vue-cli2、vue-cli3脚手架详细讲解
- 2019 年 10 月 29 日
- 筆記
前言:
vue脚手架指的是vue-cli它是vue官方提供的一个快速构建单页面(SPA)环境配置的工具,cli 就是(command-line-interface ) 命令行界面 。vue-cli是基于node环境利用webpack对文件进行编译、打包、压缩、es6转es5等一系列操作。目前vue-cli已经升级到了3.0版本,3.0所需的webpack版本是4.xxx,2.0版本目前也很流行,2.0所需的webpack版本是3.xxx,我们来讲讲两者的配置:
Vue2.0:
一.安装node.js环境:
去node官网下载node.js并安装(http://nodejs.cn/download/)。安装完成后可以在终端执行 node -v查看node 是否安装成功,下图是安装成功的提示,显示出当前安装的node的版本号。

二.全局安装webpack:
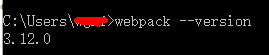
为了在其他任何目录下都能使用到webpack,进行全局安装,执行npm install webpack@3.12.0 -g 命令,npm 是Node集成的工具 npm install 是从github上下载webpack最新的包,“@3.12.0”表示安装指定的版本,因为现在已经升级到了4.0版本,如果不指定版本版本号就会安装最新的版本,同时vue-cli2需要的是3.xxx的版本,所以我们指定了一个固定版本,如果不指定则不需要,”-g” 全称是 ” global (全局) ” 表示全局安装。检查是否安装成功终端执行“webpack -v”或者”webpack –version”,如果显示具体的版本号则表示安装成功。
三.全局安装 vue-cli2:
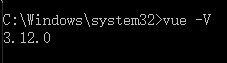
执行“npm install @vue/cli -g”命令进行安装。“npm install @vue/cli -g” 命令是脚手架3的,“npm install vue-cli -g”命令才是脚手架3的,脚手架2和脚手架3是不相同的,如果现在使用 “npm install vue-cli -g”命令进行安装的话,下次使用脚手架3的时候就得卸载脚手架2,安装脚手架3,为了减少不必要的操作我们执行 “npm install @vue/cli -g ” 命令进行安装,然后再执行 “npm install @vue-cli-init -g ” 将脚手架2下载下来,在此环境下既可以安装脚手架2的模板,有可以安装脚手架3的模板。 检查是否安装成功终端执行“vue -V”或者”vue –version”,如果显示具体的版本号则表示安装成功。具体安装方式查看官网(https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/)。
四.初始化项目:
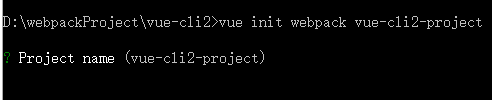
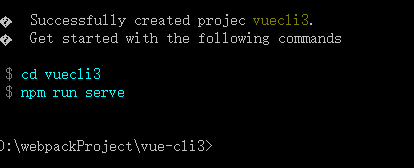
进入到自己要安装项目的文件夹目录,我这里是 “D:webpackProjectvue-cli2> ” 执行 “vue init webpack vue-cli2-project ” 命令,出现如下图提示 ,“vue-cli2-project” 是我们的项目文件夹的名字,就是最终显示在index.html中的title标签里和package.json中的,也可以自己进行修改,我们一般不会去改,直接按回车键进行下一步。
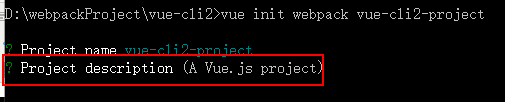
“? Project description (A Vue.js project)” 是项目的描述,自己可以修改或者使用默认的,我们一般使用默认的直接按回车键进行下一步,
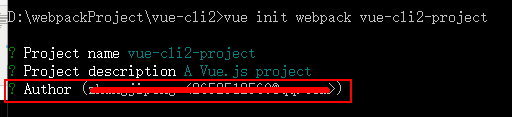
这里是作者的信息,我们使用默认的,直接下一步,
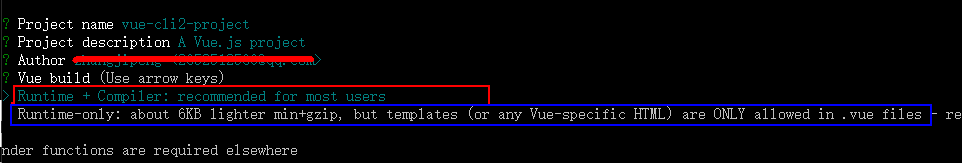
这里有两个选项:Runtime + Compiler 和Runtime-only ,Runtime-only要比Runtime + Compiler 轻大约6KB,而且效率要高, 按上下键可以进行选择,默认是第一个,选择好后按回车键进行下一步,
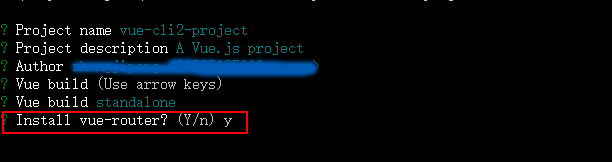
这一步是询问是否使用vue-router(路由),因为在项目中我们会用到所以这里按Y 键,进行下一步,
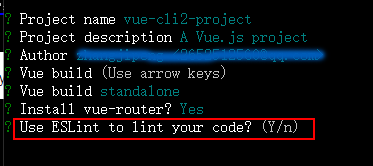
这一步是询问是否使用ESLint(语法检查器),ES (ecscript) 即 javascript ,lint 限制的意思,也就是 javascript语法限制器,使得你的语法更加规范,如果你的语法不规范编辑器就会报错,你可能在开发过程中因为一个空格导致语法不规范进而报错(其实你的代码没有问题的),所以对于初学者不建议使用此语法,所以我们选择 n,并进行下一步操作,

这一步是询问是否使用单元测试,这个用的人比较少,所以我们不适用,输入n并进行一下步,
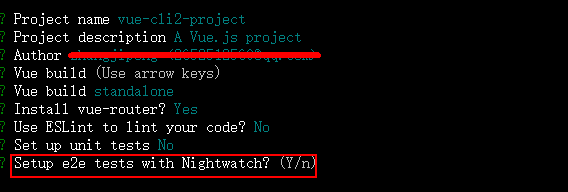
这一步询问是否要进行e2e(端到端测试),是一个自动化测试的框架,这里我们就不使用了,直接输入n,进行下一步:
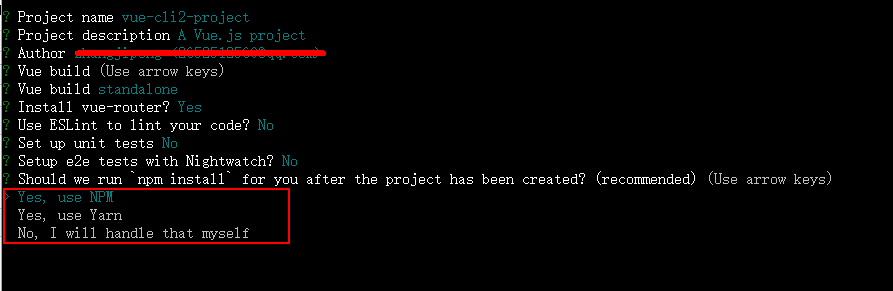
这里询问我们管理项目是用npm 还是yarn ,这里我们使用npm ,直接回车,接下来就是等待安装node_modules。下图表示安装完成:
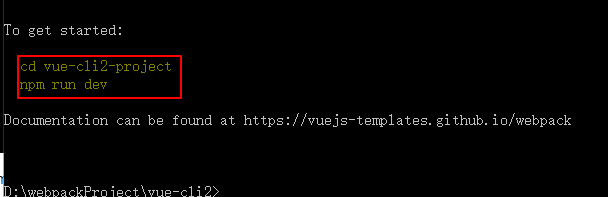
执行 cd vue-cli2-project 进入到我们的项目目录下,然后执行 npm run dev 命令进行启动我们的项目,下图是我们的项目目录:
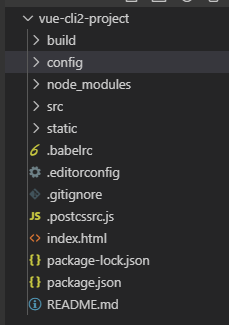
五、 项目目录介绍:
1、build 文件夹:webpack的一些相关配置;
2、config 文件夹:项目开发环境和生产环境的一些相关配置;
3、node_modules 文件夹 :这里存放的是安装包,比如webpack、第三方插件库、项目的依赖文件;
4、src 文件夹:我们将要写的代码放在这里面,打包上线时会进行编译、压缩等操作。
5、static 文件夹:这里存放的是一些静态文件比如图片、css文件、不需要进行压缩的js文件,打包时这个文件夹将原封不动的放到dist(打包时自动生产的文件夹)文件夹下面。
6、.babelrc 文件:ES6语法编译配置,主要是将ES 转成ES 需要适配那些浏览器
7、.editorconfig 文件:定义代码格式,对代码的风格进行一个统一。
8、.gitignore 文件:git上传需要忽略的文件格式
9、 .postcssrc.js 文件:postcss配置文件
10、 index.html 文件:要进行访问的首页面
11、package-lock.json 文件:锁定依赖模块和子模块的版本号
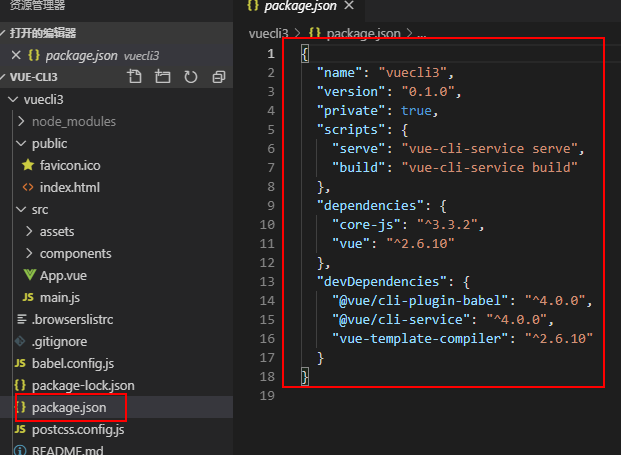
12、package.json 文件:项目基本信息,包依赖信息等
13、README.md 文件:项目说明文件
文件详解:
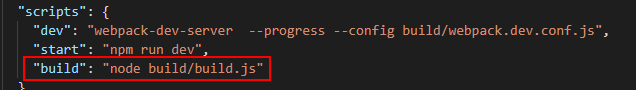
1、package.json 文件:当我们在命令行时 npm run dev 的时候程序执行的是package.json文件的“script”脚本里的“dev”命令;
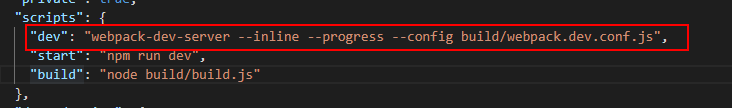
这段代码的意思是启动 “webpack-dev-server” 服务器,“–inline” 是 重新加载改变的部分,不会刷新页面,–progress是启动项目时显示进度,“–config build/webpack.dev.conf.js” 是执行build下面的webpack.dev.conf.js配置文件。我们可以添加其他属性比如 “–open” 是启动项目后自动在浏览器打开项目,其它配置可以查看相关文档(https://www.webpackjs.com/configuration/dev-server/#devserver)。“start” 和“dev”的作用是一样的,“build” 的作用是执行 build下的build.js文件,将当前的项目进行打包。打包后生成一个dist文件夹,放在其里面。webpack.dev.conf.js文件是我们在开发环境下的webpack配置文件,打开次文件,内容如下:
2.、build/webpack.dev.conf.js 文件:
1 'use strict' 2 const utils = require('./utils') //引入的工具包 3 const webpack = require('webpack') //引入webpack包 4 const config = require('../config') //引入 config下的index.js文件 5 const merge = require('webpack-merge') //合并配置文件 6 const path = require('path') //node的path模块,对路径进行处理 7 const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf') //将生产和开发环境下共用的配置文件进行了抽离形成了改文件 8 const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin') //拷贝插件 9 const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin') //加载html模块 10 const FriendlyErrorsPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin') //友好的错误提示插件 11 const portfinder = require('portfinder') //在当前机器上找一个可打开的端口号,默认是8080,如果端口号被占用则重新寻找可打开的端口号。 12 13 const HOST = process.env.HOST 14 const PORT = process.env.PORT && Number(process.env.PORT) 15 16 const devWebpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, { //利用merge插件将 baseWebpackConfig 配置与当前配置进行合并 17 module: { 18 rules: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.dev.cssSourceMap, usePostCSS: true }) //引入utils中一些css-loader和postcss-loader 19 }, 20 21 devtool: config.dev.devtool, //控制是否生成以及如何生成源码映射,这里引入的是config下的index.js的 “devtool: 'cheap-module-eval-source-map'”, 22 23 // these devServer options should be customized in /config/index.js 24 // dev-server的配置 25 devServer: { 26 clientLogLevel: 'warning', //当使用inline mode,devTools的命令行中将会显示一些调试信息 27 historyApiFallback: { //当使用 HTML5 History API 时,任意的 404 响应都可能需要被替代为 index.html 28 rewrites: [ 29 { from: /.*/, to: path.posix.join(config.dev.assetsPublicPath, 'index.html') }, 30 ], 31 }, 32 hot: true, //启用 webpack 的模块热替换特性 33 contentBase: false, // since we use CopyWebpackPlugin. 34 compress: true, 35 host: HOST || config.dev.host, //要开启的域名,可在package.json中的“dev”命令中进行配置 36 port: PORT || config.dev.port, //要开启的端口号,可在package.json中的“dev”命令中进行配置 37 open: config.dev.autoOpenBrowser,//是否自动在浏览器中打开,可在package.json中的“dev”命令中进行配置 38 overlay: config.dev.errorOverlay 39 ? { warnings: false, errors: true } 40 : false, 41 publicPath: config.dev.assetsPublicPath, // 42 proxy: config.dev.proxyTable, //当出现跨域时设置代理,这里引入了config下的index.js的配置 43 quiet: true, // necessary for FriendlyErrorsPlugin 启用 quiet 后,除了初始启动信息之外的任何内容都不会被打印到控制台。这也意味着来自 webpack 的错误或警告在控制台不可见 44 watchOptions: { 45 poll: config.dev.poll, 46 } 47 }, 48 plugins: [ //插件部分 49 new webpack.DefinePlugin({ //配置全局变量 50 'process.env': require('../config/dev.env') 51 }), 52 new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(), // 模块热替换它允许在运行时更新各种模块,而无需进行完全刷新 53 new webpack.NamedModulesPlugin(), // HMR shows correct file names in console on update. 54 new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin(), // 这个插件的作用是在热加载时直接返回更新文件名,而不是文件的id。 55 // https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin 56 new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ //打包时生成index.html并且自动加载app.js文件 <!-- built files will be auto injected --> 57 filename: 'index.html', 58 template: 'index.html', 59 inject: true 60 }), 61 // copy custom static assets 62 new CopyWebpackPlugin([ 63 { 64 from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'), //将static整个文件夹原封不动地拷贝到dist目录下。 65 to: config.dev.assetsSubDirectory, 66 ignore: ['.*'] 67 } 68 ]) 69 ] 70 }) 71 72 module.exports = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { 73 portfinder.basePort = process.env.PORT || config.dev.port //获取当前的端口号 74 portfinder.getPort((err, port) => { 75 if (err) { 76 reject(err) 77 } else { 78 // publish the new Port, necessary for e2e tests 79 process.env.PORT = port 80 // add port to devServer config 81 devWebpackConfig.devServer.port = port 82 83 // Add FriendlyErrorsPlugin 84 devWebpackConfig.plugins.push(new FriendlyErrorsPlugin({ 85 compilationSuccessInfo: { 86 messages: [`Your application is running here: http://${devWebpackConfig.devServer.host}:${port}`], 87 }, 88 onErrors: config.dev.notifyOnErrors 89 ? utils.createNotifierCallback() 90 : undefined 91 })) 92 93 resolve(devWebpackConfig) 94 } 95 }) 96 })
本文件 的核心就是将webpack.base.conf.js的配置(公共配置)与本文件配置进行合并,再看一下 webpack.base.conf.js 文件:
3、build/webpack.base.conf.js 文件
1 'use strict' 2 const path = require('path') //node的path模块,对路径进行处理 3 const utils = require('./utils') //引入的工具包 4 const config = require('../config')//引入 config下的index.js文件 5 const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf') //根据NODE_ENV这个变量分析是否是生产环境,然后根据不同的环境来加载,判断是否开启了sourceMap的功能 6 7 function resolve (dir) { 8 return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir) //对路径进行处理,获取到绝对路径 9 } 10 11 12 13 module.exports = { 14 context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'), //对路径进行处理,跳到当前项目的根目录下 15 entry: { //入口文件,即项目要引入哪个js文件 16 app: './src/main.js' //因为 context 中已经跳到了当前项目的根目录下,所以这里的路径是以 ./src 开头 17 }, 18 output: { //输出文件,即项目要输出到哪里去 19 path: config.build.assetsRoot, //输出到根目录下的dist问价夹里,具体地址可以在config下的index.js中进行修改 20 filename: '[name].js', //以文件的原始名输出 21 publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' //根据process.env.NODE_ENV 来判断是生产模式还是开发模式,将最终打包的项目要放到服务器的什么地方,默认是 '/' 即服务器的根目录下。 22 ? config.build.assetsPublicPath 23 : config.dev.assetsPublicPath 24 }, 25 resolve: { 26 extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'], //简化一些文件名,引入文件时可以不带后缀名 27 alias: { 28 'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js', 29 '@': resolve('src'), //简化文件的引入问题,如:本文件中要引入 src下的common里的demo.js,你就可以这样引入:@/common/demo.js 30 } 31 }, 32 module: { 33 34 rules: [ 35 // 配置各种loader,来处理对应的文件 36 { 37 test: /.vue$/, //使用vue-loader处理以.vue结束的文件 38 loader: 'vue-loader', 39 options: vueLoaderConfig 40 }, 41 { 42 test: /.js$/, //使用babel-loader处理以.js结束的文件,即js文件 43 loader: 'babel-loader', 44 include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')] 45 }, 46 { 47 test: /.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(?.*)?$/, //使用url-loader处理各种格式的图片资源,最大限制10000KB,这里不处理src同级目录下的static里的图片。 48 loader: 'url-loader', 49 options: { 50 limit: 10000, 51 name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]') //将处理后的放在img文件下,并且加上7位hash值。 52 } 53 }, 54 { 55 test: /.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(?.*)?$/, //使用url-loader处理视频文件。 56 loader: 'url-loader', 57 options: { 58 limit: 10000, 59 name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]') 60 } 61 }, 62 { 63 test: /.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(?.*)?$/, //使用url-loader处理字体文件。 64 loader: 'url-loader', 65 options: { 66 limit: 10000, 67 name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]') 68 } 69 } 70 ] 71 }, 72 node: { 73 // prevent webpack from injecting useless setImmediate polyfill because Vue 74 // source contains it (although only uses it if it's native). 75 setImmediate: false, 76 // prevent webpack from injecting mocks to Node native modules 77 // that does not make sense for the client 78 dgram: 'empty', 79 fs: 'empty', 80 net: 'empty', 81 tls: 'empty', 82 child_process: 'empty' 83 } 84 }
主要的说明已经注释在了文件中,这个问价的主要配置有entry(入口文件)、output(输出文件)、loader ,这些都是必备的,而一些plugins(插件)已经在对应的环境文件(webpack.dev.config.js、webpack.prod.config.js)中进行了配置,再看一下webpack.prod.config.js文件:
4、build/webpack.prod.config.js:
1 'use strict' 2 const path = require('path') 3 const utils = require('./utils') 4 const webpack = require('webpack') 5 const config = require('../config') 6 const merge = require('webpack-merge') 7 const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf') 8 const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin') 9 const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin') 10 const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin') //抽离css样式,防止将样式打包在js中引起页面样式加载错乱的现象 11 const OptimizeCSSPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin')//主要是用来压缩css文件 12 const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin') //对js文件进行压缩 13 14 const env = require('../config/prod.env') 15 16 const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, { 17 module: { 18 rules: utils.styleLoaders({ 19 sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap, 20 extract: true, 21 usePostCSS: true 22 }) 23 }, 24 devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? config.build.devtool : false, 25 output: { 26 path: config.build.assetsRoot, 27 filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'), 28 chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js') 29 }, 30 plugins: [ 31 // http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html 32 new webpack.DefinePlugin({ 33 'process.env': env 34 }), 35 new UglifyJsPlugin({ 36 uglifyOptions: { //配置项 37 compress: { 38 warnings: false 39 } 40 }, 41 sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap, //使用sourceMap将错误消息位置映射到模块(这会减慢编译速度)。 42 parallel: true //启用/禁用多进程并行运行,启用后会提高构建速度 43 }), 44 45 new ExtractTextPlugin({ 46 filename: utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css'), 47 48 allChunks: true, 49 }), 50 // Compress extracted CSS. We are using this plugin so that possible 51 // duplicated CSS from different components can be deduped. 52 new OptimizeCSSPlugin({ 53 cssProcessorOptions: config.build.productionSourceMap 54 ? { safe: true, map: { inline: false } } //判断是否生成内联映射,如果生成则会生成一个source-map文件 55 : { safe: true } 56 }), 57 // generate dist index.html with correct asset hash for caching. 58 // you can customize output by editing /index.html 59 // see https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin 60 new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ 61 filename: config.build.index, //将会生成一个index.html文件,放到dist文件下 62 template: 'index.html', 63 inject: true, //将所有js资源放在body标签的底部 64 minify: { //控制是否进行压缩 65 removeComments: true, //删除所有的注释 66 collapseWhitespace: true, //折叠构成文档树中文本节点的空白 67 removeAttributeQuotes: true //尽可能删除属性周围的引号 68 // more options: 69 // https://github.com/kangax/html-minifier#options-quick-reference 70 }, 71 // necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin 72 chunksSortMode: 'dependency' //允许控制块在包含到HTML之前按照依赖排序 73 }), 74 // keep module.id stable when vendor modules does not change 75 new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin(), //该插件会根据模块的相对路径生成一个四位数的hash作为模块id, 建议用于生产环境。 76 // enable scope hoisting 77 new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),//启用作用域提升,让代码文件更小、运行的更快 78 // split vendor js into its own file 79 new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ //主要是用来提取第三方库和公共模块,避免首屏加载的bundle文件或者按需加载的bundle文件体积过大,从而导致加载时间过长 80 name: 'vendor', 81 minChunks (module) { 82 // any required modules inside node_modules are extracted to vendor 83 return ( 84 module.resource && 85 /.js$/.test(module.resource) && 86 module.resource.indexOf( 87 path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules') 88 ) === 0 89 ) 90 } 91 }), 92 // extract webpack runtime and module manifest to its own file in order to 93 // prevent vendor hash from being updated whenever app bundle is updated 94 new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ 95 name: 'manifest', 96 minChunks: Infinity 97 }), 98 // This instance extracts shared chunks from code splitted chunks and bundles them 99 // in a separate chunk, similar to the vendor chunk 100 // see: https://webpack.js.org/plugins/commons-chunk-plugin/#extra-async-commons-chunk 101 new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({ 102 name: 'app', 103 async: 'vendor-async', 104 children: true, 105 minChunks: 3 106 }), 107 108 // copy custom static assets 109 new CopyWebpackPlugin([ //复制模块 110 { 111 from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'), 112 to: config.build.assetsSubDirectory, 113 ignore: ['.*'] 114 } 115 ]) 116 ] 117 }) 118 119 if (config.build.productionGzip) { 120 const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin') 121 122 webpackConfig.plugins.push( 123 new CompressionWebpackPlugin({ 124 asset: '[path].gz[query]', 125 algorithm: 'gzip', 126 test: new RegExp( 127 '\.(' + 128 config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') + 129 ')$' 130 ), 131 threshold: 10240, 132 minRatio: 0.8 133 }) 134 ) 135 } 136 137 if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) { 138 const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin 139 webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin()) 140 } 141 142 module.exports = webpackConfig
当我们执行 npm run build 打包时执行的是: build下的build.js文件,build.js中引入了webpack.prod.config.js,因此build.js才是生产环境所需的webpack文件。
5、build/build.js:
1 'use strict' 2 require('./check-versions')() //该文件用于检测node和npm的版本,实现版本依赖 3 4 process.env.NODE_ENV = 'production' 5 6 const ora = require('ora') //在node端加载动画模块 7 const rm = require('rimraf') //用来删除文件和文件夹的 8 const path = require('path') 9 const chalk = require('chalk') //修改控制台中字符串的样式 10 const webpack = require('webpack') 11 const config = require('../config') 12 const webpackConfig = require('./webpack.prod.conf') 13 14 const spinner = ora('building for production...') //设置一个动画的内容为 "building for production..." 15 spinner.start() //加载动画 16 17 rm(path.join(config.build.assetsRoot, config.build.assetsSubDirectory), err => { //利用 rm 模块先删除dist文件再生成新文件,因为有时候会使用hash来命名,删除整个文件可避免冗余 18 if (err) throw err 19 webpack(webpackConfig, (err, stats) => { //将一下配置内容与 webpack.prod.conf.js中的配置进行合并 20 spinner.stop() //停止动画 21 if (err) throw err 22 process.stdout.write(stats.toString({ 23 colors: true, 24 modules: false, 25 children: false, // If you are using ts-loader, setting this to true will make TypeScript errors show up during build. 26 chunks: false, 27 chunkModules: false 28 }) + 'nn') 29 30 if (stats.hasErrors()) { 31 console.log(chalk.red(' Build failed with errors.n')) 32 process.exit(1) 33 } 34 35 console.log(chalk.cyan(' Build complete.n')) 36 console.log(chalk.yellow( 37 ' Tip: built files are meant to be served over an HTTP server.n' + 38 ' Opening index.html over file:// won't work.n' 39 )) 40 }) 41 })
6、build/check-versions.js: 检测node和npm的版本,实现版本依赖
1 'use strict' 2 // 该文件用于检测node和npm的版本,实现版本依赖 3 const chalk = require('chalk') //node.js中的模块,作用是修改控制台中字符串的样式 4 const semver = require('semver') //node.js中的模块,对版本进行检查 5 const packageConfig = require('../package.json') //引入page.json文件 6 const shell = require('shelljs') 7 8 function exec (cmd) { 9 //通过child_process模块的新建子进程,执行 Unix 系统命令后转成没有空格的字符串 10 return require('child_process').execSync(cmd).toString().trim() 11 } 12 13 const versionRequirements = [ 14 { 15 name: 'node', 16 currentVersion: semver.clean(process.version), //使用semver格式化版本 17 versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.node //获取package.json中设置的node版本 18 } 19 ] 20 21 if (shell.which('npm')) { 22 versionRequirements.push({ 23 name: 'npm', 24 currentVersion: exec('npm --version'), //自动调用npm --version命令,并且把参数返回给exec函数,从而获取纯净的版本号 25 versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.npm 26 }) 27 } 28 29 module.exports = function () { 30 const warnings = [] 31 32 for (let i = 0; i < versionRequirements.length; i++) { 33 const mod = versionRequirements[i] 34 35 if (!semver.satisfies(mod.currentVersion, mod.versionRequirement)) { 36 //如果上面的版本号不符合package.json文件中指定的版本号,就执行下面错误提示的代码 37 warnings.push(mod.name + ': ' + 38 chalk.red(mod.currentVersion) + ' should be ' + 39 chalk.green(mod.versionRequirement) 40 ) 41 } 42 } 43 44 if (warnings.length) { 45 console.log('') 46 console.log(chalk.yellow('To use this template, you must update following to modules:')) 47 console.log() 48 49 for (let i = 0; i < warnings.length; i++) { 50 const warning = warnings[i] 51 console.log(' ' + warning) 52 } 53 54 console.log() 55 process.exit(1) 56 } 57 }
7、build/vue-loader.conf.js:
1 'use strict' 2 3 //根据NODE_ENV这个变量分析是否是生产环境,然后根据不同的环境来加载,判断是否开启了sourceMap的功能。方便之后在cssLoaders中加上sourceMap功能。然后判断是否设置了cacheBusting属性, 4 // 它指的是缓存破坏,特别是进行sourceMap debug时,设置成false是非常有帮助的。最后就是一个转化请求的内容,video、source、img、image等的属性进行配置。具体的还是需要去了解vue-loader这个 5 // webpack的loader加载器 6 7 const utils = require('./utils') 8 const config = require('../config') 9 const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' 10 const sourceMapEnabled = isProduction 11 ? config.build.productionSourceMap 12 : config.dev.cssSourceMap 13 //处理项目中的css文件,生产环境和测试环境默认是打开sourceMap,而extract中的提取样式到单独文件只有在生产环境中才需要 14 module.exports = { 15 loaders: utils.cssLoaders({ 16 sourceMap: sourceMapEnabled, 17 extract: isProduction 18 }), 19 cssSourceMap: sourceMapEnabled, 20 cacheBusting: config.dev.cacheBusting, 21 transformToRequire: {//在模版编译过程中,编译器可以将某些属性,如 src 路径,转换为require调用,以便目标资源可以由 webpack 处理. 22 video: ['src', 'poster'], 23 source: 'src', 24 img: 'src', 25 image: 'xlink:href' 26 } 27 }
8、build/utils:
1 'use strict' 2 const path = require('path') 3 const config = require('../config') 4 const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin') ////抽离css样式,防止将样式打包在js中引起页面样式加载错乱的现象 5 const packageConfig = require('../package.json') 6 7 8 //导出文件的位置,根据环境判断开发环境和生产环境,为config文件中index.js文件中定义的build.assetsSubDirectory或 9 exports.assetsPath = function (_path) { 10 const assetsSubDirectory = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' 11 ? config.build.assetsSubDirectory 12 : config.dev.assetsSubDirectory 13 14 return path.posix.join(assetsSubDirectory, _path) 15 } 16 17 //使用了css-loader和postcssLoader,通过options.usePostCSS属性来判断是否使用postcssLoader中压缩等方法 18 exports.cssLoaders = function (options) { //导出css-loader 19 options = options || {} 20 21 const cssLoader = { 22 loader: 'css-loader', 23 options: { 24 sourceMap: options.sourceMap 25 } 26 } 27 28 const postcssLoader = { 29 loader: 'postcss-loader', 30 options: { 31 sourceMap: options.sourceMap 32 } 33 } 34 35 // generate loader string to be used with extract text plugin 36 function generateLoaders (loader, loaderOptions) { 37 const loaders = options.usePostCSS ? [cssLoader, postcssLoader] : [cssLoader] //根据传入的参数判断是使用cssLoader、 postcssLoader还是只使用 cssLoader 38 39 if (loader) { 40 loaders.push({ 41 loader: loader + '-loader', 42 options: Object.assign({}, loaderOptions, { //将后面的两个对象合并后再进行复制 43 sourceMap: options.sourceMap 44 }) 45 }) 46 } 47 48 // Extract CSS when that option is specified 49 // (which is the case during production build) 50 if (options.extract) { 51 return ExtractTextPlugin.extract({ 52 use: loaders, 53 fallback: 'vue-style-loader' 54 }) 55 } else { 56 return ['vue-style-loader'].concat(loaders) 57 } 58 } 59 60 // https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/configurations/extract-css.html 61 return { 62 css: generateLoaders(), 63 postcss: generateLoaders(), 64 less: generateLoaders('less'), 65 sass: generateLoaders('sass', { indentedSyntax: true }), 66 scss: generateLoaders('sass'), 67 stylus: generateLoaders('stylus'), 68 styl: generateLoaders('stylus') 69 } 70 } 71 72 // Generate loaders for standalone style files (outside of .vue) 73 exports.styleLoaders = function (options) { 74 const output = [] 75 const loaders = exports.cssLoaders(options) 76 77 for (const extension in loaders) { 78 const loader = loaders[extension] 79 output.push({ 80 test: new RegExp('\.' + extension + '$'), 81 use: loader 82 }) 83 } 84 85 return output 86 } 87 88 exports.createNotifierCallback = () => { 89 const notifier = require('node-notifier') 90 91 return (severity, errors) => { 92 if (severity !== 'error') return 93 94 const error = errors[0] 95 const filename = error.file && error.file.split('!').pop() 96 97 notifier.notify({ 98 title: packageConfig.name, 99 message: severity + ': ' + error.name, 100 subtitle: filename || '', 101 icon: path.join(__dirname, 'logo.png') 102 }) 103 } 104 }
9、config/index.js: 生产 和 开发 环境下webpack的公共配置文件
1 const path = require('path') 2 3 module.exports = { 4 dev: { //开发环境下的配置 5 6 // Paths 7 assetsSubDirectory: 'static', //子目录,一般存放css,js,image等文件 8 assetsPublicPath: '/', //根目录 9 proxyTable: {}, //在这里使用代理解决跨越问题 10 11 // Various Dev Server settings 12 host: 'localhost', // 域名 13 port: 8080, // 开启的端口号,默认是8080 14 autoOpenBrowser: true, //是否自动打开浏览器 15 errorOverlay: true, //浏览器错误提示 16 notifyOnErrors: true, //跨平台错误提示 17 poll: false, // 使用文件系统(file system)获取文件改动的通知devServer.watchOptions 18 19 20 /** 21 * Source Maps 22 */ 23 24 // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#development 25 devtool: 'cheap-module-eval-source-map',//增加调试,该属性为原始源代码(仅限行)不可在生产环境中使用 26 27 cacheBusting: true,//使缓存失效 28 29 cssSourceMap: true //代码压缩后进行调bug定位将非常困难,于是引入sourcemap记录压缩前后的位置信息记录,当产生错误时直接定位到未压缩前的位置,将大大的方便我们调试 30 }, 31 32 build: { //生产发环境下的配置 33 // Template for index.html 34 index: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist/index.html'), //index.html编译后生成的位置和名字 35 36 // Paths 37 assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist'),//编译后存放生成环境代码的位置 38 assetsSubDirectory: 'static', //js,css,images存放文件夹名 39 assetsPublicPath: '/', //发布的根目录,通常本地打包dist后打开文件会报错,此处修改为./。如果是上线的文件,可根据文件存放位置进行更改路径 40 41 productionSourceMap: true, 42 43 devtool: '#source-map', 44 45 productionGzip: false, 46 productionGzipExtensions: ['js', 'css'], 47 48 bundleAnalyzerReport: process.env.npm_config_report 49 } 50 }
10、config/dev.env.js:
1 'use strict' 2 // 当在开发环境下引用(webpack.dev.config.js中的plugin中)的是此文件,次文件指定了 开发模式: node-env , 3 //利用merge方法将prod.env.js与本文件进行合并,在开发模式下输出 NODE_ENV="development" 4 5 //webpack.dev.config.js中的plugin引用如下: 6 // new webpack.DefinePlugin({ 7 // 'process.env': require('../config/dev.env') 8 // }) 9 const merge = require('webpack-merge') 10 const prodEnv = require('./prod.env') 11 module.exports = merge(prodEnv, { 12 NODE_ENV: '"development"' 13 })
11、config/prod.env.js:
1 'use strict' 2 // 在生产模式下调用此文件 3 // 在webpack.prod.config.js中的plugin中引用如下: 4 //const env = require('../config/prod.env') 5 // new webpack.DefinePlugin({ 6 // 'process.env': env 7 // }), 8 module.exports = { 9 NODE_ENV: '"production"' 10 }
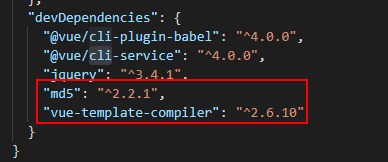
12 、node_modules文件夹:该文件夹下存放的是node的一些依赖模块,比如:require模块、path模块、http-proxy-middleware模块,还有一些我们通过npm安装的插件模块,比如vue、md5、vue-cli、ivew等。
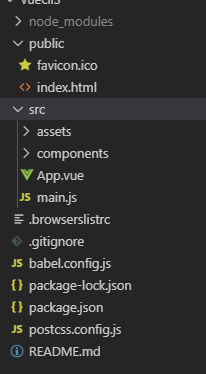
13.、src文件夹: 该文件夹下面存放的是我们项目代码以及一些文件,components文件夹存放了我们自己写的组件,router文件夹里面存放了路由配置,mian.js是整个项目的入口js,在build文件夹下的webpack.dev.config.js中的entry中有配置(


1 const fs = require('fs') 2 const path = require('path') 3 const debug = require('debug') 4 const chalk = require('chalk') 5 const readPkg = require('read-pkg') 6 const merge = require('webpack-merge') 7 const Config = require('webpack-chain') 8 const PluginAPI = require('./PluginAPI') 9 const dotenv = require('dotenv') 10 const dotenvExpand = require('dotenv-expand') 11 const defaultsDeep = require('lodash.defaultsdeep') 12 const { warn, error, isPlugin, resolvePluginId, loadModule } = require('@vue/cli-shared-utils') 13 14 const { defaults, validate } = require('./options') 15 16 module.exports = class Service { 17 constructor (context, { plugins, pkg, inlineOptions, useBuiltIn } = {}) { 18 process.VUE_CLI_SERVICE = this 19 this.initialized = false 20 this.context = context 21 this.inlineOptions = inlineOptions 22 this.webpackChainFns = [] 23 this.webpackRawConfigFns = [] 24 this.devServerConfigFns = [] 25 this.commands = {} 26 // Folder containing the target package.json for plugins 27 this.pkgContext = context 28 // package.json containing the plugins 29 this.pkg = this.resolvePkg(pkg) 30 // If there are inline plugins, they will be used instead of those 31 // found in package.json. 32 // When useBuiltIn === false, built-in plugins are disabled. This is mostly 33 // for testing. 34 this.plugins = this.resolvePlugins(plugins, useBuiltIn) 35 // pluginsToSkip will be populated during run() 36 this.pluginsToSkip = new Set() 37 // resolve the default mode to use for each command 38 // this is provided by plugins as module.exports.defaultModes 39 // so we can get the information without actually applying the plugin. 40 this.modes = this.plugins.reduce((modes, { apply: { defaultModes }}) => { 41 return Object.assign(modes, defaultModes) 42 }, {}) 43 } 44 45 resolvePkg (inlinePkg, context = this.context) { 46 if (inlinePkg) { 47 return inlinePkg 48 } else if (fs.existsSync(path.join(context, 'package.json'))) { 49 const pkg = readPkg.sync({ cwd: context }) 50 if (pkg.vuePlugins && pkg.vuePlugins.resolveFrom) { 51 this.pkgContext = path.resolve(context, pkg.vuePlugins.resolveFrom) 52 return this.resolvePkg(null, this.pkgContext) 53 } 54 return pkg 55 } else { 56 return {} 57 } 58 } 59 60 init (mode = process.env.VUE_CLI_MODE) { 61 if (this.initialized) { 62 return 63 } 64 this.initialized = true 65 this.mode = mode 66 67 // load mode .env 68 if (mode) { 69 this.loadEnv(mode) 70 } 71 // load base .env 72 this.loadEnv() 73 74 // load user config 75 const userOptions = this.loadUserOptions() 76 this.projectOptions = defaultsDeep(userOptions, defaults()) 77 78 debug('vue:project-config')(this.projectOptions) 79 80 // apply plugins. 81 this.plugins.forEach(({ id, apply }) => { 82 if (this.pluginsToSkip.has(id)) return 83 apply(new PluginAPI(id, this), this.projectOptions) 84 }) 85 86 // apply webpack configs from project config file 87 if (this.projectOptions.chainWebpack) { 88 this.webpackChainFns.push(this.projectOptions.chainWebpack) 89 } 90 if (this.projectOptions.configureWebpack) { 91 this.webpackRawConfigFns.push(this.projectOptions.configureWebpack) 92 } 93 } 94 95 loadEnv (mode) { 96 const logger = debug('vue:env') 97 const basePath = path.resolve(this.context, `.env${mode ? `.${mode}` : ``}`) 98 const localPath = `${basePath}.local` 99 100 const load = envPath => { 101 try { 102 const env = dotenv.config({ path: envPath, debug: process.env.DEBUG }) 103 dotenvExpand(env) 104 logger(envPath, env) 105 } catch (err) { 106 // only ignore error if file is not found 107 if (err.toString().indexOf('ENOENT') < 0) { 108 error(err) 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 113 load(localPath) 114 load(basePath) 115 116 // by default, NODE_ENV and BABEL_ENV are set to "development" unless mode 117 // is production or test. However the value in .env files will take higher 118 // priority. 119 if (mode) { 120 // always set NODE_ENV during tests 121 // as that is necessary for tests to not be affected by each other 122 const shouldForceDefaultEnv = ( 123 process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST && 124 !process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST_TESTING_ENV 125 ) 126 const defaultNodeEnv = (mode === 'production' || mode === 'test') 127 ? mode 128 : 'development' 129 if (shouldForceDefaultEnv || process.env.NODE_ENV == null) { 130 process.env.NODE_ENV = defaultNodeEnv 131 } 132 if (shouldForceDefaultEnv || process.env.BABEL_ENV == null) { 133 process.env.BABEL_ENV = defaultNodeEnv 134 } 135 } 136 } 137 138 setPluginsToSkip (args) { 139 const skipPlugins = args['skip-plugins'] 140 const pluginsToSkip = skipPlugins 141 ? new Set(skipPlugins.split(',').map(id => resolvePluginId(id))) 142 : new Set() 143 144 this.pluginsToSkip = pluginsToSkip 145 } 146 147 resolvePlugins (inlinePlugins, useBuiltIn) { 148 const idToPlugin = id => ({ 149 id: id.replace(/^.//, 'built-in:'), 150 apply: require(id) 151 }) 152 153 let plugins 154 155 const builtInPlugins = [ 156 './commands/serve', 157 './commands/build', 158 './commands/inspect', 159 './commands/help', 160 // config plugins are order sensitive 161 './config/base', 162 './config/css', 163 './config/prod', 164 './config/app' 165 ].map(idToPlugin) 166 167 if (inlinePlugins) { 168 plugins = useBuiltIn !== false 169 ? builtInPlugins.concat(inlinePlugins) 170 : inlinePlugins 171 } else { 172 const projectPlugins = Object.keys(this.pkg.devDependencies || {}) 173 .concat(Object.keys(this.pkg.dependencies || {})) 174 .filter(isPlugin) 175 .map(id => { 176 if ( 177 this.pkg.optionalDependencies && 178 id in this.pkg.optionalDependencies 179 ) { 180 let apply = () => {} 181 try { 182 apply = require(id) 183 } catch (e) { 184 warn(`Optional dependency ${id} is not installed.`) 185 } 186 187 return { id, apply } 188 } else { 189 return idToPlugin(id) 190 } 191 }) 192 plugins = builtInPlugins.concat(projectPlugins) 193 } 194 195 // Local plugins 196 if (this.pkg.vuePlugins && this.pkg.vuePlugins.service) { 197 const files = this.pkg.vuePlugins.service 198 if (!Array.isArray(files)) { 199 throw new Error(`Invalid type for option 'vuePlugins.service', expected 'array' but got ${typeof files}.`) 200 } 201 plugins = plugins.concat(files.map(file => ({ 202 id: `local:${file}`, 203 apply: loadModule(`./${file}`, this.pkgContext) 204 }))) 205 } 206 207 return plugins 208 } 209 210 async run (name, args = {}, rawArgv = []) { 211 // resolve mode 212 // prioritize inline --mode 213 // fallback to resolved default modes from plugins or development if --watch is defined 214 const mode = args.mode || (name === 'build' && args.watch ? 'development' : this.modes[name]) 215 216 // --skip-plugins arg may have plugins that should be skipped during init() 217 this.setPluginsToSkip(args) 218 219 // load env variables, load user config, apply plugins 220 this.init(mode) 221 222 args._ = args._ || [] 223 let command = this.commands[name] 224 if (!command && name) { 225 error(`command "${name}" does not exist.`) 226 process.exit(1) 227 } 228 if (!command || args.help || args.h) { 229 command = this.commands.help 230 } else { 231 args._.shift() // remove command itself 232 rawArgv.shift() 233 } 234 const { fn } = command 235 return fn(args, rawArgv) 236 } 237 238 resolveChainableWebpackConfig () { 239 const chainableConfig = new Config() 240 // apply chains 241 this.webpackChainFns.forEach(fn => fn(chainableConfig)) 242 return chainableConfig 243 } 244 245 resolveWebpackConfig (chainableConfig = this.resolveChainableWebpackConfig()) { 246 if (!this.initialized) { 247 throw new Error('Service must call init() before calling resolveWebpackConfig().') 248 } 249 // get raw config 250 let config = chainableConfig.toConfig() 251 const original = config 252 // apply raw config fns 253 this.webpackRawConfigFns.forEach(fn => { 254 if (typeof fn === 'function') { 255 // function with optional return value 256 const res = fn(config) 257 if (res) config = merge(config, res) 258 } else if (fn) { 259 // merge literal values 260 config = merge(config, fn) 261 } 262 }) 263 264 // #2206 If config is merged by merge-webpack, it discards the __ruleNames 265 // information injected by webpack-chain. Restore the info so that 266 // vue inspect works properly. 267 if (config !== original) { 268 cloneRuleNames( 269 config.module && config.module.rules, 270 original.module && original.module.rules 271 ) 272 } 273 274 // check if the user has manually mutated output.publicPath 275 const target = process.env.VUE_CLI_BUILD_TARGET 276 if ( 277 !process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST && 278 (target && target !== 'app') && 279 config.output.publicPath !== this.projectOptions.publicPath 280 ) { 281 throw new Error( 282 `Do not modify webpack output.publicPath directly. ` + 283 `Use the "publicPath" option in vue.config.js instead.` 284 ) 285 } 286 287 if (typeof config.entry !== 'function') { 288 let entryFiles 289 if (typeof config.entry === 'string') { 290 entryFiles = [config.entry] 291 } else if (Array.isArray(config.entry)) { 292 entryFiles = config.entry 293 } else { 294 entryFiles = Object.values(config.entry || []).reduce((allEntries, curr) => { 295 return allEntries.concat(curr) 296 }, []) 297 } 298 299 entryFiles = entryFiles.map(file => path.resolve(this.context, file)) 300 process.env.VUE_CLI_ENTRY_FILES = JSON.stringify(entryFiles) 301 } 302 303 return config 304 } 305 306 loadUserOptions () { 307 // vue.config.js 308 let fileConfig, pkgConfig, resolved, resolvedFrom 309 const configPath = ( 310 process.env.VUE_CLI_SERVICE_CONFIG_PATH || 311 path.resolve(this.context, 'vue.config.js') 312 ) 313 if (fs.existsSync(configPath)) { 314 try { 315 fileConfig = require(configPath) 316 317 if (typeof fileConfig === 'function') { 318 fileConfig = fileConfig() 319 } 320 321 if (!fileConfig || typeof fileConfig !== 'object') { 322 error( 323 `Error loading ${chalk.bold('vue.config.js')}: should export an object or a function that returns object.` 324 ) 325 fileConfig = null 326 } 327 } catch (e) { 328 error(`Error loading ${chalk.bold('vue.config.js')}:`) 329 throw e 330 } 331 } 332 333 // package.vue 334 pkgConfig = this.pkg.vue 335 if (pkgConfig && typeof pkgConfig !== 'object') { 336 error( 337 `Error loading vue-cli config in ${chalk.bold(`package.json`)}: ` + 338 `the "vue" field should be an object.` 339 ) 340 pkgConfig = null 341 } 342 343 if