从壹开始学习NetCore 45 ║ 终于解决了事务问题
- 2019 年 10 月 3 日
- 筆記
一、项目说明
哈喽,又来写文章了,原来放假可以这么爽,可以学习和分享,?嘘,大家要好好的工作哟。昨天发表的问题,嗯,给我留下了一点点冲击,夜里辗转反侧,想了很多,从好到坏再到好再到坏,从希望到失望再到希望再到失望,想起来当年高四了,不想解释什么了,四年后再见❤,不说废话,直接说说今天的内容吧。
今天这个内容,还是来源于两个多月前,我的项目的一个 issue ,当时说到了如何使用事务,(为啥要使用事务,我就不多说了,相信肯定都知道,还有那个每次面试都问的题,事务四大特性。不知道还有没有小伙伴记得,不,是都记得!)我一直也是各种尝试,直到前几天也尝试了几个办法,还是无果,然后又和 sqlsugar 的作者凯旋讨论这个问题。他说只要能保证每次http 的scope 会话中的 sugar client 是同一个就行了,而且又不能把 client 设置为单例,天天看着这个 issue,心里难免波澜,终于哟,昨天群管 @大黄瓜 小伙伴研究出来了,我很开心,表扬下他,下边就正式说说在我的项目中,如果使用事务的:
项目介绍: netcore 2.2 + Sqlsugar 5.0 + UnitOfWork + async Repository + Service 。
投稿作者:QQ群:大黄瓜(博客园地址不详)
项目已经修改,不仅仅实现了单一仓储服务的事务提交,而且也可以跨类跨仓储服务来实现事务,欢迎大家下载与公测,没问题,我会merge 到 master。
为了防止大家不必要的更新错误,我新建了一个分支,大家自己去看分支即可——https://github.com/anjoy8/Blog.Core/tree/Trans1.0 。
Tips:
我认为 sqlsugar 还是很不错,很好用,当然,不能用万能来形容客观事物,这本身就不是一个成年人该有的思维,在我推广 sqlsugar 这一年来,我也一直给凯旋提一些需求和Bug,他都特别及时的解决了,而且使用上也很顺手,目前已经实现了跨服务事务操作了,下一步就是在blog.core 中,使用主从数据库,分离了,加油。
二、重新设计SqlSugarClient
1、创建工作单元接口
首先我们需要在 Blog.Core.IRepository 层,创建一个文件夹 UnitOfWork ,然后创建接口 IUnitOfWork.cs ,用来对工作单元进行定义相应的行为操作:
public interface IUnitOfWork { // 创建 sqlsugar client 实例 ISqlSugarClient GetDbClient(); // 开始事务 void BeginTran(); // 提交事务 void CommitTran(); // 回滚事务 void RollbackTran(); }
2、对 UnitOfWork 接口进行实现
在 Blog.Core.Repository 层,创建一个文件夹 UnitOfWork,然后创建事务接口实现类 UnitOfWork.cs ,来对事务行为做实现。
public class UnitOfWork : IUnitOfWork { private readonly ISqlSugarClient _sqlSugarClient; // 注入 sugar client 实例 public UnitOfWork(ISqlSugarClient sqlSugarClient) { _sqlSugarClient = sqlSugarClient; } // 保证每次 scope 访问,多个仓储类,都用一个 client 实例 // 注意,不是单例模型!!! public ISqlSugarClient GetDbClient() { return _sqlSugarClient; } public void BeginTran() { GetDbClient().Ado.BeginTran(); } public void CommitTran() { try { GetDbClient().Ado.CommitTran(); // } catch (Exception ex) { GetDbClient().Ado.RollbackTran(); } } public void RollbackTran() { GetDbClient().Ado.RollbackTran(); } }
具体的内容,很简单,这里不过多解释。
3、用 UnitOfWork 接管 SqlguarClient
在基类泛型仓储类 BaseRepository<TEntity> 中,我们修改构造函数,注入工作单元接口,用来将 sqlsugar 实例统一起来,不是每次都 new,而且通过工作单元来控制:
private ISqlSugarClient _db; private readonly IUnitOfWork _unitOfWork; // 构造函数,通过 unitofwork,来控制sqlsugar 实例 public BaseRepository(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork) { _unitOfWork = unitOfWork; _db = unitOfWork.GetDbClient(); // 好像这个可以去掉,先保留 DbContext.Init(BaseDBConfig.ConnectionString, (DbType)BaseDBConfig.DbType); }
你可以对比下以前的代码,就知道了,这么做的目的,就是把 sugar client 统一起来,这样就能保证每次一个scope ,都能是同一个实例。
4、修改每一个仓储的构造函数
上边我们为了实现对 sugar client的控制,在基类仓储的构造函数中,注入了IUnitOfWork,但是这样会导致子类的仓储报错,毕竟父类构造函数修改了嘛,所以目前有两个方案:
1、去掉子仓储,只使用泛型基类仓储,在service层中,使用 private readonly IRepository<实体类> _repository; 这种方法。
2、去一一的修改子仓储,增加构造函数,将 IUnitOfWork 传给父类,具体的看我的代码即可:
5、依赖注入 ISqlSugarClient
这个是肯定的,大家还记得上边说的呢,我们要在 BaseRepository 中,注入 ISqlSugarClient ,所以就必须依赖注入:
// 这里我不是引用了命名空间,因为如果引用命名空间的话,会和Microsoft的一个GetTypeInfo存在二义性,所以就直接这么使用了。 services.AddScoped<SqlSugar.ISqlSugarClient>(o => { return new SqlSugar.SqlSugarClient(new SqlSugar.ConnectionConfig() { ConnectionString = BaseDBConfig.ConnectionString,//必填, 数据库连接字符串 DbType = (SqlSugar.DbType)BaseDBConfig.DbType,//必填, 数据库类型 IsAutoCloseConnection = true,//默认false, 时候知道关闭数据库连接, 设置为true无需使用using或者Close操作 IsShardSameThread=true,//共享线程 InitKeyType = SqlSugar.InitKeyType.SystemTable//默认SystemTable, 字段信息读取, 如:该属性是不是主键,标识列等等信息 }); });
这里有一个小知识点,就是我们的 IUnitOfWork 已经随着 仓储层 依赖注入了,就不许单独注入了,是不是这个时候感觉使用 Autofac 很方便?
到了这里,修改就完成了,下边就是如何使用了。
三、正式使用事务
1、直接操作跨 Service 事务
现在我们就可以使用如何使用事务了,第一个简单粗暴的,就是全部写到 controller 里,我已经写好了一个demo,大家来看看:
// 依赖注入 public TransactionController(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork, IPasswordLibServices passwordLibServices, IGuestbookServices guestbookServices) { _unitOfWork = unitOfWork; _passwordLibServices = passwordLibServices; _guestbookServices = guestbookServices; }
[HttpGet] public async Task<IEnumerable<string>> Get() { try { Console.WriteLine($""); //开始事务 Console.WriteLine($"Begin Transaction"); _unitOfWork.BeginTran(); Console.WriteLine($""); var passwords = await _passwordLibServices.Query(); // 第一次密码表的数据条数 Console.WriteLine($"first time : the count of passwords is :{passwords.Count}"); // 向密码表添加一条数据 Console.WriteLine($"insert a data into the table PasswordLib now."); var insertPassword = await _passwordLibServices.Add(new PasswordLib() { IsDeleted = false, plAccountName = "aaa", plCreateTime = DateTime.Now }); // 第二次查看密码表有多少条数据,判断是否添加成功 passwords = await _passwordLibServices.Query(d => d.IsDeleted == false); Console.WriteLine($"second time : the count of passwords is :{passwords.Count}"); //...... Console.WriteLine($""); var guestbooks = await _guestbookServices.Query(); Console.WriteLine($"first time : the count of guestbooks is :{guestbooks.Count}"); int ex = 0; // 出现了一个异常! Console.WriteLine($"nThere's an exception!!"); int throwEx = 1 / ex; Console.WriteLine($"insert a data into the table Guestbook now."); var insertGuestbook = await _guestbookServices.Add(new Guestbook() { username = "bbb", blogId = 1, createdate = DateTime.Now, isshow = true }); guestbooks = await _guestbookServices.Query(); Console.WriteLine($"second time : the count of guestbooks is :{guestbooks.Count}"); //事务提交 _unitOfWork.CommitTran(); } catch (Exception) { // 事务回滚 _unitOfWork.RollbackTran(); var passwords = await _passwordLibServices.Query(); // 第三次查看密码表有几条数据,判断是否回滚成功 Console.WriteLine($"third time : the count of passwords is :{passwords.Count}"); var guestbooks = await _guestbookServices.Query(); Console.WriteLine($"third time : the count of guestbooks is :{guestbooks.Count}"); } return new string[] { "value1", "value2" }; }
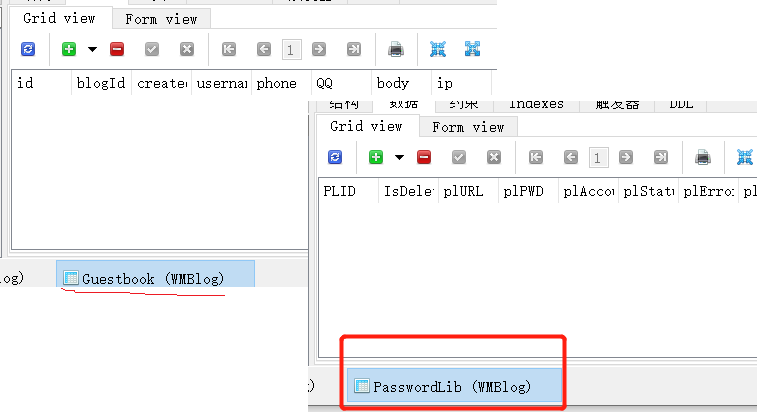
项目的过程,在上边注释已经说明了,大家可以看一下,很简单,就是查询,添加,再查询,判断是否操作成功,那现在我们就测试一下,数据库表是空的:
然后我们执行方法,动图如下: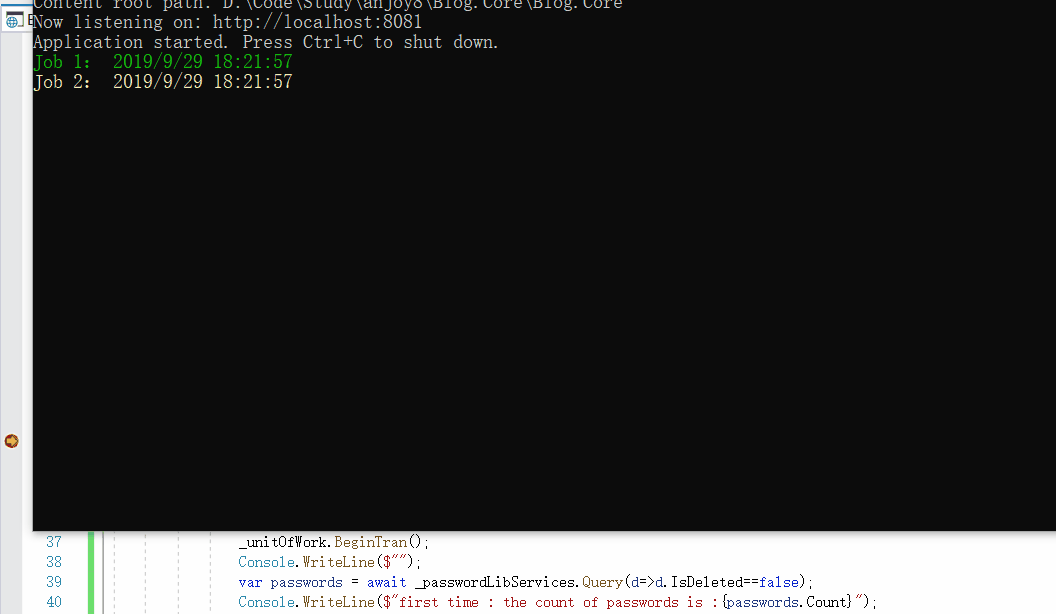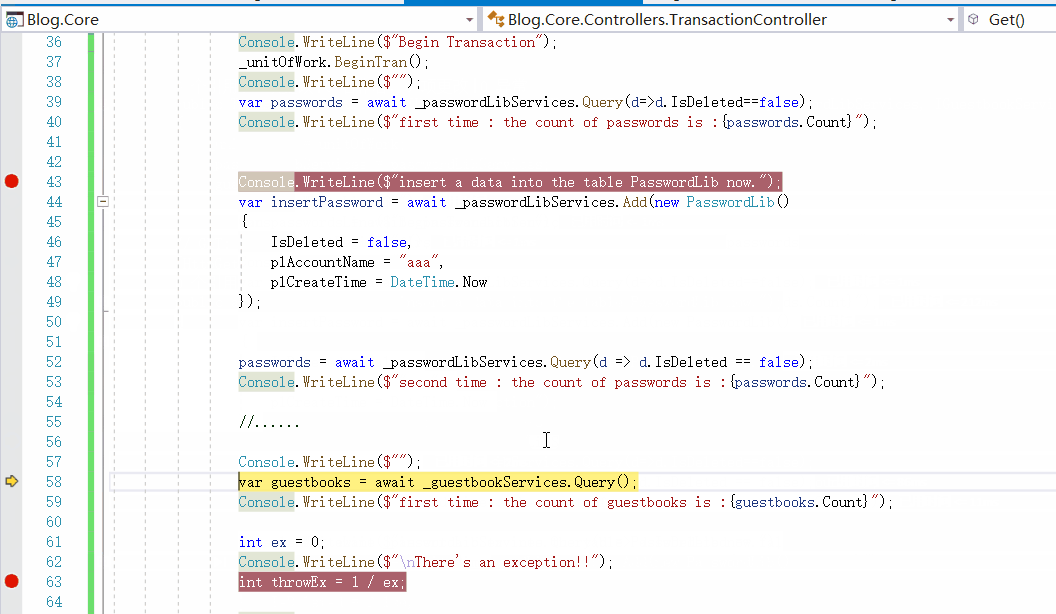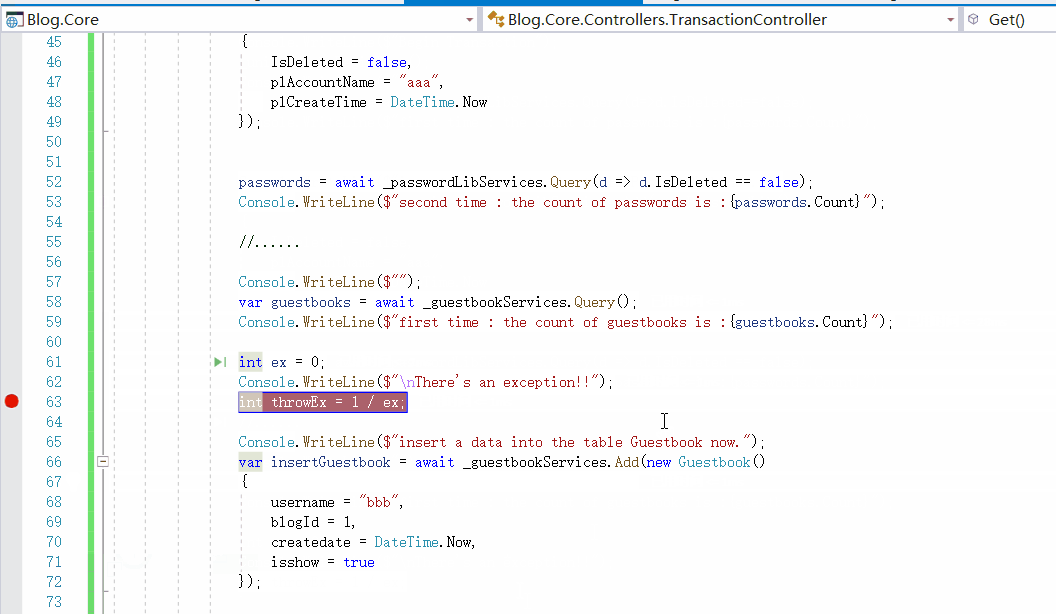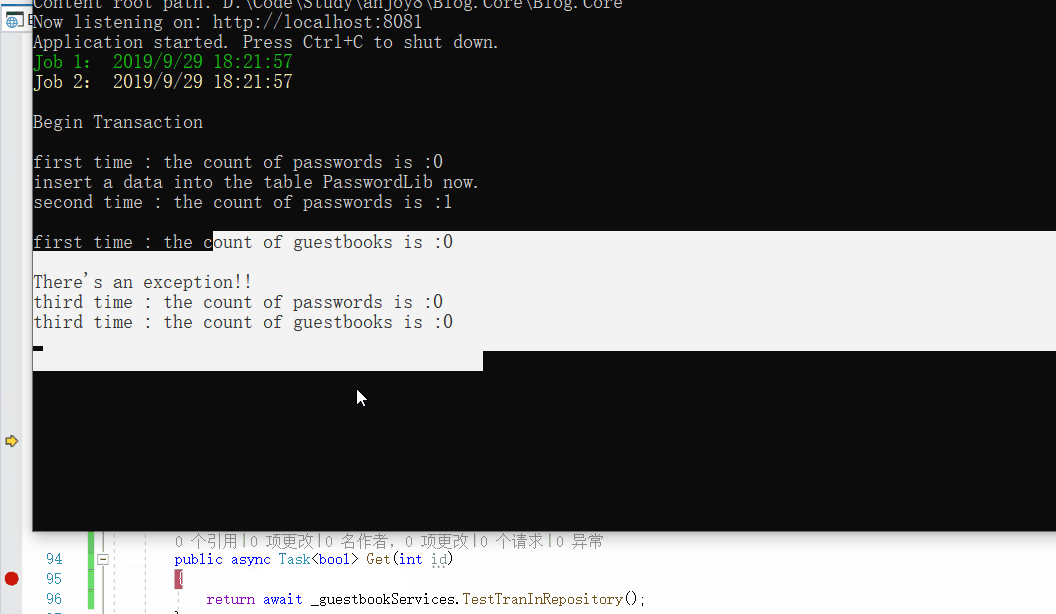
可以看到,我们是密码表已经添加了一条数据的前提下,后来回滚后,数据都被删掉了,数据库也没有对应的值,达到的目的。
但是这里有两个小问题:
1、我们控制的是 Service 类,那我们能不能控制仓储 Repository 类呢?
2、我们每次都这么写,会不会很麻烦呢,能不能用统一AOP呢?
答案都是肯定的!
2、建立事务AOP,解决多仓储内的事务操作
在 Blog.Core api 层的 AOP 文件夹下,创建 BlogTranAOP.cs 文件,用来实现事务AOP操作:
public class BlogTranAOP : IInterceptor { // 依赖注入工作单元接口 private readonly IUnitOfWork _unitOfWork; public BlogTranAOP(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork) { _unitOfWork = unitOfWork; } /// <summary> /// 实例化IInterceptor唯一方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="invocation">包含被拦截方法的信息</param> public void Intercept(IInvocation invocation) { var method = invocation.MethodInvocationTarget ?? invocation.Method; //对当前方法的特性验证 //如果需要验证 if (method.GetCustomAttributes(true).FirstOrDefault(x => x.GetType() == typeof(UseTranAttribute)) is UseTranAttribute) { try { Console.WriteLine($"Begin Transaction"); _unitOfWork.BeginTran(); invocation.Proceed(); // 异步获取异常,普通的 try catch 外层不能达到目的,毕竟是异步的 if (IsAsyncMethod(invocation.Method)) { if (invocation.Method.ReturnType == typeof(Task)) { invocation.ReturnValue = InternalAsyncHelper.AwaitTaskWithPostActionAndFinally( (Task)invocation.ReturnValue, async () => await TestActionAsync(invocation), ex => { _unitOfWork.RollbackTran();//事务回滚 }); } else //Task<TResult> { invocation.ReturnValue = InternalAsyncHelper.CallAwaitTaskWithPostActionAndFinallyAndGetResult( invocation.Method.ReturnType.GenericTypeArguments[0], invocation.ReturnValue, async () => await TestActionAsync(invocation), ex => { _unitOfWork.RollbackTran();//事务回滚 }); } } _unitOfWork.CommitTran(); } catch (Exception) { Console.WriteLine($"Rollback Transaction"); _unitOfWork.RollbackTran(); } } else { invocation.Proceed();//直接执行被拦截方法 } } public static bool IsAsyncMethod(MethodInfo method) { return ( method.ReturnType == typeof(Task) || (method.ReturnType.IsGenericType && method.ReturnType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(Task<>)) ); } private async Task TestActionAsync(IInvocation invocation) { } }
上边具体的操作很简单,如果你看过我的缓存AOP和日志AOP以后,肯定就能看懂这个事务AOP的内容,这里只是有一点,需要增加一个特性,public class UseTranAttribute : Attribute,这个和当时的缓存AOP是一样的,只有配置了才会实现事务提交,具体的请查看 UseTranAttribute.cs 类。
然后我们测试一个子仓储项目,具体的代码如下:
在 Blog.Core.Services 层下的 GuestbookServices.cs 内,增加一个 Task<bool> TestTranInRepositoryAOP() 方法,内容和上边 controller 中的控制 service 类似,只不过是用 Repository 操作类:
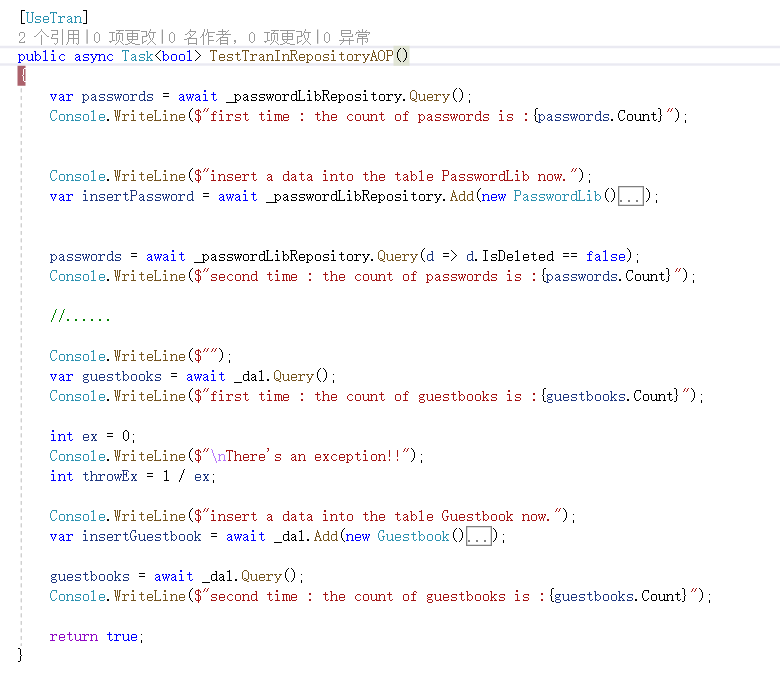
增加事务特性 [UseTran] ,然后在控制器正常的调用,具体的操作和结果就不展示了,已经测试过了,没问题。
到这里,就终于解决了事务的相关操作,当然这里还是有很多的问题需要考究,我也在考虑有没有更好的点子和方案,期待后续报道。
四、Github && Gitee
注意情况分支:Trans1.0
https://github.com/anjoy8/Blog.Core
https://gitee.com/laozhangIsPhi/Blog.Core

