无聊系列 – 字节跳动的三道编码面试题的实现
- 2019 年 10 月 19 日
- 筆記
国庆节后,自己的一个小圈子微信群的伙伴们发了一张图片,是网上流传的字节跳动的面试题编码,闲的无事就思索了下,发现都不难,都是对基础的数学知识的考量。先上图吧!
当然40分钟,我也无法把任意两题编码完成,只是知道大概的解题思路,唯一能确定的,在面试规定时间内,第二题我是肯定可以在20分钟内编码完成。
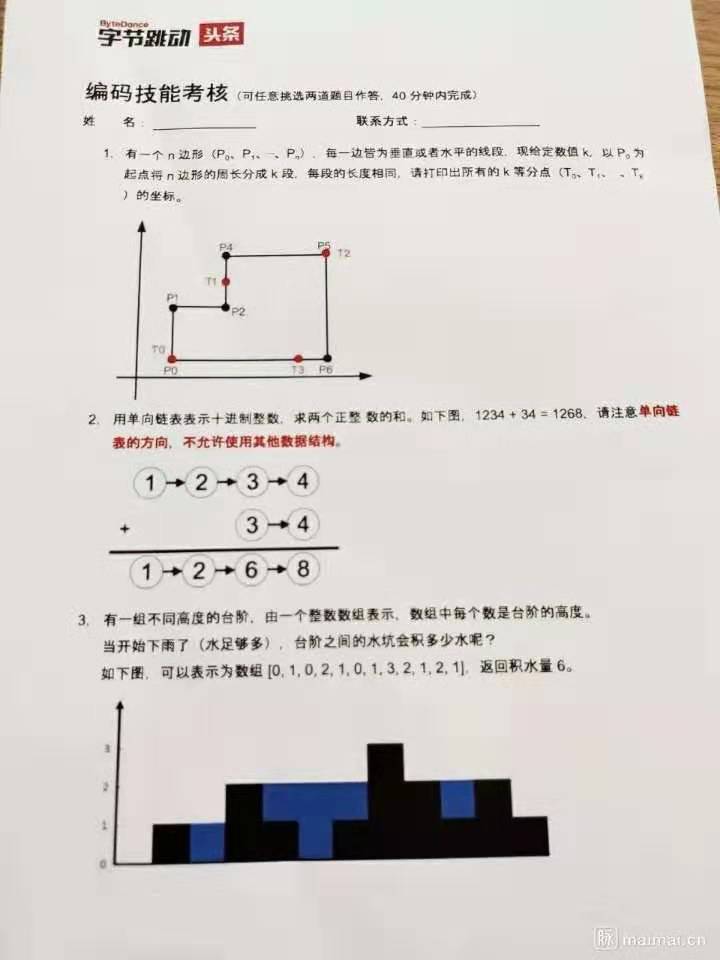
题目一
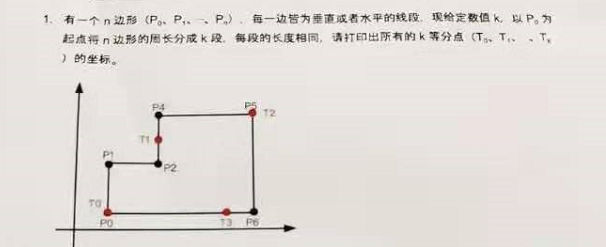
基础知识就是初中的平面直角坐标系,解析思路:
- 计算总周长;
- 将各边长的前后坐标计算出来封装好,第四步要使用;
- 根据K段值计算出平均分段后的长度;
- 然后循环K次,根据平均长度依次相加计算等分点的坐标。
不多说,上代码:
先定义坐标的Point类
class Point { float x; float y; public Point() { } public Point(float x, float y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public Point(Point point) { this(point.x, point.y); } @Override public String toString() { return "Point, x:" + x + " y:" + y; } }
N边形的边封装类
class Line { Point begin; Point end; float length; public Line() { } public Line(Point begin, Point end, float length) { this.begin = begin; this.end = end; this.length = length; } }
现在上实现计算的类
这段代码第一个版本的时候,在正方形偶数等分的时候,坐标点计算不准确,今晚上看着代码思考了10分钟的样子,稍微改动了下,暂时没有这个bug了。其他的bug,期待大家一起发现,然后修复吧!
public class Polygon { /** * 计算边的长度 * * @return */ private static float lineLength(Point a, Point b) { float length; if (a.x == b.x) { // 垂直线条 length = Math.abs(a.y - b.y); } else { length = Math.abs(a.x - b.x); } return length; } /** * 计算 周长 * * @return */ private static float totalSideLength(Point[] points, Line[] lines) { float side = 0; for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) { Point prev = points[i - 1]; Point point = points[i]; float length = lineLength(prev, point); side += length; lines[i - 1] = new Line(prev, point, length); if (i == points.length - 1) { length = lineLength(point, points[0]); side += length; lines[i] = new Line(point, points[0], length); } } return side; } public static Point[] division(Point[] points, int divisionNum) { Point[] divisionPoint = new Point[divisionNum]; // 计算周长 Line[] lines = new Line[points.length]; float side = totalSideLength(points, lines); // 等分长度 float divisionLength = side / divisionNum; int lineIndex = -1; float sumLength = 0; for (int i = 0; i < divisionNum; i++) { if (i == 0) { // 第一个等分点直接是起始点坐标 divisionPoint[i] = new Point(points[0]); continue; } divisionPoint[i] = new Point(); float lineLength = divisionLength * i; while (true) { Line line; if (sumLength < lineLength) { lineIndex++; line = lines[lineIndex]; sumLength += line.length; } else line = lines[lineIndex]; if (sumLength >= lineLength) { float temp = sumLength - lineLength; if (line.begin.x == line.end.x) { // begin和end的坐标点垂直 divisionPoint[i].x = line.begin.x; if (line.end.y > line.begin.y) divisionPoint[i].y = line.end.y - temp; else divisionPoint[i].y = line.end.y + temp; } else { // begin和end的坐标点水平 divisionPoint[i].y = line.end.y; if (line.end.x > line.begin.x) divisionPoint[i].x = line.end.x - temp; else divisionPoint[i].x = line.end.x + temp; } break; } } } return divisionPoint; } private static void print(Point[] points) { for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) { System.out.println("第" + (i + 1) + "等分点, x:" + points[i].x + ",y:" + points[i].y); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Point[] points = new Point[] { new Point(0, 0), new Point(0, 1), new Point(1, 1), new Point(1, 0) }; Point[] divPoints = division(points, 8); print(divPoints); } }
题目二

解题思路:
对应位数的数字相加,永远不会超过18,所以,我们就先把对应位置的和计算出来,然后再反复循环找到大于9的数,向高位进位。
这个比较简单,只是考察个位数的正整数加法永远不大于18这个细节。
上代码:
public class LinkAddition { static class NumNode { public int num; public NumNode next; public NumNode() { } public NumNode(int num) { this.num = num; }; public NumNode(int num, NumNode next) { this(num); this.next = next; } } private static int length(NumNode num) { int length = 0; NumNode temp = num; while (temp != null) { length++; temp = temp.next; } return length; } private static NumNode calc(NumNode a, NumNode b, int aLength, int bLength) { NumNode aNode = a; NumNode bNode = b; NumNode result = new NumNode(); NumNode resultNode = result; // 计算b链表再a中的起始索引 int aStartIndex = aLength - bLength; for (int i = 0; i < aLength; i++) { if (i >= aStartIndex) { resultNode.num = aNode.num + bNode.num; bNode = bNode.next; } else resultNode.num = aNode.num; aNode = aNode.next; if (aNode != null) { resultNode.next = new NumNode(); resultNode = resultNode.next; } } return result; } public static NumNode addition(NumNode a, NumNode b) { NumNode result = null; // 计算位数 int aLength = length(a); int bLength = length(b); if (aLength > bLength) { result = calc(a, b, aLength, bLength); } else { result = calc(b, a, bLength, aLength); } boolean isGreater9 = true; while (isGreater9) { isGreater9 = false; NumNode node = result; while (node != null) { // 检查是否有大于9的节点 if (node.num > 9) { isGreater9 = true; break; } node = node.next; } // 没有大于9且需要进位的节点 if (!isGreater9) break; node = result; if (node.num > 9) { // 头节点的内容跟大于9,需要进位 result = new NumNode(1, node); node.num = node.num - 10; } while (node.next != null) { if (node.next.num > 9) { node.num += 1; node.next.num = node.next.num - 10; } node = node.next; } } return result; } private static void print(NumNode num) { NumNode node = num; while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.num); node = node.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { NumNode a = new NumNode(9); a.next = new NumNode(9, new NumNode(9)); NumNode b = new NumNode(9); // b.next = new NumNode(9, new NumNode(9)); NumNode result = addition(a, b); print(result); } }
题目三

这个我写的第一个版本,只契合类那个举例,然后瞬间就被我推翻类,最后坐下思考类10分钟,把这个按照二维数组的思路解析了。
先找到最高处,然后就以最高处为一个维度,做循环计算出水量,还是上代码吧:
public class Water { public static int waterNum(int[] steps) { int waterNum = 0; int max = steps[0]; for (int i = 1; i < steps.length; i++) { if (max < steps[i]) max = steps[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { int num = 0, index = 0; for (int n = 0; n < steps.length; n++) { if (steps[n] - i > 0) { if (num > 0) { waterNum += n - index - 1; } num = steps[n] - i; index = n; } } } return waterNum; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] steps = new int[] { 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1 }; int water = waterNum(steps); System.out.println(water); } }
总结:
其实这几题本身的知识点并不难,都是平时用到的,就看怎么转化为代码罢了。
第一题考察的直角坐标系上怎么计算边长,然后根据均分等长从第一条边挨着走,计算对应的坐标,该知识点在初中就已学过。
第二题则是考察每位上的正整数加法到底最大能到多少,只要明白了这一点,把每一位上相加后,再统一做进位处理就可以了。
第三题的代码量是最少的,我的解题思路是二位数组的方式, 也不算难。