ArrayList源码分析–jdk1.8
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
JDK1.8
ArrayList源码分析–jdk1.8
LinkedList源码分析–jdk1.8
HashMap源码分析–jdk1.8
AQS源码分析–jdk1.8
ReentrantLock源码分析–jdk1.8
ArrayList概述
1. ArrayList是可以动态扩容和动态删除冗余容量的索引序列,基于数组实现的集合。
2. ArrayList支持随机访问、克隆、序列化,元素有序且可以重复。
3. ArrayList初始默认长度10,超出扩容1.5倍,使用Object[]存储各种数据类型。
ArrayList数据结构
数据结构是集合的精华所在,数据结构往往也限制了集合的作用和侧重点,了解各种数据结构是我们分析源码的必经之路。
ArrayList的数据结构如下:
ArrayList源码分析
/* * 用数组实现的集合,支持随机访问,元素有序且可以重复 * RandomAccess(ArrayList) 支持快速随机访问,使用for循环更加快速 * LinkedList 使用 iterator迭代器更加 快速 * RandomAccess 这是一个标记接口,一般此标记接口用于 List 实现,以表明它们支持快速(通常是恒定时间)的随机访问。 * 该接口的主要目的是允许通用算法改变其行为,以便在应用于随机或顺序访问列表时提供良好的性能 * 包含类中的基础属性和3个构造方法 */ public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { /** * 默认长度 10 */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * 默认空的数组 */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * ArrayList中的元素 是Object[]类型的数组 */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access /** * 动态数组的实际大小 ,默认为0 * @serial */ private int size; /** * 最大数组容量2147483639 */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * 集合长度构造函数 */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } /** * 无参构造函数,设置元素数组为空 注意此时初始容量是0,而不是大家以为的 10 */ public ArrayList() { super(); this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } /** * 集合参数构造函数 */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); // 转化为数组 size = elementData.length; // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) //是否成功转化为Object类型数组 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); //不为Object数组的话就进行复制 } ArrayList继承和实现分析
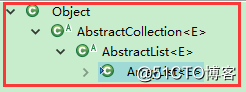
ArrayList extends AbstractList
AbstractList extends AbstractCollection
java中所有类都继承Object,所以ArrayList的继承结构如上图。
1. AbstractList是一个抽象类,实现了List<E>接口,List<E>定义了一些List通用方法,而AbstractList抽象类中可以有抽象方法,还可以有具体的实现方法,AbstractList实现接口中一些通用的方法,实现了基础的add/get/indexOf/iterator/subList/RandomAccessSubList方法,ArrayList再继承AbstractList,拿到通用基础的方法,然后自己在实现一些自己特有的方法,这样的好处是:让代码更简洁,继承结构最底层的类中通用的方法,减少重复代码。
2.ArrayList实现了List<E>、RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable接口
1)List<E>接口,ArrayList既然继承自AbstractList抽象类,而AbstractList已 经实现了List接口,那么ArrayList类为何还要再实现List接口呢?我们带着疑问往下看:
public class Demo1 extends ArrayList { public static void main(String[] args) { //返回[] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Demo1.class.getInterfaces())); } public class Demo2 implements Serializable { public static void main(String[] args) { //返回[interface java.io.Serializable] System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Demo2.class.getInterfaces())); } public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { Serializable c1 = new Demo1();//未显示实现接口 Serializable c2 = new Demo2();//显示实现接口 Serializable proxy2 = createProxy(c2); proxy2.foo(); Serializable proxy1 = createProxy(c1); proxy1.foo(); } private static <T> T createProxy(final T obj) { final InvocationHandler handler = new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { return method.invoke(obj, args); } }; //实现接口代理,Demo1报错,Demo2成功 //java.lang.ClassCastException: $Proxy1 cannot be cast to //example.Test$Serializable return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(), obj .getClass().getInterfaces(), handler); }可以看出这样这样设计是有道理的,因此,这并不是一个错误,很可能是作者Josh Bloch为了便于实现代理而精心设计的。
参考与:开发collection 的作者Josh说
2)RandomAccess接口,这是一个标记接口,一般此标记接口用于 List 实现,以表明它们支持快速(通常是恒定时间)的随机访问,该接口的主要目的是允许通用算法改变其行为,以便在应用于随机或顺序访问列表时提供良好的性能,实现了该接口的话使用普通的for循环来遍历,性能更高,而没有实现该接口的话,使用Iterator来迭代,这样性能更高,例如linkedList。所以这个标记性只是为了让我们知道我们用什么样的方式去获取数据性能更好
3)Cloneable接口,可以使用Object.Clone()方法。
4)Serializable接口,序列化接口,表明该类可以被序列化,什么是序列化?简单的说,就是能够从类变成字节流传输,反序列化,就是从字节流变成原来的类
ArrayList核心方法分析
1. add方法(4种重载实现)–增

1)add(E);//默认直接在末尾添加元素
/** * 新增元素 */ public boolean add(E e) { //赋值初始长度 或者扩容,新增元素,当前实际size+1的长度 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! //添加元素 elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** * 确保elemenData数组有合适的大小 * 如果元素为空,则复制长度默认为10 或者更大 * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 */ private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {//如果数组为空,则从size+1的值和默认值10中取最大的 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } /** * 确保elemenData数组有合适的大小 * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 * 如果长度大于元素长度则扩容 */ private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { //记录修改次数,迭代中不一致会触发fail-fast机制,因此在遍历中删除元素的正确做法应该是使用Iterator.remove() modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); //扩容 } /** * 扩容 */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 旧容量 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 新容量为旧容量的1.5倍 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 新容量小于参数指定容量,修改新容量 newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // 新容量大于最大容量 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 指定新容量 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 拷贝扩容 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } //如果小于0 就报错,如果大于最大值 则取最大值 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }2)add(int index, E element);//给指定下标,添加元素
/** * 给指定下标,添加元素 */ public void add(int index, E element) { //判断下标是否越界 rangeCheckForAdd(index); //赋值初始长度 或者扩容 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! //将源数组中从index位置开始后的size-index个元素统一后移一位 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); //赋值 elementData[index] = element; size++; } /** * 判断下标是否越界 */ private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } /** * src:源数组 * srcPos:源数组要复制的起始位置 * dest:目的数组 * destPos:目的数组放置的起始位置 * length:复制的长度 * 注意:src 和 dest都必须是同类型或者可以进行转换类型的数组 */ public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);3)addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);//添加Collection类型元素
/** * 按照指定collection的迭代器所返回的元素顺序,将该collection中的所有元素添加到此列表的尾部 */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount //将数组a[0,...,numNew-1]复制到数组elementData[size,...,size+numNew-1] System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }4)addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);//指定位置,添加Collection类型元素
/** * 从指定的位置开始,将指定collection中的所有元素插入到此列表中,新元素的顺序为指定collection的迭代器所返回的元素顺序 */ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //判断下标是否越界 rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; //先将数组elementData[index,...,index+numMoved-1]复制到elementData[index+numMoved,...,index+2*numMoved-1] //即,将源数组中从index位置开始的后numMoved个元素统一后移numNew位 if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }总结:
正常情况下会扩容1.5倍,特殊情况下(新扩展数组大小已经达到了最大值)则只取最大值。
2.remove方法(4种重载实现)–删

1)remove(int index); //根据指定下标 删除元素
/** * 根据指定下标 删除元素 */ public E remove(int index) { //判断索引是否越界 rangeCheck(index); modCount++; //获取旧元素 E oldValue = elementData(index); //将数组elementData中index位置之后的所有元素向前移一位 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); //将原数组最后一个位置置为null,由GC清理 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } 2)remove(Object o); //根据指定元素 删除元素
/** * 移除ArrayList中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在),ArrayList中允许存放重复的元素 */ public boolean remove(Object o) { // 由于ArrayList中允许存放null,因此下面通过两种情况来分别处理。 if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { //私有的移除方法,跳过index参数的边界检查以及不返回任何值 fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } /* * 根据下标快速删除元素 */ private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; //将数组elementData中index位置之后的所有元素向前移一位 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work } /** * 清空ArrayList,将全部的元素设为null,等待垃圾回收将这个给回收掉,所以叫clear */ public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; }
3)removeAll(Collection<?> c); //删除包含在指定容器c中的所有元素
/** * 删除ArrayList中包含在指定容器c中的所有元素 */ public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { //检查指定的对象c是否为空 Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false); } /** * 删除全部 * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 */ private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; int r = 0, w = 0; //读写双指针 boolean modified = false; try { for (; r < size; r++) if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) //判断指定容器c中是否含有elementData[r]元素 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, // even if c.contains() throws. if (r != size) { System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } if (w != size) { // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; }4)removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter); //按照一定规则过滤(删除)集合中的元素
/** * 按照一定规则过滤(删除)集合中的元素 * 如:idList.removeIf(id -> id == nul); * 去掉 List idList 集合中id 为 null 的 * @param filter * @return */ @Override public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) { Objects.requireNonNull(filter); // figure out which elements are to be removed // any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage // will leave the collection unmodified int removeCount = 0; final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size); final int expectedModCount = modCount; final int size = this.size; for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final E element = (E) elementData[i]; if (filter.test(element)) { removeSet.set(i); removeCount++; } } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } // shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0; if (anyToRemove) { final int newSize = size - removeCount; for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) { i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i); elementData[j] = elementData[i]; } for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) { elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work } this.size = newSize; if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } modCount++; } return anyToRemove; }总结:
remove函数用户移除指定下标的元素,此时会把指定下标到数组末尾的元素向前移动一个单位,并且会把数组最后一个元素设置为null,这样是为了方便之后将整个数组不被使用时,会被GC,可以作为小的技巧使用。
3.set方法–改
/** * 覆盖指定下标元素 */ public E set(int index, E element) { //判断索引是否越界 rangeCheck(index); //获取旧元素 E oldValue = elementData(index); //覆盖为新元素 elementData[index] = element; //返回旧元素 return oldValue; } /** * 判断下标是否越界 */ private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }4.get方法–查
/** * 返回指定索引的值 */ public E get(int index) { //判断索引是否越界 rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } /** * @author jiaxiaoxian * @date 2019年2月12日 * 返回下标元素的 值 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; }5.indexOf方法–查找下标
/** * 查找下标, 如果为null,直接和null比较,返回下标 */ public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } /** * 查找最后出现的下标,从大往下循环查找 */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }6.clone方法–克隆
/** * 复制,返回此ArrayList 的浅拷贝 */ public Object clone() { try { ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable throw new InternalError(e); } }7.trimToSize方法–删除冗余容量
/** * 判断数据实际容量大小,删除自动增长后冗余的容量 * 该方法用于回收多余的内存。也就是说一旦我们确定集合不在添加多余的元素之后,调用 trimToSize() 方法会将实现集合的数组大小刚好调整为集合元素的大小。 * 注意:该方法会花时间来复制数组元素,所以应该在确定不会添加元素之后在调用 */ public void trimToSize() { modCount++; if (size < elementData.length) { elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } }ArrayList总结
1)arrayList可以存放null,本质是Object[]类型的数组。 2)arrayList区别于数组的地方在于能够自动扩展大小,其中关键的方法就是gorw()方法。 3)arrayList由于本质是数组,所以它在数据的查询方面会很快,而在插入删除这些方面,性能下降很多,有移动很多数据才能达到应有的效果,而LinkedList则相反。 4)arrayList实现了RandomAccess,所以在遍历它的时候推荐使用for循环。 5)初始化数组时推荐给初始长度,反复扩容会增加时耗,影响性能效率。