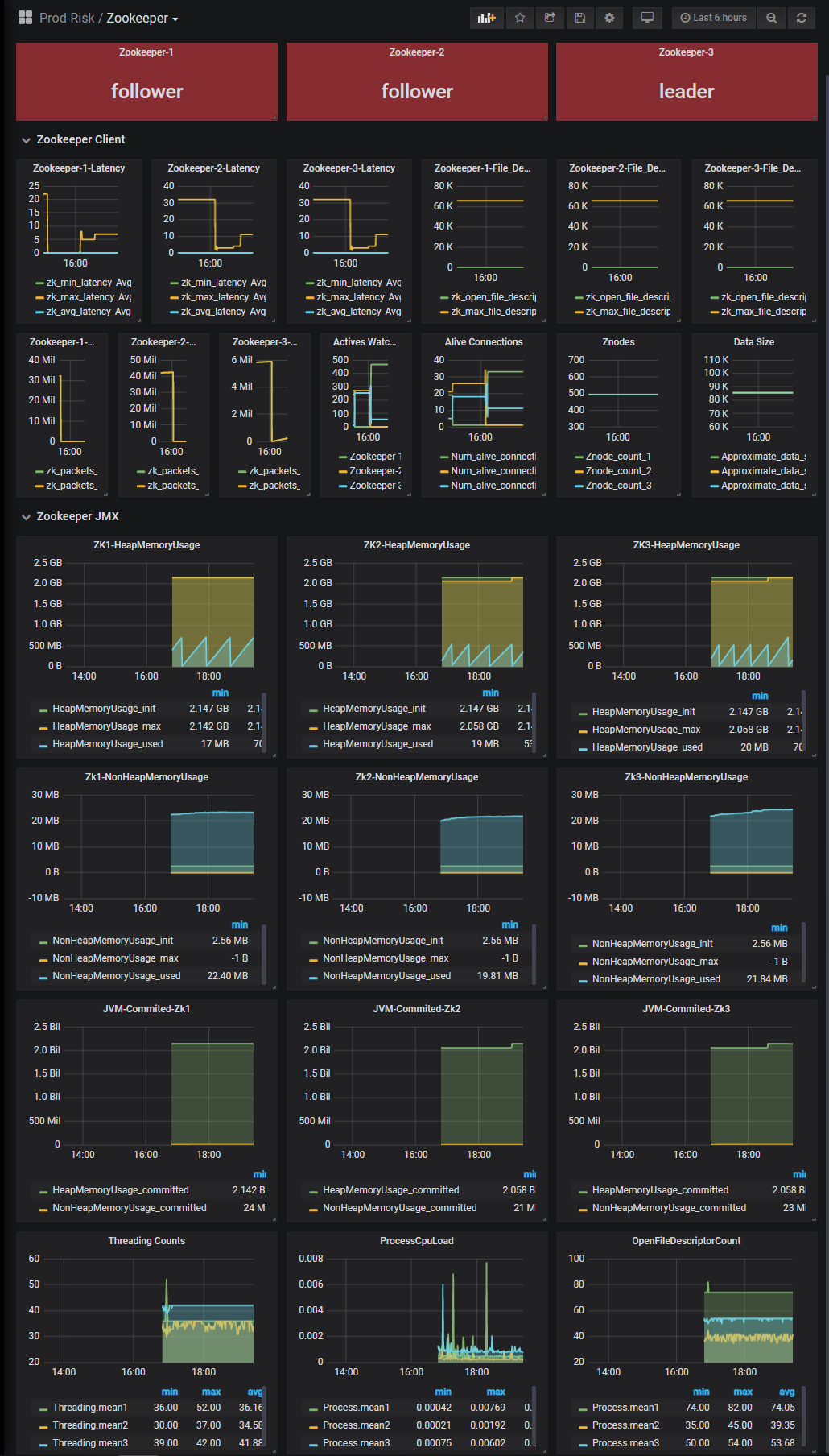
Java ThreadLocal 的使用与源码解析
- 2019 年 10 月 22 日
- 筆記
GitHub Page: http://blog.cloudli.top/posts/Java-ThreadLocal-的使用与源码解析/
ThreadLocal 主要解决的是每个线程绑定自己的值,可以将 ThreadLocal 看成全局存放数据的盒子,盒子中存储每个线程的私有数据。
验证线程变量的隔离性
import static java.lang.System.out; public class Run { private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>(); static class Work extends Thread { @Override public void run() { threadLocal.set(0); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { // 获取数据 int sum = threadLocal.get(); out.printf("%s's sum = %sn", getName(), threadLocal.get()); sum += i; // 写回数据 threadLocal.set(sum); } out.printf("END %s's sum = %dnn", getName(), threadLocal.get()); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Work work1 = new Work(), work2 = new Work(); work1.start(); work2.start(); } }运行结果:
Thread-0's sum = null Thread-1's sum = null Thread-1's sum = 1 Thread-1's sum = 3 Thread-1's sum = 6 Thread-1's sum = 10 END Thread-1's sum = 15 Thread-0's sum = 1 Thread-0's sum = 3 Thread-0's sum = 6 Thread-0's sum = 10 END Thread-0's sum = 15 Process finished with exit code 0从结果来看,两个线程的计算结果一致,ThreadLocal 中隔离了两个线程的数据。
ThreadLocal 源码解析
ThreadLocalMap 内部类
在 ThreadLocal 中有一个 ThreadLocalMap 内部类,所以 ThreadLocal 实际上是使用一个哈希表来存储每个线程的数据的。
ThreadLocalMap 与 HashMap 不同,其中 Entry 是一个弱引用,这意味着每次垃圾回收运行时都会将储存的数据回收掉。而且它只使用了数组来存储键值对。
ThreadLocalMap 中的 Entry :
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } }get() 方法
public T get() { // 得到当前线程 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程的哈希表 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) { // 从哈希表中获取当前线程的数据 ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } return setInitialValue(); }get() 方法首先得到当前线程,然后获取当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap 对象,然后从中取出数据。
这里的 map.getEntry(this) 看起来很奇怪,在前面有这样一行代码:
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);这个方法获取当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap 对象,所以,虽然 map.getEntry() 中的 key 总是 ThreadLocal 对象本身,但是每个线程都持有有自己的 ThreadLocalMap 对象。
getMap() 方法
/** * Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in * InheritableThreadLocal. * * @param t the current thread * @return the map */ ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; }看到这个方法,get() 方法中 map.getEntry(this) 的迷雾就解开了。这里可以看到返回的是线程中的 threadLocals 属性。那么这里瞟一眼 Thread 的源码:
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained * by the ThreadLocal class. */ ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;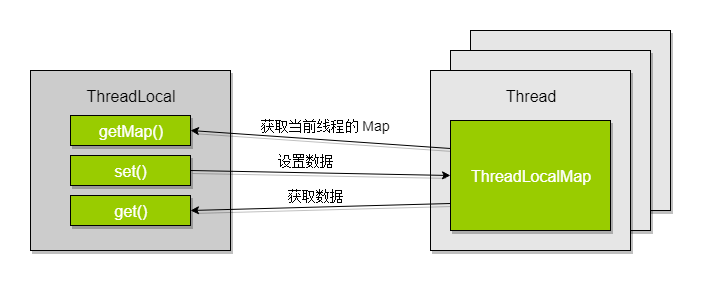
其实每次 get() 时都是先获取了线程自己的 ThreadLocalMap 对象,然后对这个对象进行操作。
set() 方法
public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else // 为当前线程创建一个 ThreadLocalMap 对象 createMap(t, value); }set() 方法也是先获取当前线程自己的 ThreadLocalMap 对象,然后再设置数据。如果获取的哈希表为 null,则创建一个。
createMap() 方法
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); }createMap() 方法创建一个 ThreadLocalMap 对象,该对象由线程持有。
总结
ThreadLocal可以隔离线程的变量,每个线程只能从这个对象中获取到属于自己的数据。ThreadLocal使用哈希表来存储线程的数据,而且这个哈希表是由线程自己持有的,每次获取和设值都会先获取当前线程持有的ThreadLocalMap对象。ThreadLocalMap中的key总是ThreadLocal对象本身。ThreadLocalMap中的Entry是弱引用,每次 GC 运行都会被回收。