曹工杂谈:Java 类加载还会死锁?这是什么情况?
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
一、前言
今天事不是很多,正好在Java交流群里,看到一个比较有意思的问题,于是花了点时间研究了一下,这里做个简单的分享。
先贴一份测试代码,大家可以先猜测一下,执行结果会是怎样的:
2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 5 6 public class TestClassLoading { 7 public static class A{ 8 static { 9 System.out.println("class A init"); 10 try { 11 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 new B(); 16 } 17 18 public static void test() { 19 System.out.println("aaa"); 20 } 21 } 22 23 public static class B{ 24 static { 25 System.out.println("class B init"); 26 new A(); 27 } 28 29 30 public static void test() { 31 System.out.println("bbb"); 32 } 33 } 34 public static void main(String[] args) { 35 new Thread(() -> A.test()).start(); 36 new Thread(() -> B.test()).start(); 37 } 38 }
不知道,你猜对了没有呢,实际的执行结果会是下面这样的:
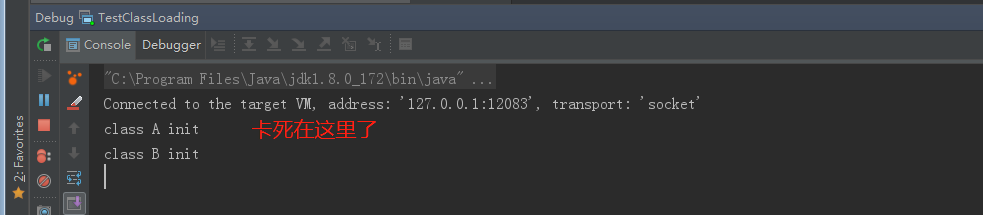
二、原因分析
这里,一开始大家分析的是,和new有关系;但下面的代码和上面的结果完全一致,基本可以排除 new 的嫌疑:
1 public class TestClassLoadingNew { 2 public static class A{ 3 static { 4 System.out.println("class A init"); 5 try { 6 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 7 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 B.test(); 11 } 12 13 public static void test() { 14 System.out.println("aaa"); 15 } 16 } 17 18 public static class B{ 19 static { 20 System.out.println("class B init"); 21 A.test(); 22 } 23 24 25 public static void test() { 26 System.out.println("bbb"); 27 } 28 } 29 public static void main(String[] args) { 30 new Thread(() -> A.test()).start(); 31 new Thread(() -> B.test()).start(); 32 } 33 }
这里,问题的根本原因,其实是:
classloader在初始化一个类的时候,会对当前类加锁,加锁后,再执行类的静态初始化块。
所以,上面会发生:
1、线程1:类A对class A加锁,加锁后,执行类的静态初始化块(在堆栈里体现为<clinit>函数),发现用到了class B,于是去加载B;
2、线程2:类B对class B加锁,加锁后,执行类的静态初始化块(在堆栈里体现为<clinit>函数),发现用到了class A,于是去加载A;
3、死锁发生。
有经验的同学,对于死锁是毫无畏惧的,因为我们有神器,jstack。 jstack 加上 -l 参数,即可打印出各个线程持有的锁的信息。(windows上直接jconsole就行,还能死锁检测):
"Thread-1" #15 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000002178a000 nid=0x2df8 in Object.wait() [0x0000000021f4e000] java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE at com.dmtest.netty_learn.TestClassLoading$B.<clinit>(TestClassLoading.java:32) at com.dmtest.netty_learn.TestClassLoading.lambda$main$1(TestClassLoading.java:42) at com.dmtest.netty_learn.TestClassLoading$$Lambda$2/736709391.run(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) Locked ownable synchronizers: - None "Thread-0" #14 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000021787800 nid=0x2618 in Object.wait() [0x00000000213be000] java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE at com.dmtest.netty_learn.TestClassLoading$A.<clinit>(TestClassLoading.java:21) at com.dmtest.netty_learn.TestClassLoading.lambda$main$0(TestClassLoading.java:41) at com.dmtest.netty_learn.TestClassLoading$$Lambda$1/611437735.run(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748) Locked ownable synchronizers: - None
这里,很奇怪的一个原因是,明明这两个线程发生了死锁,为什么没有显示呢?
因为,这是 jvm 内部加了锁,所以,jconsole、jstack都失效了。
三、一起深入JVM,探个究竟
1、单步跟踪
class 的加载都是由 classloader 来完成的,而且部分工作是在 jvm 层面完成,我们可以看到,在 java.lang.ClassLoader#defineClass1 的定义中: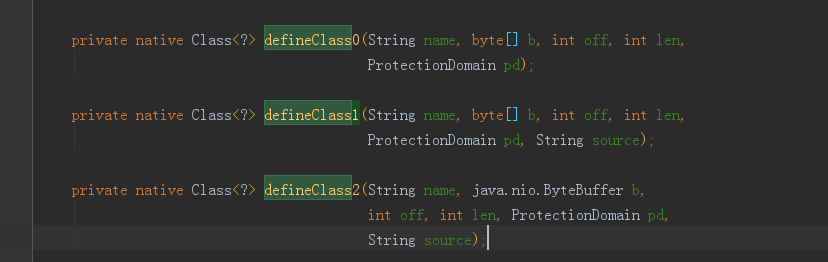
以上几个方法都是本地方法。
其实际的实现在:/home/ckl/openjdk-jdk8u/jdk/src/share/native/java/lang/ClassLoader.c,
1 JNIEXPORT jclass JNICALL 2 Java_java_lang_ClassLoader_defineClass1(JNIEnv *env, 3 jobject loader, 4 jstring name, 5 jbyteArray data, 6 jint offset, 7 jint length, 8 jobject pd, 9 jstring source) 10 { 11 jbyte *body; 12 char *utfName; 13 jclass result = 0; 14 char buf[128]; 15 char* utfSource; 16 char sourceBuf[1024]; 17 18 if (data == NULL) { 19 JNU_ThrowNullPointerException(env, 0); 20 return 0; 21 } 22 23 /* Work around 4153825. malloc crashes on Solaris when passed a 24 * negative size. 25 */ 26 if (length < 0) { 27 JNU_ThrowArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(env, 0); 28 return 0; 29 } 30 31 body = (jbyte *)malloc(length); 32 33 if (body == 0) { 34 JNU_ThrowOutOfMemoryError(env, 0); 35 return 0; 36 } 37 38 (*env)->GetByteArrayRegion(env, data, offset, length, body); 39 40 if ((*env)->ExceptionOccurred(env)) 41 goto free_body; 42 43 if (name != NULL) { 44 utfName = getUTF(env, name, buf, sizeof(buf)); 45 if (utfName == NULL) { 46 goto free_body; 47 } 48 VerifyFixClassname(utfName); 49 } else { 50 utfName = NULL; 51 } 52 53 if (source != NULL) { 54 utfSource = getUTF(env, source, sourceBuf, sizeof(sourceBuf)); 55 if (utfSource == NULL) { 56 goto free_utfName; 57 } 58 } else { 59 utfSource = NULL; 60 } 61 result = JVM_DefineClassWithSource(env, utfName, loader, body, length, pd, utfSource); 62 63 if (utfSource && utfSource != sourceBuf) 64 free(utfSource); 65 66 free_utfName: 67 if (utfName && utfName != buf) 68 free(utfName); 69 70 free_body: 71 free(body); 72 return result; 73 }
大家可以跟着标红的代码,我们一起大概看一下,这个方法的实现在/home/ckl/openjdk-jdk8u/hotspot/src/share/vm/prims/jvm.cpp 中,
1 JVM_ENTRY(jclass, JVM_DefineClassWithSource(JNIEnv *env, const char *name, jobject loader, const jbyte *buf, jsize len, jobject pd, const char *source)) 2 JVMWrapper2("JVM_DefineClassWithSource %s", name); 3 4 return jvm_define_class_common(env, name, loader, buf, len, pd, source, true, THREAD); 5 JVM_END
jvm_define_class_common 的实现,还是在 jvm.cpp 中,
1 // common code for JVM_DefineClass() and JVM_DefineClassWithSource() 2 // and JVM_DefineClassWithSourceCond() 3 static jclass jvm_define_class_common(JNIEnv *env, const char *name, 4 jobject loader, const jbyte *buf, 5 jsize len, jobject pd, const char *source, 6 jboolean verify, TRAPS) { 7 if (source == NULL) source = "__JVM_DefineClass__"; 8 9 assert(THREAD->is_Java_thread(), "must be a JavaThread"); 10 JavaThread* jt = (JavaThread*) THREAD; 11 12 PerfClassTraceTime vmtimer(ClassLoader::perf_define_appclass_time(), 13 ClassLoader::perf_define_appclass_selftime(), 14 ClassLoader::perf_define_appclasses(), 15 jt->get_thread_stat()->perf_recursion_counts_addr(), 16 jt->get_thread_stat()->perf_timers_addr(), 17 PerfClassTraceTime::DEFINE_CLASS); 18 19 if (UsePerfData) { 20 ClassLoader::perf_app_classfile_bytes_read()->inc(len); 21 } 22 23 // Since exceptions can be thrown, class initialization can take place 24 // if name is NULL no check for class name in .class stream has to be made. 25 TempNewSymbol class_name = NULL; 26 if (name != NULL) { 27 const int str_len = (int)strlen(name); 28 if (str_len > Symbol::max_length()) { 29 // It's impossible to create this class; the name cannot fit 30 // into the constant pool. 31 THROW_MSG_0(vmSymbols::java_lang_NoClassDefFoundError(), name); 32 } 33 class_name = SymbolTable::new_symbol(name, str_len, CHECK_NULL); 34 } 35 36 ResourceMark rm(THREAD); 37 ClassFileStream st((u1*) buf, len, (char *)source); 38 Handle class_loader (THREAD, JNIHandles::resolve(loader)); 39 if (UsePerfData) { 40 is_lock_held_by_thread(class_loader, 41 ClassLoader::sync_JVMDefineClassLockFreeCounter(), 42 THREAD); 43 } 44 Handle protection_domain (THREAD, JNIHandles::resolve(pd)); 45 Klass* k = SystemDictionary::resolve_from_stream(class_name, class_loader, 46 protection_domain, &st, 47 verify != 0, 48 CHECK_NULL); 49 50 if (TraceClassResolution && k != NULL) { 51 trace_class_resolution(k); 52 } 53 54 return (jclass) JNIHandles::make_local(env, k->java_mirror()); 55 }
resolve_from_stream 的实现在 SystemDictionary 类中,下面我们看下:
1 Klass* SystemDictionary::resolve_from_stream(Symbol* class_name, 2 Handle class_loader, 3 Handle protection_domain, 4 ClassFileStream* st, 5 bool verify, 6 TRAPS) { 7 8 // Classloaders that support parallelism, e.g. bootstrap classloader, 9 // or all classloaders with UnsyncloadClass do not acquire lock here 10 bool DoObjectLock = true; 11 if (is_parallelCapable(class_loader)) { 12 DoObjectLock = false; 13 } 14 15 ClassLoaderData* loader_data = register_loader(class_loader, CHECK_NULL); 16 17 // Make sure we are synchronized on the class loader before we proceed
18 Handle lockObject = compute_loader_lock_object(class_loader, THREAD); 19 check_loader_lock_contention(lockObject, THREAD); 20 ObjectLocker ol(lockObject, THREAD, DoObjectLock); 21 22 TempNewSymbol parsed_name = NULL; 23 24 // Parse the stream. Note that we do this even though this klass might 25 // already be present in the SystemDictionary, otherwise we would not 26 // throw potential ClassFormatErrors. 27 // 28 // Note: "name" is updated. 29 30 instanceKlassHandle k = ClassFileParser(st).parseClassFile(class_name, 31 loader_data, 32 protection_domain, 33 parsed_name, 34 verify, 35 THREAD); 36 37 const char* pkg = "java/"; 38 size_t pkglen = strlen(pkg); 39 if (!HAS_PENDING_EXCEPTION && 40 !class_loader.is_null() && 41 parsed_name != NULL && 42 parsed_name->utf8_length() >= (int)pkglen && 43 !strncmp((const char*)parsed_name->bytes(), pkg, pkglen)) { 44 // It is illegal to define classes in the "java." package from 45 // JVM_DefineClass or jni_DefineClass unless you're the bootclassloader 46 ResourceMark rm(THREAD); 47 char* name = parsed_name->as_C_string(); 48 char* index = strrchr(name, '/'); 49 assert(index != NULL, "must be"); 50 *index = ''; // chop to just the package name 51 while ((index = strchr(name, '/')) != NULL) { 52 *index = '.'; // replace '/' with '.' in package name 53 } 54 const char* fmt = "Prohibited package name: %s"; 55 size_t len = strlen(fmt) + strlen(name); 56 char* message = NEW_RESOURCE_ARRAY(char, len); 57 jio_snprintf(message, len, fmt, name); 58 Exceptions::_throw_msg(THREAD_AND_LOCATION, 59 vmSymbols::java_lang_SecurityException(), message); 60 } 61 62 if (!HAS_PENDING_EXCEPTION) { 63 assert(parsed_name != NULL, "Sanity"); 64 assert(class_name == NULL || class_name == parsed_name, "name mismatch"); 65 // Verification prevents us from creating names with dots in them, this 66 // asserts that that's the case. 67 assert(is_internal_format(parsed_name), 68 "external class name format used internally"); 69 70 // Add class just loaded 71 // If a class loader supports parallel classloading handle parallel define requests 72 // find_or_define_instance_class may return a different InstanceKlass 73 if (is_parallelCapable(class_loader)) { 74 k = find_or_define_instance_class(class_name, class_loader, k, THREAD); 75 } else { 76 define_instance_class(k, THREAD); 77 } 78 } 79 96 97 return k(); 98 }
上面的方法里,有几处值得注意的:
1:18-20行,进行了加锁,18行获取锁对象,这里是当前类加载器(从注释可以看出),20行就是加锁的语法
2:37-60行,这里是判断要加载的类的包名是否以 java 开头,以 java 开头的类是非法的,不能加载
3:第76行, define_instance_class(k, THREAD); 进行后续操作
接下来,我们看看 define_instance_class 的实现:
1 void SystemDictionary::define_instance_class(instanceKlassHandle k, TRAPS) { 2 3 ClassLoaderData* loader_data = k->class_loader_data(); 4 Handle class_loader_h(THREAD, loader_data->class_loader()); 5 6 for (uintx it = 0; it < GCExpandToAllocateDelayMillis; it++){} 7 8 // for bootstrap and other parallel classloaders don't acquire lock, 9 // use placeholder token 10 // If a parallelCapable class loader calls define_instance_class instead of 11 // find_or_define_instance_class to get here, we have a timing 12 // hole with systemDictionary updates and check_constraints 13 if (!class_loader_h.is_null() && !is_parallelCapable(class_loader_h)) { 14 assert(ObjectSynchronizer::current_thread_holds_lock((JavaThread*)THREAD, 15 compute_loader_lock_object(class_loader_h, THREAD)), 16 "define called without lock"); 17 } 18 19 // Check class-loading constraints. Throw exception if violation is detected. 20 // Grabs and releases SystemDictionary_lock 21 // The check_constraints/find_class call and update_dictionary sequence 22 // must be "atomic" for a specific class/classloader pair so we never 23 // define two different instanceKlasses for that class/classloader pair. 24 // Existing classloaders will call define_instance_class with the 25 // classloader lock held 26 // Parallel classloaders will call find_or_define_instance_class 27 // which will require a token to perform the define class 28 Symbol* name_h = k->name(); 29 unsigned int d_hash = dictionary()->compute_hash(name_h, loader_data); 30 int d_index = dictionary()->hash_to_index(d_hash); 31 check_constraints(d_index, d_hash, k, class_loader_h, true, CHECK); 32 33 // Register class just loaded with class loader (placed in Vector) 34 // Note we do this before updating the dictionary, as this can 35 // fail with an OutOfMemoryError (if it does, we will *not* put this 36 // class in the dictionary and will not update the class hierarchy). 37 // JVMTI FollowReferences needs to find the classes this way. 38 if (k->class_loader() != NULL) { 39 methodHandle m(THREAD, Universe::loader_addClass_method()); 40 JavaValue result(T_VOID); 41 JavaCallArguments args(class_loader_h); 42 args.push_oop(Handle(THREAD, k->java_mirror())); 43 JavaCalls::call(&result, m, &args, CHECK); 44 } 45 46 // Add the new class. We need recompile lock during update of CHA. 47 { 48 unsigned int p_hash = placeholders()->compute_hash(name_h, loader_data); 49 int p_index = placeholders()->hash_to_index(p_hash); 50 51 MutexLocker mu_r(Compile_lock, THREAD); 52 53 // Add to class hierarchy, initialize vtables, and do possible 54 // deoptimizations. 55 add_to_hierarchy(k, CHECK); // No exception, but can block 56 57 // Add to systemDictionary - so other classes can see it. 58 // Grabs and releases SystemDictionary_lock 59 update_dictionary(d_index, d_hash, p_index, p_hash, 60 k, class_loader_h, THREAD); 61 } 62 k->eager_initialize(THREAD); 63 64 // notify jvmti 65 if (JvmtiExport::should_post_class_load()) { 66 assert(THREAD->is_Java_thread(), "thread->is_Java_thread()"); 67 JvmtiExport::post_class_load((JavaThread *) THREAD, k()); 68 69 } 70 71 }
这里,由于我们的案例中,是class A 在初始化过程中出现死锁,所以我们关注第62行,eager_initialize:
1 void InstanceKlass::eager_initialize(Thread *thread) { 2 if (!EagerInitialization) return; 3 4 if (this->is_not_initialized()) { 5 // abort if the the class has a class initializer 6 if (this->class_initializer() != NULL) return; 7 8 // abort if it is java.lang.Object (initialization is handled in genesis) 9 Klass* super = this->super(); 10 if (super == NULL) return; 11 12 // abort if the super class should be initialized 13 if (!InstanceKlass::cast(super)->is_initialized()) return; 14 15 // call body to expose the this pointer 16 instanceKlassHandle this_oop(thread, this); 17 eager_initialize_impl(this_oop); 18 } 19 }
我们接着进入 eager_initialize_impl,该方法进入到了 InstanceKlass:
1 void InstanceKlass::eager_initialize_impl(instanceKlassHandle this_oop) { 2 EXCEPTION_MARK; 3 oop init_lock = this_oop->init_lock(); 4 ObjectLocker ol(init_lock, THREAD, init_lock != NULL); 5 6 // abort if someone beat us to the initialization 7 if (!this_oop->is_not_initialized()) return; // note: not equivalent to is_initialized() 8 9 ClassState old_state = this_oop->init_state(); 10 link_class_impl(this_oop, true, THREAD); 11 if (HAS_PENDING_EXCEPTION) { 12 CLEAR_PENDING_EXCEPTION; 13 // Abort if linking the class throws an exception. 14 15 // Use a test to avoid redundantly resetting the state if there's 16 // no change. Set_init_state() asserts that state changes make 17 // progress, whereas here we might just be spinning in place. 18 if( old_state != this_oop->_init_state ) 19 this_oop->set_init_state (old_state); 20 } else { 21 // linking successfull, mark class as initialized 22 this_oop->set_init_state (fully_initialized); 23 this_oop->fence_and_clear_init_lock(); 24 // trace 25 if (TraceClassInitialization) { 26 ResourceMark rm(THREAD); 27 tty->print_cr("[Initialized %s without side effects]", this_oop->external_name()); 28 } 29 } 30 }
这里,我们重点关注第3,4行:
1、第3行,获取初始化锁;
2、第4行,加锁
2、获取初始化锁并加锁
这里,我们首先获取锁的操作,
1 oop InstanceKlass::init_lock() const { 2 // return the init lock from the mirror 3 oop lock = java_lang_Class::init_lock(java_mirror()); 4 // Prevent reordering with any access of initialization state 5 OrderAccess::loadload(); 6 assert((oop)lock != NULL || !is_not_initialized(), // initialized or in_error state 7 "only fully initialized state can have a null lock"); 8 return lock; 9 }
其中,java_mirror() 方法就是返回 Klass 类中的以下字段:
1 // java/lang/Class instance mirroring this class 2 oop _java_mirror;
再看 init_lock 方法:
1 oop java_lang_Class::init_lock(oop java_class) { 2 assert(_init_lock_offset != 0, "must be set"); 3 return java_class->obj_field(_init_lock_offset); 4 }
这里呢,应该就是获取 我们传入的 java_class 中的某个字段,该字段就是充当 init_lock。(个人水平有限,还请指正)
下面为加锁操作的语句:
1 ObjectLocker ol(init_lock, THREAD, init_lock != NULL);
1 / ObjectLocker enforced balanced locking and can never thrown an 2 // IllegalMonitorStateException. However, a pending exception may 3 // have to pass through, and we must also be able to deal with 4 // asynchronous exceptions. The caller is responsible for checking 5 // the threads pending exception if needed. 6 // doLock was added to support classloading with UnsyncloadClass which 7 // requires flag based choice of locking the classloader lock. 8 class ObjectLocker : public StackObj { 9 private: 10 Thread* _thread; 11 Handle _obj; 12 BasicLock _lock; 13 bool _dolock; // default true 14 public: 15 ObjectLocker(Handle obj, Thread* thread, bool doLock = true);
1 // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 // Internal VM locks on java objects 3 // standard constructor, allows locking failures 4 ObjectLocker::ObjectLocker(Handle obj, Thread* thread, bool doLock) { 5 _dolock = doLock; 6 _thread = thread; 8 _obj = obj; 9 10 if (_dolock) { 11 TEVENT (ObjectLocker) ; 12 13 ObjectSynchronizer::fast_enter(_obj, &_lock, false, _thread); 14 } 15 }
接下来会进入到 synchronizer.cpp,
1 // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 // Fast Monitor Enter/Exit 3 // This the fast monitor enter. The interpreter and compiler use 4 // some assembly copies of this code. Make sure update those code 5 // if the following function is changed. The implementation is 6 // extremely sensitive to race condition. Be careful. 7 8 void ObjectSynchronizer::fast_enter(Handle obj, BasicLock* lock, bool attempt_rebias, TRAPS) { 9 if (UseBiasedLocking) { 10 if (!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint()) { 11 BiasedLocking::Condition cond = BiasedLocking::revoke_and_rebias(obj, attempt_rebias, THREAD); 12 if (cond == BiasedLocking::BIAS_REVOKED_AND_REBIASED) { 13 return; 14 } 15 } else { 16 assert(!attempt_rebias, "can not rebias toward VM thread"); 17 BiasedLocking::revoke_at_safepoint(obj); 18 } 19 assert(!obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern(), "biases should be revoked by now"); 20 } 21 22 slow_enter (obj, lock, THREAD) ; 23 }
上面会判断,是否使用偏向锁,如果不使用,则走 slow_enter 。
1 // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 // Interpreter/Compiler Slow Case 3 // This routine is used to handle interpreter/compiler slow case 4 // We don't need to use fast path here, because it must have been 5 // failed in the interpreter/compiler code. 6 void ObjectSynchronizer::slow_enter(Handle obj, BasicLock* lock, TRAPS) { 7 markOop mark = obj->mark(); 8 assert(!mark->has_bias_pattern(), "should not see bias pattern here"); 9 10 if (mark->is_neutral()) { 11 // Anticipate successful CAS -- the ST of the displaced mark must 12 // be visible <= the ST performed by the CAS. 13 lock->set_displaced_header(mark); 14 if (mark == (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(lock, obj()->mark_addr(), mark)) { 15 TEVENT (slow_enter: release stacklock) ; 16 return ; 17 } 18 // Fall through to inflate() ... 19 } else 20 if (mark->has_locker() && THREAD->is_lock_owned((address)mark->locker())) { 21 assert(lock != mark->locker(), "must not re-lock the same lock"); 22 assert(lock != (BasicLock*)obj->mark(), "don't relock with same BasicLock"); 23 lock->set_displaced_header(NULL); 24 return; 25 } 26 34 35 // The object header will never be displaced to this lock, 36 // so it does not matter what the value is, except that it 37 // must be non-zero to avoid looking like a re-entrant lock, 38 // and must not look locked either. 39 lock->set_displaced_header(markOopDesc::unused_mark()); 40 ObjectSynchronizer::inflate(THREAD, obj())->enter(THREAD); 41 }
这里的代码结合注释,能大概看出来是,前面部分为轻量级锁,这里先不展开了,锁这块都可以单独写了。有兴趣的读者可以自行阅读。
四、总结
这里再说下结论吧,类初始化的过程,会对class加锁,再执行class的初始化,如果这时候发生了循环依赖,就会导致死锁。
如果有读者对上面的c++代码感兴趣,可以参考下面的文章,搭建调试环境:
源码编译OpenJdk 8,Netbeans调试Java原子类在JVM中的实现(Ubuntu 16.04)
