flatbuffer介绍和用法
介绍
flatbuffer是google发布的一个跨平台序列化框架具有如下特点
1、对序列化的数据不需要打包和拆包
2、内存和效率速度高,扩展灵活
3、代码依赖较少
4、强类型设计,编译期即可完成类型检查
5、使用简单、可跨平台使用
安装
git clone [email protected]:google/flatbuffers.git
cd flatbuffers
brew install cmake
cmake -G "Unix Makefiles"
make
make install
flatc --version
编写flatbuffer文件
// Example IDL file for our monster's schema. namespace com.frank.learning; enum Color:byte { Red = 0, Green, Blue = 2 } union Equipment { Weapon } // Optionally add more tables. struct Vec3 { x:float; y:float; z:float; } table Monster { pos:Vec3; // Struct. mana:short = 150; hp:short = 100; name:string; friendly:bool = false (deprecated); inventory:[ubyte]; // Vector of scalars. color:Color = Blue; // Enum. weapons:[Weapon]; // Vector of tables. equipped:Equipment; // Union. } table Weapon { name:string; damage:short; } root_type Monster;
将文件保存为monster.fbs,下面进行编译
flatc --java monster.fbs
执行完后会在当前目录下生成Java文件
IntelliJ测试flatbuffer
将生成的Java代码拷到项目中,新建SampleBinary类
package com.frank.learning; import com.google.flatbuffers.FlatBufferBuilder; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; public class SampleBinary { public static void main(String[] args){ //使用FlatBufferBuilder 完成对象序列化 FlatBufferBuilder builder = new FlatBufferBuilder(1024); //返回该String的偏移地址 int weaponOneName = builder.createString("Sword"); short weaponOneDamage = 3; int weaponTwoName = builder.createString("Axe"); short weaponTwoDamage = 5; // 使用createWeapon创建Weapon对象,并返回该对象的偏移地址 int sword = Weapon.createWeapon(builder, weaponOneName, weaponOneDamage); int axe = Weapon.createWeapon(builder, weaponTwoName, weaponTwoDamage); // Serialize a name for our monster, called "Orc". int name = builder.createString("Orc"); // 创建一个Vector对象,并且返回它的偏移地址 byte[] treasure = {0, 1, 13, 12, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; int inv = Monster.createInventoryVector(builder, treasure); // Place the two weapons into an array, and pass it to the `createWeaponsVector()` method to // create a FlatBuffer vector. int[] weaps = new int[2]; weaps[0] = sword; weaps[1] = axe; // Pass the `weaps` array into the `createWeaponsVector()` method to create a FlatBuffer vector. int weapons = Monster.createWeaponsVector(builder, weaps); // startMonster声明开始创建Monster对象,使用endMonster声明完成Monster对象 Monster.startMonster(builder); Monster.addPos(builder, Vec3.createVec3(builder, 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f)); Monster.addName(builder, name); Monster.addColor(builder, Color.Red); Monster.addHp(builder, (short)300); Monster.addInventory(builder, inv); Monster.addWeapons(builder, weapons); Monster.addEquippedType(builder, Equipment.Weapon); Monster.addEquipped(builder, axe); int orc = Monster.endMonster(builder); // 调用finish方法完成Monster对象 builder.finish(orc); // You could also call `Monster.finishMonsterBuffer(builder, orc);`. // 生成二进制文件 byte[] buf = builder.sizedByteArray(); // 至此完成对象数据序列化 //模拟从获取到二进制数据 进行反序列化对象 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(buf); //根据该二进制数据列生成Monster对象 Monster monster = Monster.getRootAsMonster(buffer); short hp = monster.hp(); System.out.println(hp); short mana = monster.mana(); System.out.println(mana); String resultName = monster.name(); System.out.println(resultName); Vec3 pos = monster.pos(); float x = pos.x(); float y = pos.y(); float z = pos.z(); System.out.println("X: "+x+" Y: "+y+" Z: "+z); int invLength = monster.inventoryLength(); int thirdItem = monster.inventory(2); System.out.println(thirdItem); int weaponsLength = monster.weaponsLength(); String secondWeaponName = monster.weapons(1).name(); short secondWeaponDamage = monster.weapons(1).damage(); System.out.println("weaponsLength: "+weaponsLength+" secondWeaponName: "+secondWeaponName+" secondWeaponDamage: "+secondWeaponDamage); int unionType = monster.equippedType(); if (unionType == Equipment.Weapon) { Weapon weapon = (Weapon)monster.equipped(new Weapon()); // Requires explicit cast // to `Weapon`. String weaponName = weapon.name(); // "Axe" short weaponDamage = weapon.damage(); // 5 System.out.println("weaponName: "+weaponName+" weaponDamage: "+weaponDamage); } } }
pom文件加入flatbuffer相关jar包
<dependency> <groupId>com.google.flatbuffers</groupId> <artifactId>flatbuffers-java</artifactId> <version>1.12.0</version> </dependency>
输出结果如下
300 150 Orc X: 1.0 Y: 2.0 Z: 3.0 13 weaponsLength: 2 secondWeaponName: Axe secondWeaponDamage: 5 weaponName: Axe weaponDamage: 5
flatbuffer原理
flatbuffer将数据存在一个一维数组当中,缓存在一个bytebuffer当中。一个flatbuffer对象在数组中被分为两部分,元数据部分和数据部分。元数据负责存放相对于中间部分的索引,数据部分存放真实的value。分割的节点为(pivot point)。它的将数据以及对应的数据位置都保存在一个线性的数组中。使用的时候只需要把byte流发送出去,解析的时候只需要根据保存的位置,截取对应的数值即可。
假设我们创建了一个Person对象,它的name是John,friendshipStatus是2.那么对应图中元数据部分第一个byte是1—>从中心点处数一个位置,开始的字符就是name的值即john。第二个byte是6,从中心点数6个位置值是2.
class Person { String name;//john int friendshipStatus;//2 Person spouse; List<Person>friends; }
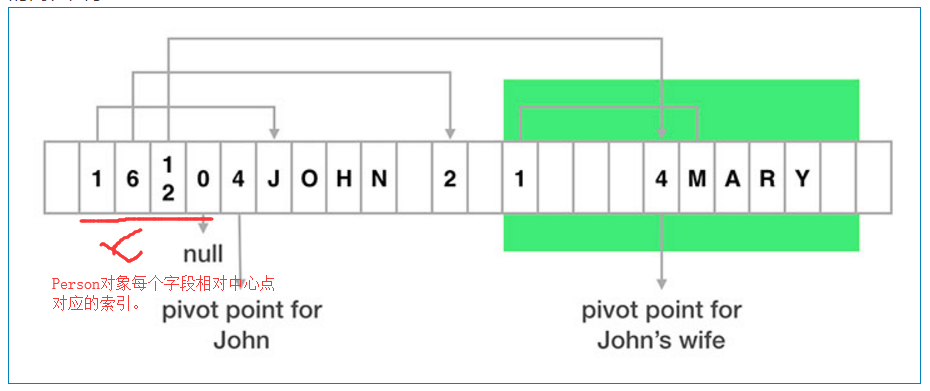
从图中可以看出来,flatbuffer将索引和数据文件存在一个一位数组中通过查找,还原对象,所以不需要打包和拆包的过程相对高效。
参考学习链接
1、//www.jianshu.com/p/8df23cd182ec
2、//www.jianshu.com/p/fa999434776a
3、//google.github.io/flatbuffers/flatbuffers_guide_tutorial.html

