPayServiceStrategyFactory.register(UserPayServiceEnum.PARTICULALYVIP.getValue(),this); } } 编写工厂类
注意这里工厂的register方法,该方法会在spring容器启动初始化bean即各个不同等级的用户策略类完成后调用afterPropertiesSet方法里调用register方法,当容器启动完成后,我们的spring容器中即有了一个键为用户等级,值为用户等级策略类的map,在对不同用户进行优惠打折的时候,可以根据用户等级来取得当前用户的策略类
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** * 版本二:工厂使用(高级版) */ //@Service public class UserPayServiceStrategyFactory { private static Map<String,UserPayService> services = new ConcurrentHashMap<String,UserPayService>(); public static UserPayService getByUserType(String type){ return services.get(type); } public static void register(String userType,UserPayService userPayService){ Assert.notNull(userType,"userType can't be null"); services.put(userType,userPayService); } } 编写测试类
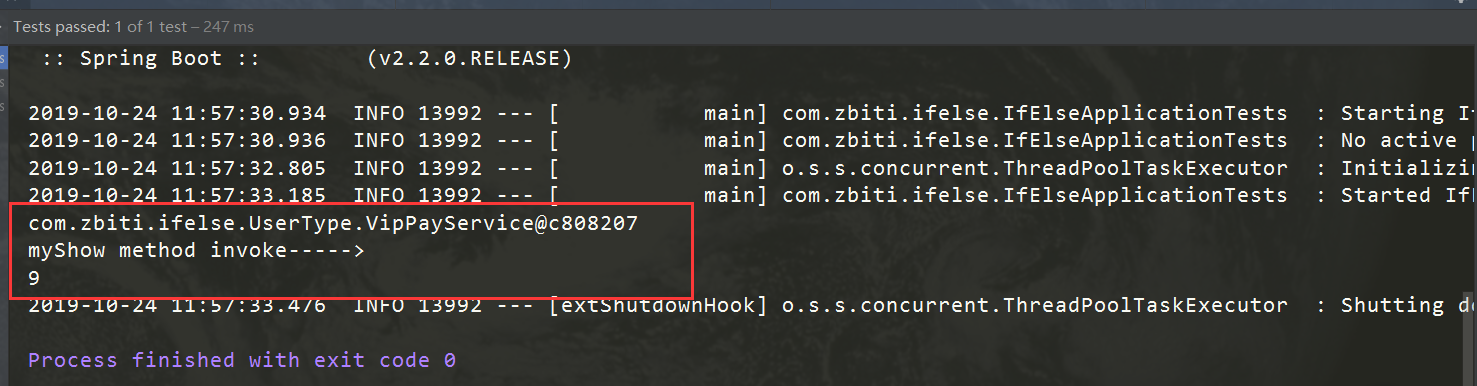
package com.zbiti.ifelse; import com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType.UserPayService; import com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType.UserPayServiceStrategyFactory; import com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType.VipPayService; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import java.math.BigDecimal; @SpringBootTest @Slf4j class IfElseApplicationTests { @Test void contextLoads() { calPrice(); } public void calPrice() { BigDecimal orderPrice = new BigDecimal("100"); String vipType = "Vip"; //指定用户类型,获得相对应的策略 UserPayService strategy = UserPayServiceStrategyFactory.getByUserType(vipType); // UserPayService strategy2 = UserPayServiceStrategyFactory2.getByUserType(vipType); System.out.println(strategy); // System.out.println(strategy2); BigDecimal quote = strategy.quote(orderPrice); if(strategy instanceof VipPayService){ ((VipPayService) strategy).myShow(); } System.out.println(quote); } } 结果
可以看到vip用户打9折,在这个不同用户等级购买商品时采取的不同打折策略里,我们没有出现了多层的if-else的嵌套
tips
编写工厂类的实现方式上面是其中一种实现(比较推荐),另外也有其它的方式,可以参考如下
提前将策略写入到map,但是这里需要手动new策略对象
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** * 版本一:工厂使用 */ public class UserPayServiceStrategyFactory2 { private static Map<String,UserPayService> services = new ConcurrentHashMap<String,UserPayService>(); public static UserPayService getByUserType(String type){ return services.get(type); } static{ services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.VIP.getValue(), new VipPayService()); services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.SUPERVIP.getValue(), new SuperVipPayService()); services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.PARTICULALYVIP.getValue(), new ParticularlyVipPayService()); services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.NORMAL.getValue(), new NormalPayService()); } } 也可以通过反射,编写工厂类
package com.zbiti.ifelse.UserType; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** * 版本一:工厂使用 */ public class UserPayServiceStrategyFactory3 { private static Map<String, Class<? extends UserPayService>> services = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); //初始化map,存放策略 static { services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.VIP.getValue(), VipPayService.class); services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.SUPERVIP.getValue(), SuperVipPayService.class); services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.PARTICULALYVIP.getValue(), ParticularlyVipPayService.class); services.put(UserPayServiceEnum.NORMAL.getValue(), NormalPayService.class); } //获取策略 public static UserPayService getByUserType(String type) { try { Class<? extends UserPayService> userPayServiceClass = services.get(type); return userPayServiceClass.newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return new NormalPayService(); } } } 其实也可以搭配注解的使用,自定义一个注解类,在策略类上标识上注解(值为不同的用户等级),容器启动的时候通过扫描我们的自定义注解,写入map中也是可以的。
参考
本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布!