Tomcat源码分析 (四)—– Pipeline和Valve
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
在 Tomcat源码分析 (二)—– Tomcat整体架构及组件 中我们简单分析了一下Pipeline和Valve,并给出了整体的结构图。而这一节,我们将详细分析Tomcat里面的源码。
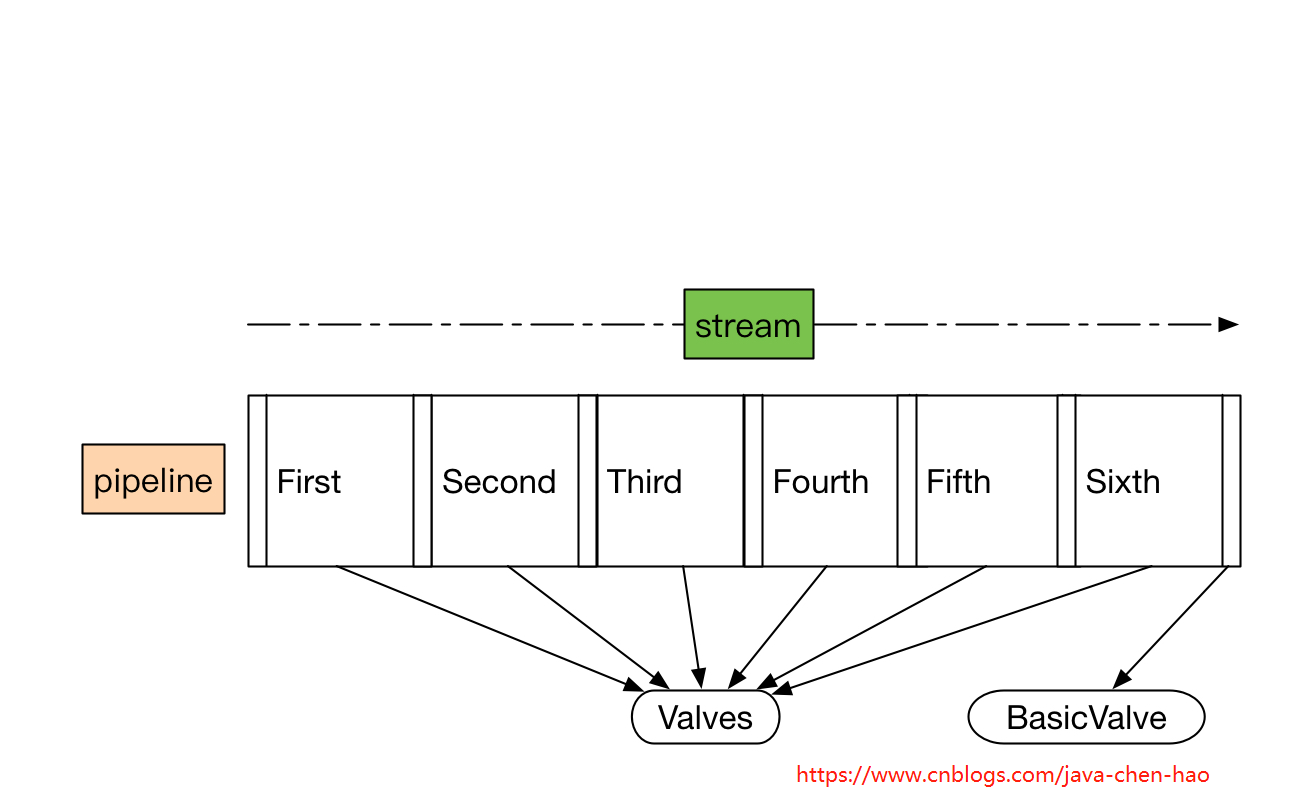
Valve
Valve作为一个个基础的阀门,扮演着业务实际执行者的角色。我们看看Valve这个接口有哪些方法。
public interface Valve { // 获取下一个阀门 public Valve getNext(); // 设置下一个阀门 public void setNext(Valve valve); // 后台执行逻辑,主要在类加载上下文中使用到 public void backgroundProcess(); // 执行业务逻辑 public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException; // 是否异步执行 public boolean isAsyncSupported(); }
Contained
ValveBase、Pipeline及其他相关组件都实现了Contained接口,我们看看这个接口有哪些方法。很简单,就是get/set容器操作。
public interface Contained { /** * Get the {@link Container} with which this instance is associated. * * @return The Container with which this instance is associated or * <code>null</code> if not associated with a Container */ Container getContainer(); /** * Set the <code>Container</code> with which this instance is associated. * * @param container The Container instance with which this instance is to * be associated, or <code>null</code> to disassociate this instance * from any Container */ void setContainer(Container container); }
ValveBase
从Valve的类层次结构,我们发现几乎所有Valve都继承了ValveBase这个抽象类,所以这儿我们需要分析一下它。
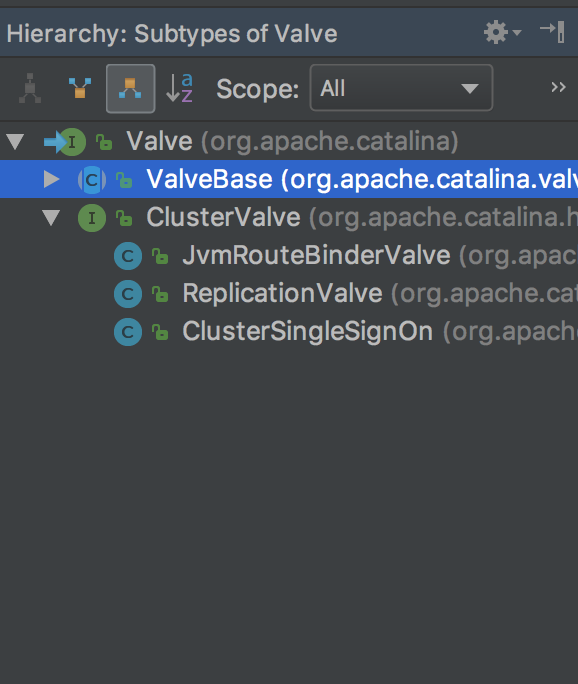
public abstract class ValveBase extends LifecycleMBeanBase implements Contained, Valve { // 国际化管理器,可以支持多国语言 protected static final StringManager sm = StringManager.getManager(ValveBase.class); //------------------------------------------------------ Instance Variables // 无参构造方法,默认不支持异步 public ValveBase() { this(false); } // 有参构造方法,可传入异步支持标记 public ValveBase(boolean asyncSupported) { this.asyncSupported = asyncSupported; } //------------------------------------------------------ Instance Variables // 异步标记 protected boolean asyncSupported; // 所属容器 protected Container container = null; // 容器日志组件对象 protected Log containerLog = null; // 下一个阀门 protected Valve next = null; //-------------------------------------------------------------- Properties // 获取所属容器 @Override public Container getContainer() { return container; } // 设置所属容器 @Override public void setContainer(Container container) { this.container = container; } // 是否异步执行 @Override public boolean isAsyncSupported() { return asyncSupported; } // 设置是否异步执行 public void setAsyncSupported(boolean asyncSupported) { this.asyncSupported = asyncSupported; } // 获取下一个待执行的阀门 @Override public Valve getNext() { return next; } // 设置下一个待执行的阀门 @Override public void setNext(Valve valve) { this.next = valve; } //---------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods // 后台执行,子类实现 @Override public void backgroundProcess() { // NOOP by default } // 初始化逻辑 @Override protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException { super.initInternal(); // 设置容器日志组件对象到当前阀门的containerLog属性 containerLog = getContainer().getLogger(); } // 启动逻辑 @Override protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); } // 停止逻辑 @Override protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException { setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING); } // 重写toString,格式为[${containerName}] @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(this.getClass().getName()); sb.append('['); if (container == null) { sb.append("Container is null"); } else { sb.append(container.getName()); } sb.append(']'); return sb.toString(); } // -------------------- JMX and Registration -------------------- // 设置获取MBean对象的keyProperties,格式如:a=b,c=d,e=f... @Override public String getObjectNameKeyProperties() { StringBuilder name = new StringBuilder("type=Valve"); Container container = getContainer(); name.append(container.getMBeanKeyProperties()); int seq = 0; // Pipeline may not be present in unit testing Pipeline p = container.getPipeline(); if (p != null) { for (Valve valve : p.getValves()) { // Skip null valves if (valve == null) { continue; } // Only compare valves in pipeline until we find this valve if (valve == this) { break; } if (valve.getClass() == this.getClass()) { // Duplicate valve earlier in pipeline // increment sequence number seq ++; } } } if (seq > 0) { name.append(",seq="); name.append(seq); } String className = this.getClass().getName(); int period = className.lastIndexOf('.'); if (period >= 0) { className = className.substring(period + 1); } name.append(",name="); name.append(className); return name.toString(); } // 获取所属域,从container获取 @Override public String getDomainInternal() { Container c = getContainer(); if (c == null) { return null; } else { return c.getDomain(); } } }
Pipeline
Pipeline作为一个管道,我们可以简单认为是一个Valve的集合,内部会对这个集合进行遍历,调用每个元素的业务逻辑方法invoke()。
是不是这样呢?我们还是分析一下源码,先看看接口定义。
public interface Pipeline { // ------------------------------------------------------------- Properties // 获取基本阀门 public Valve getBasic(); // 设置基本阀门 public void setBasic(Valve valve); // --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods // 添加阀门 public void addValve(Valve valve); // 获取阀门数组 public Valve[] getValves(); // 删除阀门 public void removeValve(Valve valve); // 获取首个阀门 public Valve getFirst(); // 管道内所有阀门是否异步执行 public boolean isAsyncSupported(); // 获取管道所属的容器 public Container getContainer(); // 设置管道所属的容器 public void setContainer(Container container); // 查找非异步执行的所有阀门,并放置到result参数中,所以result不允许为null public void findNonAsyncValves(Set<String> result); }
StandardPipeline
接着我们分析一下Pipeline唯一的实现StandardPipeline。代码很长,但是都很简单。
public class StandardPipeline extends LifecycleBase implements Pipeline, Contained { private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(StandardPipeline.class); // ----------------------------------------------------------- Constructors // 构造一个没有所属容器的管道 public StandardPipeline() { this(null); } // 构造一个有所属容器的管道 public StandardPipeline(Container container) { super(); setContainer(container); } // ----------------------------------------------------- Instance Variables /** * 基本阀门,最后执行的阀门 */ protected Valve basic = null; /** * 管道所属的容器 */ protected Container container = null; /** * 管道里面的首个执行的阀门 */ protected Valve first = null; // --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods // 是否异步执行,如果一个阀门都没有,或者所有阀门都是异步执行的,才返回true @Override public boolean isAsyncSupported() { Valve valve = (first!=null)?first:basic; boolean supported = true; while (supported && valve!=null) { supported = supported & valve.isAsyncSupported(); valve = valve.getNext(); } return supported; } // 查找所有未异步执行的阀门 @Override public void findNonAsyncValves(Set<String> result) { Valve valve = (first!=null) ? first : basic; while (valve != null) { if (!valve.isAsyncSupported()) { result.add(valve.getClass().getName()); } valve = valve.getNext(); } } // ------------------------------------------------------ Contained Methods // 获取所属容器 @Override public Container getContainer() { return (this.container); } // 设置所属容器 @Override public void setContainer(Container container) { this.container = container; } // 初始化逻辑,默认没有任何逻辑 @Override protected void initInternal() { // NOOP } // 开始逻辑,调用所有阀门的start方法 @Override protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any Valve current = first; if (current == null) { current = basic; } while (current != null) { if (current instanceof Lifecycle) ((Lifecycle) current).start(); current = current.getNext(); } setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); } // 停止逻辑,调用所有阀门的stop方法 @Override protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException { setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING); // Stop the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any Valve current = first; if (current == null) { current = basic; } while (current != null) { if (current instanceof Lifecycle) ((Lifecycle) current).stop(); current = current.getNext(); } } // 销毁逻辑,移掉所有阀门,调用removeValve方法 @Override protected void destroyInternal() { Valve[] valves = getValves(); for (Valve valve : valves) { removeValve(valve); } } /** * 重新toString方法 */ @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Pipeline["); sb.append(container); sb.append(']'); return sb.toString(); } // ------------------------------------------------------- Pipeline Methods // 获取基础阀门 @Override public Valve getBasic() { return (this.basic); } // 设置基础阀门 @Override public void setBasic(Valve valve) { // Change components if necessary Valve oldBasic = this.basic; if (oldBasic == valve) return; // Stop the old component if necessary // 老的基础阀门会被调用stop方法且所属容器置为null if (oldBasic != null) { if (getState().isAvailable() && (oldBasic instanceof Lifecycle)) { try { ((Lifecycle) oldBasic).stop(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error("StandardPipeline.setBasic: stop", e); } } if (oldBasic instanceof Contained) { try { ((Contained) oldBasic).setContainer(null); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); } } } // Start the new component if necessary // 新的阀门会设置所属容器,并调用start方法 if (valve == null) return; if (valve instanceof Contained) { ((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container); } if (getState().isAvailable() && valve instanceof Lifecycle) { try { ((Lifecycle) valve).start(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error("StandardPipeline.setBasic: start", e); return; } } // Update the pipeline // 替换pipeline中的基础阀门,就是讲基础阀门的前一个阀门的next指向当前阀门 Valve current = first; while (current != null) { if (current.getNext() == oldBasic) { current.setNext(valve); break; } current = current.getNext(); } this.basic = valve; } // 添加阀门 @Override public void addValve(Valve valve) { // Validate that we can add this Valve // 设置所属容器 if (valve instanceof Contained) ((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container); // Start the new component if necessary // 调用阀门的start方法 if (getState().isAvailable()) { if (valve instanceof Lifecycle) { try { ((Lifecycle) valve).start(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error("StandardPipeline.addValve: start: ", e); } } } // Add this Valve to the set associated with this Pipeline // 设置阀门,将阀门添加到基础阀门的前一个 if (first == null) { first = valve; valve.setNext(basic); } else { Valve current = first; while (current != null) { if (current.getNext() == basic) { current.setNext(valve); valve.setNext(basic); break; } current = current.getNext(); } } container.fireContainerEvent(Container.ADD_VALVE_EVENT, valve); } // 获取阀门数组 @Override public Valve[] getValves() { ArrayList<Valve> valveList = new ArrayList<>(); Valve current = first; if (current == null) { current = basic; } while (current != null) { valveList.add(current); current = current.getNext(); } return valveList.toArray(new Valve[0]); } // JMX方法,在此忽略 public ObjectName[] getValveObjectNames() { ArrayList<ObjectName> valveList = new ArrayList<>(); Valve current = first; if (current == null) { current = basic; } while (current != null) { if (current instanceof JmxEnabled) { valveList.add(((JmxEnabled) current).getObjectName()); } current = current.getNext(); } return valveList.toArray(new ObjectName[0]); } // 移除阀门 @Override public void removeValve(Valve valve) { Valve current; if(first == valve) { // 如果待移出的阀门是首个阀门,则首个阀门的下一个阀门变成首个阀门 first = first.getNext(); current = null; } else { current = first; } // 遍历阀门集合,并进行移除 while (current != null) { if (current.getNext() == valve) { current.setNext(valve.getNext()); break; } current = current.getNext(); } if (first == basic) first = null; // 设置阀门所属容器为null if (valve instanceof Contained) ((Contained) valve).setContainer(null); // 调用待移除阀门的stop方法和destroy方法,并触发移除阀门事件 if (valve instanceof Lifecycle) { // Stop this valve if necessary if (getState().isAvailable()) { try { ((Lifecycle) valve).stop(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error("StandardPipeline.removeValve: stop: ", e); } } try { ((Lifecycle) valve).destroy(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error("StandardPipeline.removeValve: destroy: ", e); } } container.fireContainerEvent(Container.REMOVE_VALVE_EVENT, valve); } // 获取首个阀门,如果阀门列表为null,返回基础阀门 @Override public Valve getFirst() { if (first != null) { return first; } return basic; } }
总结
通过上面的代码分析,我们发现了几个关键的设计模式:
- 模板方法模式,父类定义框架,子类实现
- 责任链模式,就是这儿的管道/阀门的实现方式,每个阀门维护一个next属性指向下一个阀门
