Redis(十一):哨兵模式架构设计分析
- 2020 年 3 月 8 日
- 筆記
业务最初的应用场景中,我们也许使用单机redis就可以应付业务要求,但并非一直可行。
比如单机的读写能力问题,单机的可用性问题,单机的数据安全性问题。这些都是许多互联网应用经常会遇到的问题,也基本上都有一套理论去解决它,只是百花齐放。
哨兵是Redis中解决高可用问题的解决方案之一,我们就一起来看看 Redis是如何实现的吧!不过此方案,仅提供思路供参考,不要以此为标准方案。
前面介绍的主从复制功能,可以说已经一定程度上解决了数据安全性问题问题,即有了备份数据,我们可以可以做读写分离了。只是,可用性问题还未解决,即当 master 宕机或出现其他故障时,整个写服务就不可用了。解决方法是,手动操作,要么重启master使其恢复服务,要么把master切换为其他slave机器。
如果服务的可用性需要人工介入的话,那就算不得高可用了,所以我们需要一个自动处理机制。这就是哨兵模式。
一、哨兵系统介绍
哨兵系统要解决的问题核心,自然是高可用问题。而如何解决,则是其设计问题。而最终呈现给用户的,应该一个个的功能单元,即其提供的能力。如下:
监控(Monitoring): Sentinel 会不断地检查你的主服务器和从服务器是否运作正常。
提醒(Notification): 当被监控的某个 Redis 服务器出现问题时, Sentinel 可以通过 API 向管理员或者其他应用程序发送通知。
自动故障迁移(Automatic failover): 当一个主服务器不能正常工作时, Sentinel 会开始一次自动故障迁移操作, 它会将失效主服务器的其中一个从服务器升级为新的主服务器, 并让失效主服务器的其他从服务器改为复制新的主服务器;
配置提供者: Sentinel充当客户端服务发现的授权来源:客户端连接到Sentinels,以询问负责给定服务的当前Redis主服务器的地址。 如果发生故障转移,Sentinels将报告新地址。(这也是客户端接入入口)
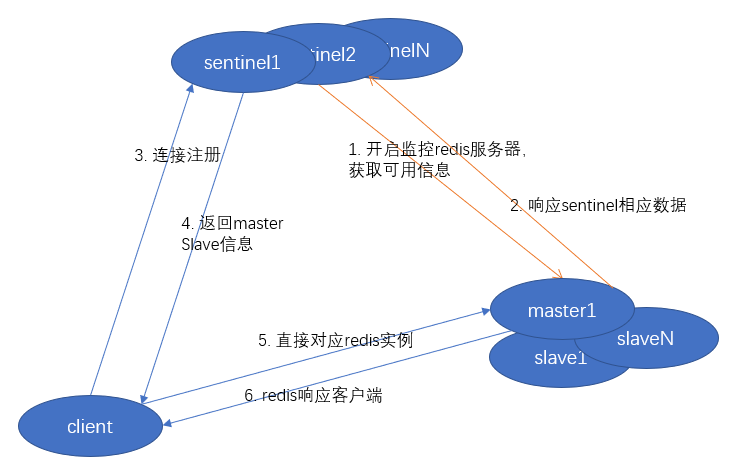
哨兵系统的架构图如下:
(一)服务端架构

(二)请求处理流程图
二、哨兵系统搭建步骤
哨兵可以搭建在 redis服务所在机器,也可以在单独的机器实例上搭建。
1. 有多个在运行的 redis master/slave 实例;
主从服务的搭建,slaveof 设置,请参照主从配置篇。
2. 编写哨兵配置文件;
# Example sentinel.conf # 定义sentinel 服务端口号 port 26379 # 针对 使用端口映射的方式的启动,指定ip:port # sentinel announce-ip <ip> # sentinel announce-port <port> # 工作目录定义 dir /tmp # 要监视的redis master 定义, 可配置多个 master-name 不同即可 # sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum> sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2 # 定义master/slave 的密码,要求同一主从服务所有密码必须保持一致 # sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password> # 定义master 不可达持续多少毫秒后开始定义为节点下线,默认30s sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000 # sentinel parallel-syncs <master-name> <numslaves> # 在故障转移期间同时与新的master同步的slave数量 sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1 # 定义进行故障转移的超时时间,默认3分钟 sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000 # 发生故障转移时调用的通知脚本,被调用时会传递两个参数: eventType, eventDescription # sentinel notification-script mymaster /var/redis/notify.sh # master 变更时调用脚本配置 # 调用时会传递如下参数 # <master-name> <role> <state> <from-ip> <from-port> <to-ip> <to-port> # sentinel client-reconfig-script mymaster /var/redis/reconfig.sh
3. 启动哨兵节点;
# 使用 redis-sentinel 程序启动, 这个程序不一定会有,需要自己编译 redis-sentinel /path/to/sentinel.conf # 使用 redis-server 程序启动, 一定可用 # 测试时可以加上 --protected-mode no, 在不设置密码情况下访问redis redis-server /path/to/sentinel.conf --sentinel
4. 验证哨兵运行情况
通过redis-cli 连接到sentinel 服务内部: redis-cli -p 26379 # 连接到sentinel info sentinel # 查看哨兵信息 SENTINEL slaves mymaster # 查看master下的slave服务器情况 SENTINEL sentinels mymaster # 查看master的哨兵服务器列表 SENTINEL get-master-addr-by-name mymaster # 获取master地址信息
5. 故障模拟
将master节点关闭后,等待一段时间,再获取master地址看看。master已经切换了。
SENTINEL get-master-addr-by-name mymaster # 获取master地址信息
三、客户端使用哨兵系统
哨兵系统搭建好之后,就可以提供服务了。那么,如何提供服务呢?从最前面的两张架构图中,我们可以看到,sentinel 差不多是作为一个配置中心或者存在的,它只会为客户端提供master/slave的相关信息,而并不会直接代替redis实例进行存取操作。所以,哨兵模式,需要客户端做更多的工作,原来的直接连接redis变为间接从sentinel获取信息,再连接,还要维护可能的信息变更。
当然,这种工作一般是要交给sdk做的,实现原理也差不多,我们就以 jedis 作为切入点,详解下客户端如何使用sentinel.
1. 引入pom依赖
<dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>2.9.0</version> </dependency>
2. 单元测试
public class RedisSentinelTest { @Test public void testSentinel() throws Exception { String masterName = "mymaster"; // 只需设置sentinel信息,真实的 redis实例信息由 sentinel 提供 Set<String> sentinels = new HashSet<>(); sentinels.add("127.0.0.1:26379"); sentinels.add("127.0.0.1:26378"); sentinels.add("127.0.0.1:26377"); JedisSentinelPool pool = new JedisSentinelPool(masterName, sentinels); Jedis jedis = pool.getResource(); String key = "key1"; String value = "Value1"; // set get 测试哨兵系统是否可用 jedis.set(key, value); System.out.println("set a value to Redis over. " + key + "->" + value); value = jedis.get("key1"); System.out.println("get a value from Redis over. " + key + "->" + value); pool.close(); } }
3. sentinel 处理过程解析
jedis的sdk中已经将哨兵封装得和普通的redis实例请求差不多了,所以,我们需要深入理解下其处理过程。
首先是在初始化 JedisSentinelPool 时,其会与sentinel列表中选择一个与其建立连接:
// redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool#JedisSentinelPool public JedisSentinelPool(String masterName, Set<String> sentinels) { this(masterName, sentinels, new GenericObjectPoolConfig(), Protocol.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT, null, Protocol.DEFAULT_DATABASE); } public JedisSentinelPool(String masterName, Set<String> sentinels, final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, int timeout, final String password, final int database) { this(masterName, sentinels, poolConfig, timeout, timeout, password, database); } public JedisSentinelPool(String masterName, Set<String> sentinels, final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, final int timeout, final int soTimeout, final String password, final int database) { this(masterName, sentinels, poolConfig, timeout, soTimeout, password, database, null); } public JedisSentinelPool(String masterName, Set<String> sentinels, final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, final int connectionTimeout, final int soTimeout, final String password, final int database, final String clientName) { this.poolConfig = poolConfig; this.connectionTimeout = connectionTimeout; this.soTimeout = soTimeout; this.password = password; this.database = database; this.clientName = clientName; // 从sentinel中获取master信息,关键 HostAndPort master = initSentinels(sentinels, masterName); // 初始化连接池,非本文重点 initPool(master); } private HostAndPort initSentinels(Set<String> sentinels, final String masterName) { HostAndPort master = null; boolean sentinelAvailable = false; log.info("Trying to find master from available Sentinels..."); // 依次遍历 sentinels, 直到找到一个可用的sentinel for (String sentinel : sentinels) { final HostAndPort hap = HostAndPort.parseString(sentinel); log.fine("Connecting to Sentinel " + hap); Jedis jedis = null; try { jedis = new Jedis(hap.getHost(), hap.getPort()); // 向sentinel发送命令请求: SENTINEL get-master-addr-by-name mymaster, 获取master地址信息 List<String> masterAddr = jedis.sentinelGetMasterAddrByName(masterName); // connected to sentinel... sentinelAvailable = true; if (masterAddr == null || masterAddr.size() != 2) { log.warning("Can not get master addr, master name: " + masterName + ". Sentinel: " + hap + "."); continue; } master = toHostAndPort(masterAddr); log.fine("Found Redis master at " + master); break; } catch (JedisException e) { // resolves #1036, it should handle JedisException there's another chance // of raising JedisDataException log.warning("Cannot get master address from sentinel running @ " + hap + ". Reason: " + e + ". Trying next one."); } finally { if (jedis != null) { jedis.close(); } } } if (master == null) { if (sentinelAvailable) { // can connect to sentinel, but master name seems to not // monitored throw new JedisException("Can connect to sentinel, but " + masterName + " seems to be not monitored..."); } else { throw new JedisConnectionException("All sentinels down, cannot determine where is " + masterName + " master is running..."); } } log.info("Redis master running at " + master + ", starting Sentinel listeners..."); // 为每个 sentinel, 建立一个监听线程, 监听 sentinel 的 +switch-master 信息 // 当master发生变化时,重新初始化连接池 for (String sentinel : sentinels) { final HostAndPort hap = HostAndPort.parseString(sentinel); MasterListener masterListener = new MasterListener(masterName, hap.getHost(), hap.getPort()); // whether MasterListener threads are alive or not, process can be stopped masterListener.setDaemon(true); masterListeners.add(masterListener); masterListener.start(); } return master; } // 每个 sentinel 监听线程事务处理流程如下 // redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool.MasterListener#run @Override public void run() { running.set(true); while (running.get()) { j = new Jedis(host, port); try { // double check that it is not being shutdown if (!running.get()) { break; } // SUBSCRIBE +switch-master j.subscribe(new JedisPubSub() { @Override public void onMessage(String channel, String message) { log.fine("Sentinel " + host + ":" + port + " published: " + message + "."); String[] switchMasterMsg = message.split(" "); // 格式为: masterName xx xx masterHost masterPort if (switchMasterMsg.length > 3) { if (masterName.equals(switchMasterMsg[0])) { initPool(toHostAndPort(Arrays.asList(switchMasterMsg[3], switchMasterMsg[4]))); } else { log.fine("Ignoring message on +switch-master for master name " + switchMasterMsg[0] + ", our master name is " + masterName); } } else { log.severe("Invalid message received on Sentinel " + host + ":" + port + " on channel +switch-master: " + message); } } }, "+switch-master"); } catch (JedisConnectionException e) { if (running.get()) { log.log(Level.SEVERE, "Lost connection to Sentinel at " + host + ":" + port + ". Sleeping 5000ms and retrying.", e); try { Thread.sleep(subscribeRetryWaitTimeMillis); } catch (InterruptedException e1) { log.log(Level.SEVERE, "Sleep interrupted: ", e1); } } else { log.fine("Unsubscribing from Sentinel at " + host + ":" + port); } } finally { j.close(); } } }
从上面流程我们也就可以看出客户端是如何处理 sentinel 和 redis 的关系的了。简单来说就是通过 sentinel get-master-addr-by-name xxx, 获取master地址信息,然后连接过去就可以了。在master发生变化时,通过pub/sub订阅sentinel信息,从而进行连接池的重置。
这个连接池又是如何处理的呢?我们可以简单看一下:
// redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool#initPool private void initPool(HostAndPort master) { if (!master.equals(currentHostMaster)) { currentHostMaster = master; if (factory == null) { factory = new JedisFactory(master.getHost(), master.getPort(), connectionTimeout, soTimeout, password, database, clientName, false, null, null, null); initPool(poolConfig, factory); } else { factory.setHostAndPort(currentHostMaster); // although we clear the pool, we still have to check the // returned object // in getResource, this call only clears idle instances, not // borrowed instances internalPool.clear(); } log.info("Created JedisPool to master at " + master); } } // redis.clients.util.Pool#initPool public void initPool(final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, PooledObjectFactory<T> factory) { if (this.internalPool != null) { try { closeInternalPool(); } catch (Exception e) { } } this.internalPool = new GenericObjectPool<T>(factory, poolConfig); }
当要向redis写入数据时,会先从连接池里获取一个连接实例,其池化框架使用的是 GenericObjectPool 的通用能力,调用 JedisFactory 的 makeObject() 方法进行创建 :
// redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool#getResource @Override public Jedis getResource() { while (true) { // 调用父类方法获取实例 Jedis jedis = super.getResource(); jedis.setDataSource(this); // get a reference because it can change concurrently final HostAndPort master = currentHostMaster; final HostAndPort connection = new HostAndPort(jedis.getClient().getHost(), jedis.getClient() .getPort()); // host:port 比对,如果master未变化,说明获取到了正确的连接,返回 if (master.equals(connection)) { // connected to the correct master return jedis; } // 如果master 发生了切换,则将当前连接释放,继续尝试获取master连接 else { returnBrokenResource(jedis); } } } // redis.clients.util.Pool#getResource public T getResource() { try { return internalPool.borrowObject(); } catch (NoSuchElementException nse) { throw new JedisException("Could not get a resource from the pool", nse); } catch (Exception e) { throw new JedisConnectionException("Could not get a resource from the pool", e); } } // org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPool#borrowObject() @Override public T borrowObject() throws Exception { return borrowObject(getMaxWaitMillis()); } // org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPool#borrowObject(long) public T borrowObject(final long borrowMaxWaitMillis) throws Exception { assertOpen(); final AbandonedConfig ac = this.abandonedConfig; if (ac != null && ac.getRemoveAbandonedOnBorrow() && (getNumIdle() < 2) && (getNumActive() > getMaxTotal() - 3) ) { removeAbandoned(ac); } PooledObject<T> p = null; // Get local copy of current config so it is consistent for entire // method execution final boolean blockWhenExhausted = getBlockWhenExhausted(); boolean create; final long waitTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while (p == null) { create = false; p = idleObjects.pollFirst(); if (p == null) { // 没有获取到连接时,主动创建一个 p = create(); if (p != null) { create = true; } } if (blockWhenExhausted) { if (p == null) { if (borrowMaxWaitMillis < 0) { p = idleObjects.takeFirst(); } else { p = idleObjects.pollFirst(borrowMaxWaitMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } if (p == null) { throw new NoSuchElementException( "Timeout waiting for idle object"); } } else { if (p == null) { throw new NoSuchElementException("Pool exhausted"); } } if (!p.allocate()) { p = null; } if (p != null) { try { // 确保激活当前数据库 factory.activateObject(p); } catch (final Exception e) { try { destroy(p); } catch (final Exception e1) { // Ignore - activation failure is more important } p = null; if (create) { final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException( "Unable to activate object"); nsee.initCause(e); throw nsee; } } if (p != null && (getTestOnBorrow() || create && getTestOnCreate())) { boolean validate = false; Throwable validationThrowable = null; try { validate = factory.validateObject(p); } catch (final Throwable t) { PoolUtils.checkRethrow(t); validationThrowable = t; } if (!validate) { try { destroy(p); destroyedByBorrowValidationCount.incrementAndGet(); } catch (final Exception e) { // Ignore - validation failure is more important } p = null; if (create) { final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException( "Unable to validate object"); nsee.initCause(validationThrowable); throw nsee; } } } } } updateStatsBorrow(p, System.currentTimeMillis() - waitTime); return p.getObject(); } /** * Attempts to create a new wrapped pooled object. * <p> * If there are {@link #getMaxTotal()} objects already in circulation * or in process of being created, this method returns null. * * @return The new wrapped pooled object * * @throws Exception if the object factory's {@code makeObject} fails */ private PooledObject<T> create() throws Exception { int localMaxTotal = getMaxTotal(); // This simplifies the code later in this method if (localMaxTotal < 0) { localMaxTotal = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } // Flag that indicates if create should: // - TRUE: call the factory to create an object // - FALSE: return null // - null: loop and re-test the condition that determines whether to // call the factory Boolean create = null; while (create == null) { synchronized (makeObjectCountLock) { final long newCreateCount = createCount.incrementAndGet(); if (newCreateCount > localMaxTotal) { // The pool is currently at capacity or in the process of // making enough new objects to take it to capacity. createCount.decrementAndGet(); if (makeObjectCount == 0) { // There are no makeObject() calls in progress so the // pool is at capacity. Do not attempt to create a new // object. Return and wait for an object to be returned create = Boolean.FALSE; } else { // There are makeObject() calls in progress that might // bring the pool to capacity. Those calls might also // fail so wait until they complete and then re-test if // the pool is at capacity or not. makeObjectCountLock.wait(); } } else { // The pool is not at capacity. Create a new object. makeObjectCount++; create = Boolean.TRUE; } } } if (!create.booleanValue()) { return null; } final PooledObject<T> p; try { // 调用指定factory的 makeObject() 方法 p = factory.makeObject(); } catch (final Exception e) { createCount.decrementAndGet(); throw e; } finally { synchronized (makeObjectCountLock) { makeObjectCount--; makeObjectCountLock.notifyAll(); } } final AbandonedConfig ac = this.abandonedConfig; if (ac != null && ac.getLogAbandoned()) { p.setLogAbandoned(true); } createdCount.incrementAndGet(); allObjects.put(new IdentityWrapper<T>(p.getObject()), p); return p; } // 使用 JedisFactory 创建一个连接到 master // redis.clients.jedis.JedisFactory#makeObject @Override public PooledObject<Jedis> makeObject() throws Exception { final HostAndPort hostAndPort = this.hostAndPort.get(); final Jedis jedis = new Jedis(hostAndPort.getHost(), hostAndPort.getPort(), connectionTimeout, soTimeout, ssl, sslSocketFactory, sslParameters, hostnameVerifier); try { jedis.connect(); // 如果存在密码设置,则进行 auth xxx 操作 // redis 配置: requirepass xxx if (null != this.password) { jedis.auth(this.password); } if (database != 0) { jedis.select(database); } if (clientName != null) { jedis.clientSetname(clientName); } } catch (JedisException je) { jedis.close(); throw je; } return new DefaultPooledObject<Jedis>(jedis); } // redis.clients.jedis.JedisFactory#activateObject @Override public void activateObject(PooledObject<Jedis> pooledJedis) throws Exception { final BinaryJedis jedis = pooledJedis.getObject(); if (jedis.getDB() != database) { jedis.select(database); } }
获取到client连接后,主可以任意地通过网络io与真实redis进行交互了。哨兵也不会成为性能问题了。
四、思考
哨兵模式的出现,仅为了解决单机的高可用问题,而并不会解决单机容量问题(集群模式会处理这个问题)。在当前的互联网环境中,应用面也许没有那么广。但思路是值得借鉴的。
Sentinel 在配置时只需配置master地址即可,其slave信息,sentinel信息,都是通过master来推断的。所以,一定要确保在启动时master是可用的,否则系统本身必须无法启动。
如果redis中设置了密码,则要求必须保持全部一致,这在一定程度上会有些误会。
redis Sentinel 本身是一个对等集群系统,连接任意节点结果都是一样的,节点间保持通过pub/sub两两通信。