Kafka源码研究–Comsumer获取partition下标
- 2019 年 10 月 27 日
- 筆記
背景
由于项目上Flink在设置parallel多于1的情况下,job没法正确地获取watermark,所以周末来研究一下一部分,大概已经锁定了原因:
虽然我们的topic只设置了1的partition,但是Kafka的Comsumer还是起了好几个subtask去读索引是2、3的partition,然后这几个subtask的watermark一直不更新,导致我们job整体的watermark一直是Long.MIN_VALUE。现在需要去了解一下subtask获取partition的流程,等上班的时候debug一遍应该就可以知道原因。
翻源码的过程
通过log找到分配partition的大概位置
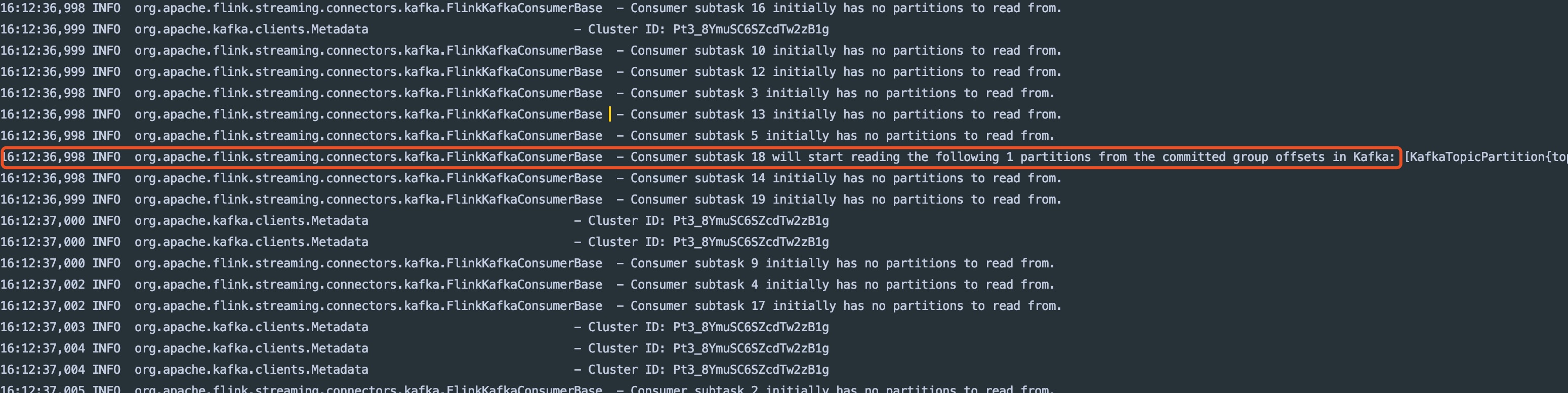
从图中可以看到,在org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.FlinkKafkaConsumerBase这个类中可以找到一些关键信息。
跟踪源码
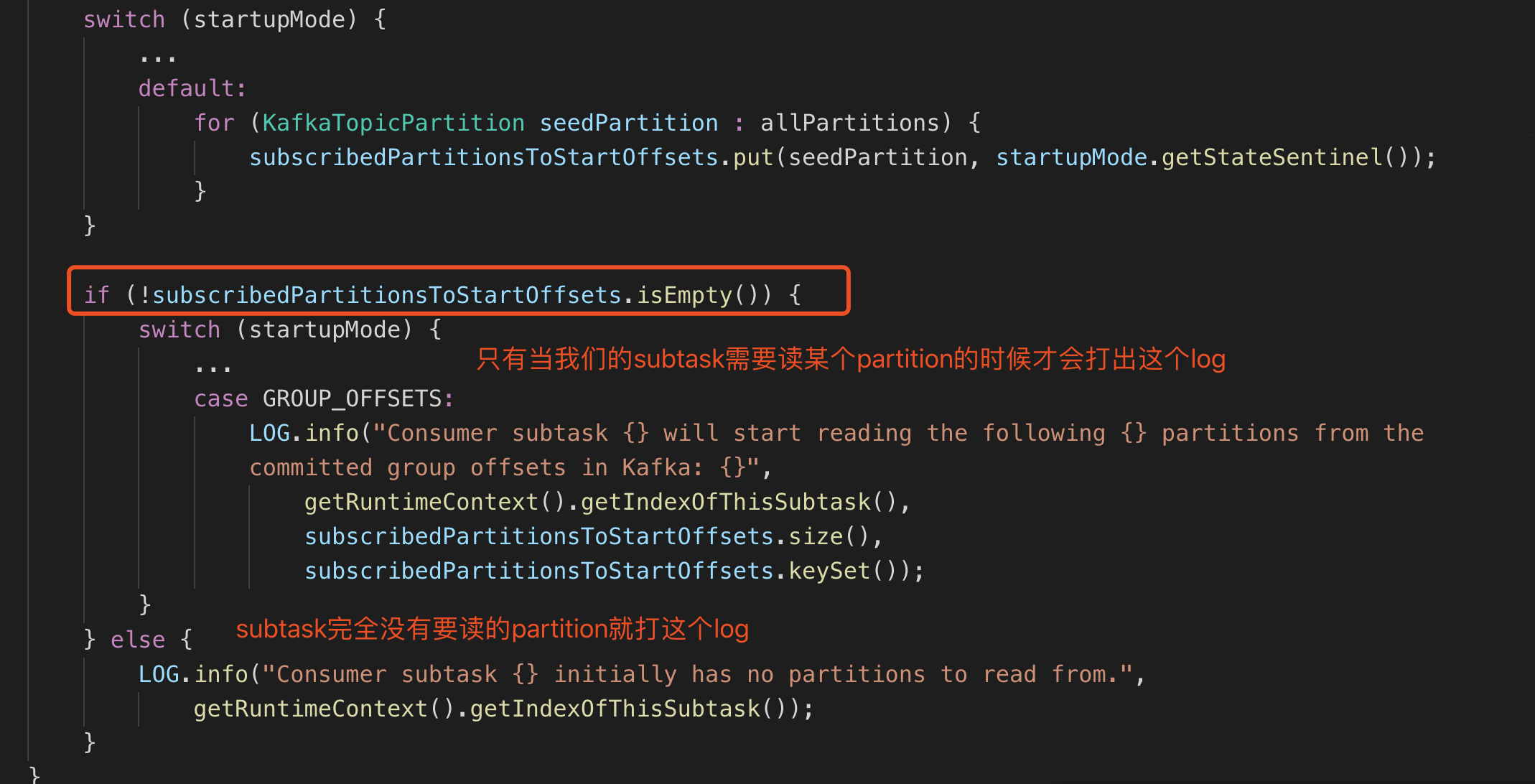
往上翻翻,看有没有有用信息
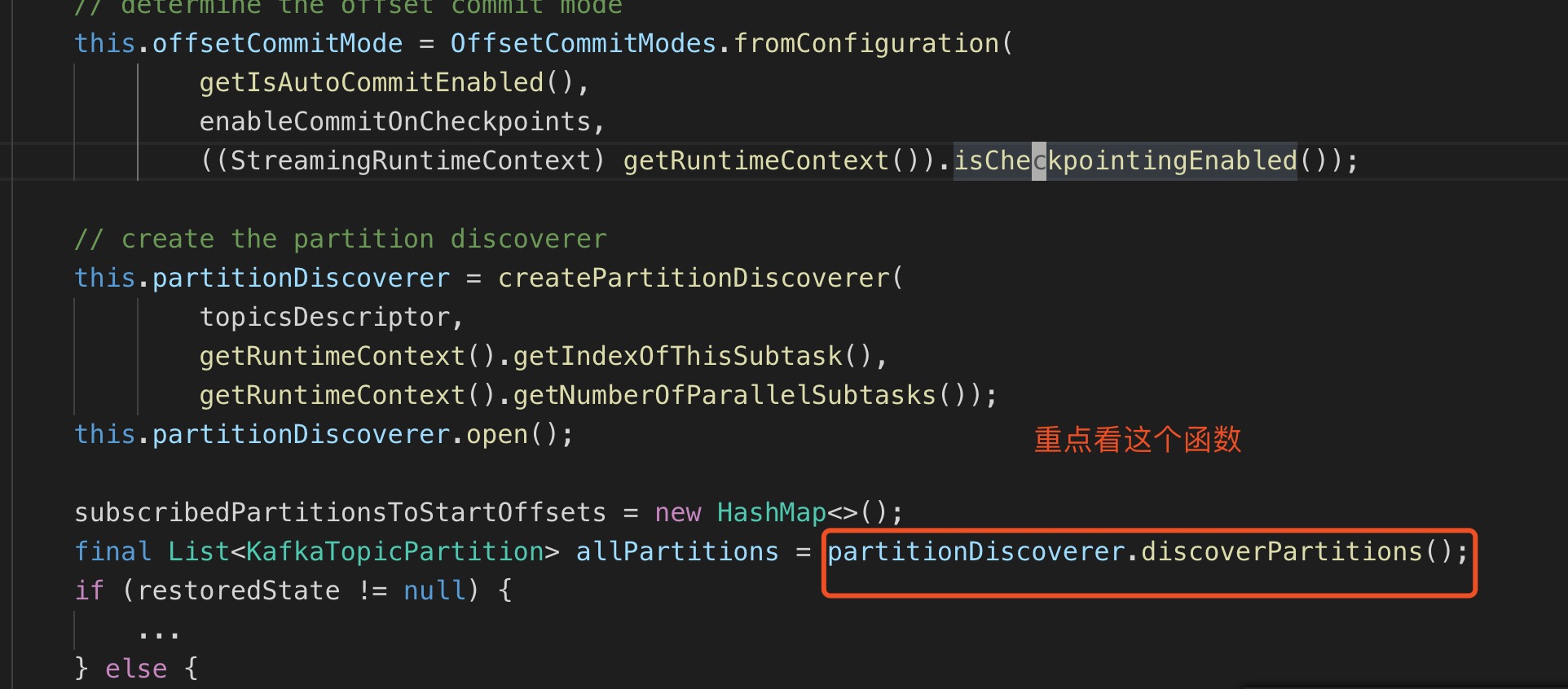
关键源码,附上注释
public void open(Configuration configuration) throws Exception { // determine the offset commit mode this.offsetCommitMode = OffsetCommitModes.fromConfiguration( getIsAutoCommitEnabled(), enableCommitOnCheckpoints, ((StreamingRuntimeContext) getRuntimeContext()).isCheckpointingEnabled()); // create the partition discoverer this.partitionDiscoverer = createPartitionDiscoverer( topicsDescriptor, getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask(), getRuntimeContext().getNumberOfParallelSubtasks()); this.partitionDiscoverer.open(); subscribedPartitionsToStartOffsets = new HashMap<>(); // 重点函数,这个函数或获取到subtask的所有partition。 final List<KafkaTopicPartition> allPartitions = partitionDiscoverer.discoverPartitions(); if (restoredState != null) { ... } else { // use the partition discoverer to fetch the initial seed partitions, // and set their initial offsets depending on the startup mode. // for SPECIFIC_OFFSETS and TIMESTAMP modes, we set the specific offsets now; // for other modes (EARLIEST, LATEST, and GROUP_OFFSETS), the offset is lazily determined // when the partition is actually read. switch (startupMode) { ... default: for (KafkaTopicPartition seedPartition : allPartitions) { subscribedPartitionsToStartOffsets.put(seedPartition, startupMode.getStateSentinel()); } } if (!subscribedPartitionsToStartOffsets.isEmpty()) { switch (startupMode) { ... case GROUP_OFFSETS: LOG.info("Consumer subtask {} will start reading the following {} partitions from the committed group offsets in Kafka: {}", getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask(), subscribedPartitionsToStartOffsets.size(), subscribedPartitionsToStartOffsets.keySet()); } } else { LOG.info("Consumer subtask {} initially has no partitions to read from.", getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask()); } } public List<KafkaTopicPartition> discoverPartitions() throws WakeupException, ClosedException { if (!closed && !wakeup) { try { List<KafkaTopicPartition> newDiscoveredPartitions; // (1) get all possible partitions, based on whether we are subscribed to fixed topics or a topic pattern if (topicsDescriptor.isFixedTopics()) { // 对于没有使用通配符的topic,直接获取topic的所有partition newDiscoveredPartitions = getAllPartitionsForTopics(topicsDescriptor.getFixedTopics()); } else { // 对于使用了通配符的topic, 先找到所有topic,再一一match List<String> matchedTopics = getAllTopics(); // retain topics that match the pattern Iterator<String> iter = matchedTopics.iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { if (!topicsDescriptor.isMatchingTopic(iter.next())) { iter.remove(); } } if (matchedTopics.size() != 0) { // get partitions only for matched topics newDiscoveredPartitions = getAllPartitionsForTopics(matchedTopics); } else { newDiscoveredPartitions = null; } } // (2) eliminate partition that are old partitions or should not be subscribed by this subtask if (newDiscoveredPartitions == null || newDiscoveredPartitions.isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("Unable to retrieve any partitions with KafkaTopicsDescriptor: " + topicsDescriptor); } else { Iterator<KafkaTopicPartition> iter = newDiscoveredPartitions.iterator(); KafkaTopicPartition nextPartition; while (iter.hasNext()) { nextPartition = iter.next(); // 只保留符合要求的partition,这就是我们要找的函数 if (!setAndCheckDiscoveredPartition(nextPartition)) { iter.remove(); } } } return newDiscoveredPartitions; }... }... } public boolean setAndCheckDiscoveredPartition(KafkaTopicPartition partition) { if (isUndiscoveredPartition(partition)) { discoveredPartitions.add(partition); // 在这 return KafkaTopicPartitionAssigner.assign(partition, numParallelSubtasks) == indexOfThisSubtask; } return false; } public static int assign(KafkaTopicPartition partition, int numParallelSubtasks) { // 先算出此topic的hash(partition.getTopic().hashCode() * 31),这里不知道为什么不直接用hash,还要再*31,然后取正数(& 0x7FFFFFFF),最后获取到此topic的起始位置。 int startIndex = ((partition.getTopic().hashCode() * 31) & 0x7FFFFFFF) % numParallelSubtasks; // here, the assumption is that the id of Kafka partitions are always ascending // starting from 0, and therefore can be used directly as the offset clockwise from the start index // 计算当前的partition应该属于哪个subtask。例如:一共有20个subtask,算出来的起始位置是5,partition是5,那么最后就是 // (5 + 5) % 20 = 10, 这个partition应该分给10号subtask。 return (startIndex + partition.getPartition()) % numParallelSubtasks; }思考
某topic的每个partition会分给哪个subtask其实是确定的
topic名字是确定的 -> topic的hashCode是确定的 && subtask的数量是确定的 -> startIndex是确定的 -> 某partition会分给哪个subtask其实是确定的
为什么要算startIndex
大概是为了平均分配不同的topic,如果topic很多,每个topic都只从0开始,那么subtask 0,1,2之类的靠前subtask就需要读大量的partition。