【MySQL 原理分析】之 Explain & Trace 深入分析全模糊查询走索引的原理
- 2020 年 3 月 9 日
- 筆記
一、背景
今天,交流群有一位同学提出了一个问题。看下图:
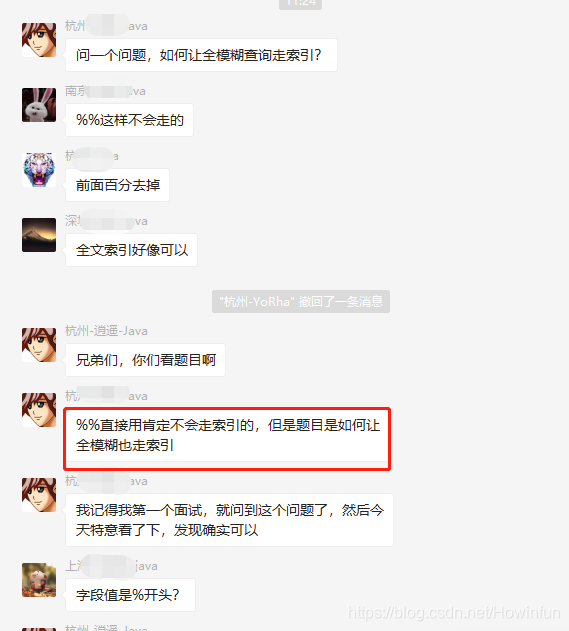
之后,这位同学确实也发了一个全模糊查询走索引的例子:

到这我们可以发现,这两个sql最大的区别是:一个是查询全字段(select *),而一个只查询主键(select id)。
此时,又有其他同学讲了其他方案:
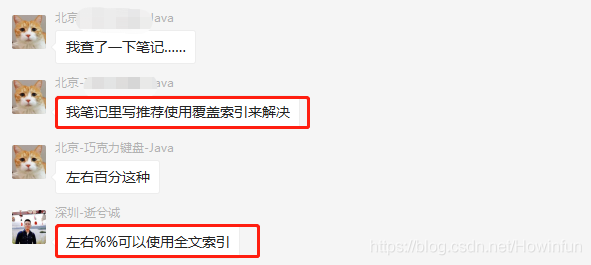
全文索引这个不用说,那是能让全模糊查询走索引的。但是索引覆盖这个方案,我觉得才是符合背景的:
1、因为提问的背景就是模糊查询字段是普通索引,而普通索引只查询主键就能用上覆盖索引。
2、并且背景中,就是只查询主键(ID)就显示用上索引了。
二、数据准备和场景重现
1、准备表和数据:
创建 user 表,给 phone 字段加了个普通索引:
CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `phone` varchar(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `index_phone` (`phone`) USING BTREE COMMENT 'phone索引' ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=200007 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;准备10万条数据意思意思:
delimiter ; CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `iniData`() begin declare i int; set i=1; while(i<=100000)do insert into user(name,age,phone) values('测试', i, 15627230000+i); set i=i+1; end while; end;; delimiter ; call iniData();2、执行 SQL ,查看执行计划:
explain select * from user where phone like '%156%'; explain select id from user where phone like '%156%';3、执行结果:
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SIMPLE | user | ALL | 99927 | 11.11 | Using where |
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SIMPLE | user | index | index_phone | 36 | 99927 | 11.11 | Using where; Using index |
我们可以发现,第二条 SQL 确实是显示用上了 index_phone 索引。
但是细心的同学可能会发现:possible_keys 竟然为空!有猫腻。。。
我这里先说一下 prossible_keys 和 key 的关系:
1、
possible_keys为可能使用的索引,而key是实际使用的索引;2、正常是:
key的索引,必然会包含在possible_keys中。
还有猫腻一点就是:使用索引和不使用索引读取的行数(rows)竟然是一样的!
三、验证和阶段性猜想
上面讲到,possible_keys 和 key 的关系,那么我们利用正常的走索引来验证一下。
下面的 SQL, 不是全模糊查询,而是右模糊查询,保证是一定走索引的,我们分别看看此时 possible_keys 和 key 的值:
explain select id from user where phone like '156%';执行结果:
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SIMPLE | user | range | index_phone | index_phone | 36 | 49963 | 100 | Using where; Using index |
这里太明显了:
1、possible_keys 里确实包含了 key 里的索引。
2、 并且rows 瞬间降到 49963,整整降了一倍,并且 filtered 也达到了 100。
阶段猜想:
1、首先,select id from user where phone like '%156%'; 因为覆盖索引而用上了索引 index_phone。
2、possible_keys 为 null,证明用不上索引的树形查找。很明显,select id from user where phone like '%156%'; 即使显示走了索引,但是读取行数 rows 和 select * from user where phone like '%156%'; 没有走索引的 rows 是一样的。
3、那么,我们可以猜测到,select id from user where phone like '%156%'; 即使因为覆盖索引而用上了 index_phone 索引,但是却没用上树形查找,只是正常顺序遍历了索引树。所以说,其实这两条 SQL 在表字段不多的情况下,查询性能应该差不了多少。
四、通过 Trace 分析来验证
我们分别利用 Trace 分析对于这两个 SQL 优化器是如何选择的。
1、查询全字段:
-- 开启优化器跟踪 set session optimizer_trace='enabled=on'; select * from user where phone like '%156%'; -- 查看优化器追踪 select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace;下面我们只看 TRACE 就行了:
{ "steps": [ { "join_preparation": { "select#": 1, "steps": [ { "expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `user`.`id` AS `id`,`user`.`name` AS `name`,`user`.`age` AS `age`,`user`.`phone` AS `phone` from `user` where (`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" } ] } }, { "join_optimization": { "select#": 1, "steps": [ { "condition_processing": { "condition": "WHERE", "original_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')", "steps": [ { "transformation": "equality_propagation", "resulting_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" }, { "transformation": "constant_propagation", "resulting_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" }, { "transformation": "trivial_condition_removal", "resulting_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" } ] } }, { "substitute_generated_columns": { } }, { "table_dependencies": [ { "table": "`user`", "row_may_be_null": false, "map_bit": 0, "depends_on_map_bits": [ ] } ] }, { "ref_optimizer_key_uses": [ ] }, { "rows_estimation": [ { "table": "`user`", "table_scan": { "rows": 99927, "cost": 289 } } ] }, { "considered_execution_plans": [ { "plan_prefix": [ ], "table": "`user`", "best_access_path": { "considered_access_paths": [ { "rows_to_scan": 99927, "access_type": "scan", // 顺序扫描 "resulting_rows": 99927, "cost": 20274, "chosen": true } ] }, "condition_filtering_pct": 100, "rows_for_plan": 99927, "cost_for_plan": 20274, "chosen": true } ] }, { "attaching_conditions_to_tables": { "original_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')", "attached_conditions_computation": [ ], "attached_conditions_summary": [ { "table": "`user`", "attached": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" } ] } }, { "refine_plan": [ { "table": "`user`" } ] } ] } }, { "join_execution": { "select#": 1, "steps": [ ] } } ] }2、只查询主键
set session optimizer_trace='enabled=on'; select id from user where phone like '%156%'; -- 查看优化器追踪 select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace;下面我们继续只看 TRACE 就行了:
{ "steps": [ { "join_preparation": { "select#": 1, "steps": [ { "expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `user`.`id` AS `id` from `user` where (`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" } ] } }, { "join_optimization": { "select#": 1, "steps": [ { "condition_processing": { "condition": "WHERE", "original_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')", "steps": [ { "transformation": "equality_propagation", "resulting_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" }, { "transformation": "constant_propagation", "resulting_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" }, { "transformation": "trivial_condition_removal", "resulting_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" } ] } }, { "substitute_generated_columns": { } }, { "table_dependencies": [ { "table": "`user`", "row_may_be_null": false, "map_bit": 0, "depends_on_map_bits": [ ] } ] }, { "ref_optimizer_key_uses": [ ] }, { "rows_estimation": [ { "table": "`user`", "table_scan": { "rows": 99927, "cost": 289 } } ] }, { "considered_execution_plans": [ { "plan_prefix": [ ], "table": "`user`", "best_access_path": { "considered_access_paths": [ { "rows_to_scan": 99927, "access_type": "scan", // 顺序扫描 "resulting_rows": 99927, "cost": 20274, "chosen": true } ] }, "condition_filtering_pct": 100, "rows_for_plan": 99927, "cost_for_plan": 20274, "chosen": true } ] }, { "attaching_conditions_to_tables": { "original_condition": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')", "attached_conditions_computation": [ ], "attached_conditions_summary": [ { "table": "`user`", "attached": "(`user`.`phone` like '%156%')" } ] } }, { "refine_plan": [ { "table": "`user`" } ] } ] } }, { "join_execution": { "select#": 1, "steps": [ ] } } ] }好了,到这里我们可以发现,在 Trace 分析里面,都没显示优化器为这两个 SQL 实际选择了什么索引,而只是显示了都是用了 顺序扫描 的方式去查找数据。
可能唯一不同点就是:一个使用了主键索引的全表扫描,而另外一个是使用了普通索引的全表扫描;但是两个都没用上树形查找,也就是没用上 B+Tree 的特性来提升查询性能。
六、最后总结
1、当全模糊查询的 SQL 只查询主键作为结果集时,因为覆盖索引,会用上查询字段对应的索引。
2、即使用上了索引,但是却没用上树形查找的特性,只是正常的顺序遍历。
3、而正常的全表扫描也是主键索引的顺序遍历,所以说,其实这两者的性能其实是差不多的。


